- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Research Tools and Apps

Research Process Steps: What they are + How To Follow

There are various approaches to conducting basic and applied research. This article explains the research process steps you should know. Whether you are doing basic research or applied research, there are many ways of doing it. In some ways, each research study is unique since it is conducted at a different time and place.
Conducting research might be difficult, but there are clear processes to follow. The research process starts with a broad idea for a topic. This article will assist you through the research process steps, helping you focus and develop your topic.
Research Process Steps
The research process consists of a series of systematic procedures that a researcher must go through in order to generate knowledge that will be considered valuable by the project and focus on the relevant topic.
To conduct effective research, you must understand the research process steps and follow them. Here are a few steps in the research process to make it easier for you:
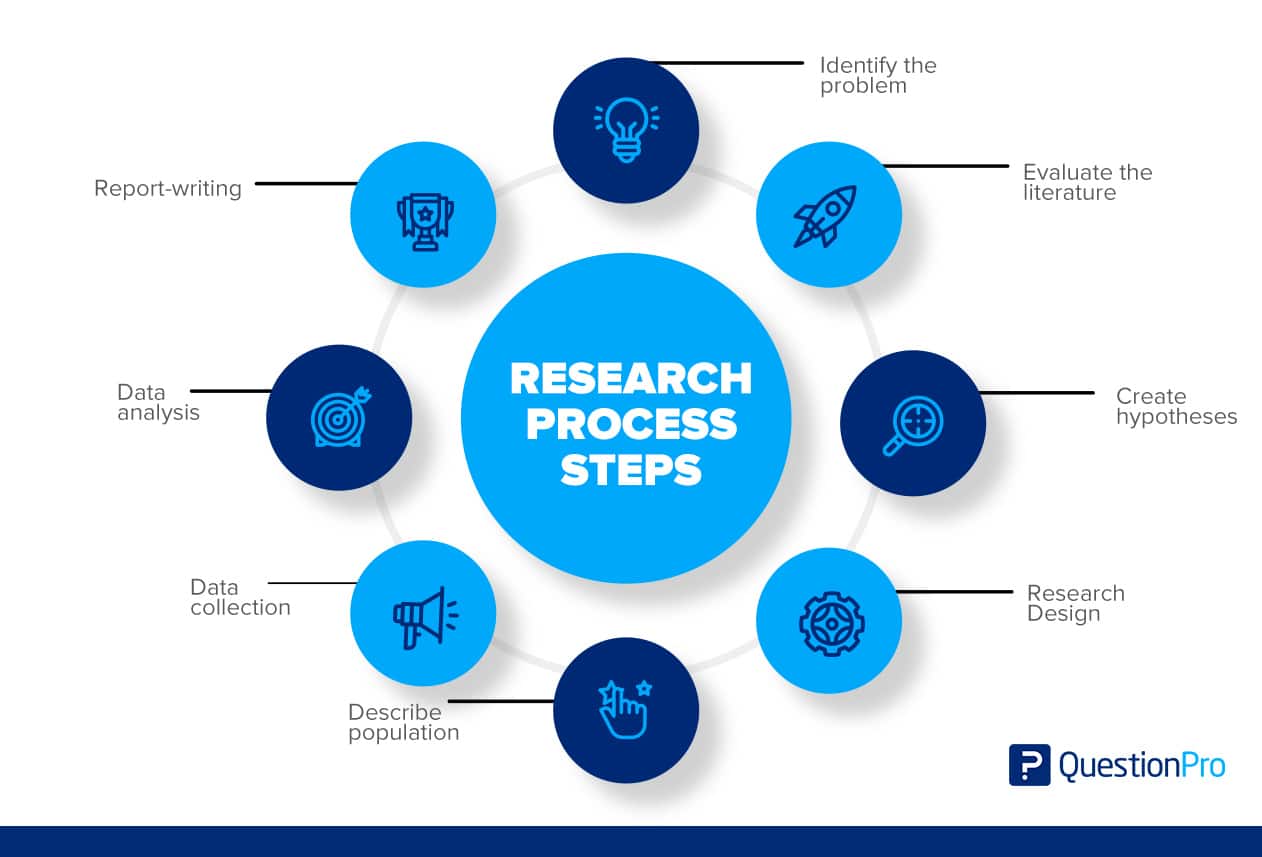
Step 1: Identify the Problem
Finding an issue or formulating a research question is the first step. A well-defined research problem will guide the researcher through all stages of the research process, from setting objectives to choosing a technique. There are a number of approaches to get insight into a topic and gain a better understanding of it. Such as:
- A preliminary survey
- Case studies
- Interviews with a small group of people
- Observational survey
Step 2: Evaluate the Literature
A thorough examination of the relevant studies is essential to the research process . It enables the researcher to identify the precise aspects of the problem. Once a problem has been found, the investigator or researcher needs to find out more about it.
This stage gives problem-zone background. It teaches the investigator about previous research, how they were conducted, and its conclusions. The researcher can build consistency between his work and others through a literature review. Such a review exposes the researcher to a more significant body of knowledge and helps him follow the research process efficiently.
Step 3: Create Hypotheses
Formulating an original hypothesis is the next logical step after narrowing down the research topic and defining it. A belief solves logical relationships between variables. In order to establish a hypothesis, a researcher must have a certain amount of expertise in the field.
It is important for researchers to keep in mind while formulating a hypothesis that it must be based on the research topic. Researchers are able to concentrate their efforts and stay committed to their objectives when they develop theories to guide their work.
Step 4: The Research Design
Research design is the plan for achieving objectives and answering research questions. It outlines how to get the relevant information. Its goal is to design research to test hypotheses, address the research questions, and provide decision-making insights.
The research design aims to minimize the time, money, and effort required to acquire meaningful evidence. This plan fits into four categories:
- Exploration and Surveys
- Data Analysis
- Observation
Step 5: Describe Population
Research projects usually look at a specific group of people, facilities, or how technology is used in the business. In research, the term population refers to this study group. The research topic and purpose help determine the study group.
Suppose a researcher wishes to investigate a certain group of people in the community. In that case, the research could target a specific age group, males or females, a geographic location, or an ethnic group. A final step in a study’s design is to specify its sample or population so that the results may be generalized.
Step 6: Data Collection
Data collection is important in obtaining the knowledge or information required to answer the research issue. Every research collected data, either from the literature or the people being studied. Data must be collected from the two categories of researchers. These sources may provide primary data.
- Questionnaire
Secondary data categories are:
- Literature survey
- Official, unofficial reports
- An approach based on library resources
Step 7: Data Analysis
During research design, the researcher plans data analysis. After collecting data, the researcher analyzes it. The data is examined based on the approach in this step. The research findings are reviewed and reported.
Data analysis involves a number of closely related stages, such as setting up categories, applying these categories to raw data through coding and tabulation, and then drawing statistical conclusions. The researcher can examine the acquired data using a variety of statistical methods.
Step 8: The Report-writing
After completing these steps, the researcher must prepare a report detailing his findings. The report must be carefully composed with the following in mind:
- The Layout: On the first page, the title, date, acknowledgments, and preface should be on the report. A table of contents should be followed by a list of tables, graphs, and charts if any.
- Introduction: It should state the research’s purpose and methods. This section should include the study’s scope and limits.
- Summary of Findings: A non-technical summary of findings and recommendations will follow the introduction. The findings should be summarized if they’re lengthy.
- Principal Report: The main body of the report should make sense and be broken up into sections that are easy to understand.
- Conclusion: The researcher should restate his findings at the end of the main text. It’s the final result.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
The research process involves several steps that make it easy to complete the research successfully. The steps in the research process described above depend on each other, and the order must be kept. So, if we want to do a research project, we should follow the research process steps.
QuestionPro’s enterprise-grade research platform can collect survey and qualitative observation data. The tool’s nature allows for data processing and essential decisions. The platform lets you store and process data. Start immediately!
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

QuestionPro Workforce Has All The Feels – Release of the New Sentiment Analysis
Dec 19, 2024

The Impact Of Synthetic Data On Modern Research

Companies are losing $ billions with gaps in market research – are you?
Dec 18, 2024

CultureAmp vs Qualtrics: The Best Employee Experience Platform
Dec 16, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

The Defense Acquisition Encyclopedia
Program Management
The research process entails systematically acquiring knowledge, resolving issues, or addressing particular inquiries. It is a series of systematic procedures that a researcher must undertake to generate valuable knowledge relevant to the project and focused on the relevant subject matter. The process is iterative, with each subsequent step influenced by the preceding one. The successful execution of this task necessitates meticulous strategic planning, meticulous attention to intricate particulars, and an unwavering dedication to acquiring knowledge and comprehension.
5 Steps in the Research Process Overview
The following steps outline a simple and effective process for conducting both basic and practical research. The five (5) steps in the research process are: [1]
- Step 1: Locating and Defining Issues or Problems – Understanding the questions that need to be answered or studied
- Step 2: Designing the Research Project – Creating a research plan
- Step 3: Collecting Data – Obtaining the information needed to solve the identified issue or problem
- Step 4: Interpreting Research Data – examining the research data and coming up with a conclusion that solves the problem
- Step 5: Report Research Findings – Presenting the information
Step 1 – Locating and Defining Issues or Problems
This step focuses on uncovering the nature and boundaries of a situation or question that needs to be answered or studied. In defining the issues or problems, the researcher should consider the study’s purpose, the relevant background information, what information is needed, and how it will be used in decision-making. A well-defined problem will help the researcher through all research process steps, from setting goals to choosing a method. There are a number of ways to learn more about a subject and get a better grasp on it in Step 2.
Step 2 – Designing the Research Project
This step focuses on creating a research plan or overall approach to how you will solve the issue or problem identified. A research plan or approach is a framework or blueprint for conducting a research project. It details the procedures necessary for obtaining the required information, and its purpose is to design a study that will test the hypotheses of interest, determine possible answers to the research questions, and provide the information needed for decision-making.
The research design involves the following steps:
- Step 1: Conduct secondary data analysis
- Step 2: Do qualitative research
- Step 3: Determine methods of collecting quantitative data (survey, observation, and experimentation)
- Step 4: Determine the definition of the information needed
- Step 5: Determine measurement and scaling procedures
- Step 6: Design a questionnaire
- Step 7: Sampling process and sample size
- Step 8: Plan of data analysis
Step 3 – Collecting Data
This step revolved around obtaining the information needed to solve the identified issue or problem. Data collection can involve experiments, observations, personal interviewing (in-home, mall intercept, or computer-assisted personal interviewing), from an office by telephone (telephone or computer-assisted telephone interviewing), or through the mail (traditional mail and mail panel surveys with recruited households). The two groups of researchers must provide data.
Data collection techniques can include:
- Interviews: Asking people questions about their known information
- Observations: collecting data without asking questions.
- Questionnaires: Ask questions among a group of people
- Focus Groups: Interviewing and observing a group of people
- Documents and Records: Old-fashioned research
- Literature review: Old-fashioned research
- Library Sources: Old reports and articles/books
Step 4 – Interpreting Research Data
This step is focused on interpreting and examining the research data and coming up with a conclusion that solves the problem. Based on the data collected, make sure the conclusion is easy to understand and well thought out.
Analysis Steps
- Step A: Review your research plan
- Step B: Organize your findings and the information you have collected from Step 3.
- Step C: Create a rough draft of your findings, recommendations, and conclusion. This will help you organize your thoughts.
- Step D: Polish the rough draft into your final research finding. You will most likely revise the draft many times before the final product is ready for Step 5.
Step 5 – Report Research Findings
The final step is to report the research findings to those who need the data to make decisions. The findings should be presented in an understandable format so that they can be readily used in the decision-making process. In addition, an oral presentation should be made to management using tables, figures, and graphs to enhance clarity and impact.
Research Reporting Formats:
- Formal Paper
- Published Article
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Audio or Video
- Spreadsheet
Typical Formal Research Report Format
A formal research report typically consists of several sections organized in a specific order to present the research findings clearly and structured. Here is a notional format of a research report, including the typical sections:
- Title Page: – Title of the Research Report – Name(s) of the Author(s) – Affiliation(s) of the Author(s) – Date of Submission
- Abstract: – A brief summary of the research objectives, methods, key findings, and conclusions. – Usually limited to a specific word count or length.
- Table of Contents: – A list of the main sections, subsections, and page numbers in the report. – Helps readers navigate through the report easily.
- Introduction: – Provides an overview of the research topic, including background information, context, and significance. – States the research problem, objectives, and research questions. – Outlines the scope and limitations of the study.
- Literature Review: – Reviews relevant literature and previous studies related to the research topic. – Summarizes existing knowledge, theories, and methodologies. – Identifies gaps, controversies, or unresolved issues that the current research aims to address.
- Methodology: – Describes the research design, methods, and procedures used to collect and analyze data. – Includes information on the sample size, data sources, data collection tools, and data analysis techniques. – Provides sufficient details for replication and validation of the study.
- Results: – Presents the findings of the research in a clear and organized manner. – Utilizes tables, figures, charts, or graphs to present data. – Includes descriptive statistics, qualitative analysis, or any other relevant analysis outputs.
- Discussion: – Interprets and discusses the research findings in relation to the research objectives. – Compares the results with existing literature and theories. – Analyzes patterns, trends, correlations, or discrepancies in the data. – Provides explanations, justifications, or hypotheses to support the findings.
- Conclusion: – Summarizes the main findings of the research. – Restate the research objectives and address the research questions. – Highlights the contributions and implications of the study. – Suggests recommendations for future research or practical applications.
- References: – Lists all the sources cited within the research report. – Follows a specific referencing style (e.g., APA, MLA, IEEE) as per the guidelines.
- Appendices: – Includes supplementary information or additional data that supports the research findings but is not necessary for the main body of the report. – May include survey questionnaires, interview transcripts, data tables, software code, or any other relevant materials.
It’s important to note that the structure and specific section names may vary depending on the discipline, research field, or journal requirements. Always refer to the specific guidelines your institution or publisher provided when preparing a research report.

AcqNotes Tutorial
Research Process Lessons Learned
Embarking on a research journey is a dynamic and enlightening experience that often leads to a multitude of lessons learned. The research process is not merely a sequence of steps but a complex exploration that demands critical thinking, adaptability, and perseverance. Through the course of conducting research, individuals encounter challenges, make discoveries, and refine their methodologies. These lessons extend beyond the acquisition of academic knowledge, encompassing skills such as effective communication, time management, and the ability to navigate through the vast sea of information.
- Define the research challenge and goals in detail: It’s crucial to grasp exactly what you’re attempting to learn and what you want to achieve. This will make it easier to direct your research efforts and guarantee that you are gathering pertinent facts.
- Select the best research design possible: Various research designs are applicable for various research topics. Choosing the proper design will help ensure your study’s validity and reliability.
- Collect reliable information: because it will directly impact how well your research turns out. Use the right data-gathering techniques, and make sure the data is gathered reliably and consistently.
- Analyze the data correctly: If you want to draw reliable findings from your research, your data analysis must be done correctly. It is crucial to employ the proper statistical methods and interpret the findings cautiously.
- Effectively explain your findings: It’s critical to provide your research’s conclusions in a clear, succinct manner. Writing a research report, presenting your findings at a conference, or publishing your study in a journal are all examples of how to do this.
Qualitative Research in the Research Process
Information, industry experts, and secondary data may not be sufficient to define the research problem. Sometimes, qualitative research must be undertaken to gain a qualitative understanding of the problem and its underlying factors. Qualitative research is unstructured, exploratory in nature, based on small samples, and may utilize popular qualitative techniques such as focus groups (group interviews), word association (asking respondents to indicate their first responses to stimulus words), and depth interviews (one-on-one interviews which probe the respondents’ thoughts in detail). Other exploratory research techniques, such as pilot surveys with small samples of respondents, may also be undertaken.
There are various steps in the research process, which makes it simple to accomplish the research successfully. The above-described steps in the research process are interdependent, hence the order must be followed. So, if we want to conduct research, we should adhere to the steps of the research process to obtain good and reliable results.
AcqLinks and References:
- [1] Pride, Ferel (2010). Marketing. South-Western Cengage Learning
Updated: 5/2/2024
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Key Steps in the Research Process - A Comprehensive Guide

Embarking on a research journey can be both thrilling and challenging. Whether you're a student, journalist, or simply inquisitive about a subject, grasping the research process steps is vital for conducting thorough and efficient research. In this all-encompassing guide, we'll navigate you through the pivotal stages of what is the research process, from pinpointing your topic to showcasing your discoveries.
We'll delve into how to formulate a robust research question, undertake preliminary research, and devise a structured research plan. You'll acquire strategies for gathering and scrutinizing data, along with advice for effectively disseminating your findings. By adhering to these steps in the research process, you'll be fully prepared to confront any research endeavor that presents itself.
Step 1: Identify and Develop Your Topic
Identifying and cultivating a research topic is the foundational first step in the research process. Kick off by brainstorming potential subjects that captivate your interest, as this will fuel your enthusiasm throughout the endeavor.
Employ the following tactics to spark ideas and understand what is the first step in the research process:
- Review course materials, lecture notes, and assigned readings for inspiration
- Engage in discussions with peers, professors, or experts in the field
- Investigate current events, news pieces, or social media trends pertinent to your field of study to uncover valuable market research insights.
- Reflect on personal experiences or observations that have sparked your curiosity
Once you've compiled a roster of possible topics, engage in preliminary research to evaluate the viability and breadth of each concept. This initial probe may encompass various research steps and procedures to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the topics at hand.
- Scanning Wikipedia articles or other general reference sources for an overview
- Searching for scholarly articles, books, or media related to your topic
- Identifying key concepts, theories, or debates within the field
- Considering the availability of primary sources or data for analysis
While amassing background knowledge, begin to concentrate your focus and hone your topic. Target a subject that is specific enough to be feasible within your project's limits, yet expansive enough to permit substantial analysis. Mull over the following inquiries to steer your topic refinement and address the research problem effectively:
- What aspect of the topic am I most interested in exploring?
- What questions or problems related to this topic remain unanswered or unresolved?
- How can I contribute new insights or perspectives to the existing body of knowledge?
- What resources and methods will I need to investigate this topic effectively?
Step 2: Conduct Preliminary Research
Having pinpointed a promising research topic, it's time to plunge into preliminary research. This essential phase enables you to deepen your grasp of the subject and evaluate the practicality of your project. Here are some pivotal tactics for executing effective preliminary research using various library resources:
- Literature Review
To effectively embark on your scholarly journey, it's essential to consult a broad spectrum of sources, thereby enriching your understanding with the breadth of academic research available on your topic. This exploration may encompass a variety of materials.
- Online catalogs of libraries (local, regional, national, and special)
- Meta-catalogs and subject-specific online article databases
- Digital institutional repositories and open access resources
- Works cited in scholarly books and articles
- Print bibliographies and internet sources
- Websites of major nonprofit organizations, research institutes, museums, universities, and government agencies
- Trade and scholarly publishers
- Discussions with fellow scholars and peers
- Identify Key Debates
Engaging with the wealth of recently published materials and seminal works in your field is a pivotal part of the research process definition. Focus on discerning the core ideas, debates, and arguments that define your topic, which will in turn sharpen your research focus and guide you toward formulating pertinent research questions.
- Narrow Your Focus
Hone your topic by leveraging your initial findings to tackle a specific issue or facet within the larger subject, a fundamental step in the research process steps. Consider various factors that could influence the direction and scope of your inquiry.
- Subtopics and specific issues
- Key debates and controversies
- Timeframes and geographical locations
- Organizations or groups of people involved
A thorough evaluation of existing literature and a comprehensive assessment of the information at hand will pinpoint the exact dimensions of the issue you aim to explore. This methodology ensures alignment with prior research, optimizes resources, and can bolster your case when seeking research funding by demonstrating a well-founded approach.
Step 3: Establish Your Research Question
Having completed your preliminary research and topic refinement, the next vital phase involves formulating a precise and focused research question. This question, a cornerstone among research process steps, will steer your investigation, keeping it aligned with relevant data and insights. When devising your research question, take into account these critical factors:
Initiate your inquiry by defining the requirements and goals of your study, a key step in the research process steps. Whether you're testing a hypothesis, analyzing data, or constructing and supporting an argument, grasping the intent of your research is crucial for framing your question effectively.
Ensure that your research question is feasible, given your constraints in time and word count, an important consideration in the research process steps. Steer clear of questions that are either too expansive or too constricted, as they may impede your capacity to conduct a comprehensive analysis.
Your research question should transcend a mere 'yes' or 'no' response, prompting a thorough engagement with the research process steps. It should foster a comprehensive exploration of the topic, facilitating the analysis of issues or problems beyond just a basic description.
- Researchability
Ensure that your research question opens the door to quality research materials, including academic books and refereed journal articles. It's essential to weigh the accessibility of primary data and secondary data that will bolster your investigative efforts.
When establishing your research question, take the following steps:
- Identify the specific aspect of your general topic that you want to explore
- Hypothesize the path your answer might take, developing a hypothesis after formulating the question
- Steer clear of certain types of questions in your research process steps, such as those that are deceptively simple, fictional, stacked, semantic, impossible-to-answer, opinion or ethical, and anachronistic, to maintain the integrity of your inquiry.
- Conduct a self-test on your research question to confirm it adheres to the research process steps, ensuring it is flexible, testable, clear, precise, and underscores a distinct reason for its importance.
By meticulously formulating your research question, you're establishing a solid groundwork for the subsequent research process steps, guaranteeing that your efforts are directed, efficient, and yield productive outcomes.
Step 4: Develop a Research Plan
Having formulated a precise research question, the ensuing phase involves developing a detailed research plan. This plan, integral to the research process steps, acts as a navigational guide for your project, keeping you organized, concentrated, and on a clear path to accomplishing your research objectives. When devising your research plan, consider these pivotal components:
- Project Goals and Objectives
Articulate the specific aims and objectives of your research project with clarity. These should be in harmony with your research question and provide a structured framework for your investigation, ultimately aligning with your overarching business goals.
- Research Methods
Select the most appropriate research tools and statistical methods to address your question effectively. This may include a variety of qualitative and quantitative approaches to ensure comprehensive analysis.
- Quantitative methods (e.g., surveys, experiments)
- Qualitative methods (e.g., interviews, focus groups)
- Mixed methods (combining quantitative and qualitative approaches)
- Access to databases, archives, or special collections
- Specialized equipment or software
- Funding for travel, materials, or participant compensation
- Assistance from research assistants, librarians, or subject matter experts
- Participant Recruitment
If your research involves human subjects, develop a strategic plan for recruiting participants. Consider factors such as the inclusion of diverse ethnic groups and the use of user interviews to gather rich, qualitative data.
- Target population and sample size
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Recruitment strategies (e.g., flyers, social media, snowball sampling)
- Informed consent procedures
- Instruments or tools for gathering data (e.g., questionnaires, interview guides)
- Data storage and management protocols
- Statistical or qualitative analysis techniques
- Software or tools for data analysis (e.g., SPSS, NVivo)
Create a realistic project strategy for your research project, breaking it down into manageable stages or milestones. Consider factors such as resource availability and potential bottlenecks.
- Literature review and background research
- IRB approval (if applicable)
- Participant recruitment and data collection
- Data analysis and interpretation
- Writing and revising your findings
- Dissemination of results (e.g., presentations, publications)
By developing a comprehensive research plan, incorporating key research process steps, you'll be better equipped to anticipate challenges, allocate resources effectively, and ensure the integrity and rigor of your research process. Remember to remain flexible and adaptable to navigate unexpected obstacles or opportunities that may arise.
Step 5: Conduct the Research
With your research plan in place, it's time to dive into the data collection phase. As you conduct your research, adhere to the established research process steps to ensure the integrity and quality of your findings.
Conduct your research in accordance with federal regulations, state laws, institutional SOPs, and policies. Familiarize yourself with the IRB-approved protocol and follow it diligently, as part of the essential research process steps.
- Roles and Responsibilities
Understand and adhere to the roles and responsibilities of the principal investigator and other research team members. Maintain open communication lines with all stakeholders, including the sponsor and IRB, to foster cross-functional collaboration.
- Data Management
Develop and maintain an effective system for data collection and storage, utilizing advanced research tools. Ensure that each member of the research team has seamless access to the most up-to-date documents, including the informed consent document, protocol, and case report forms.
- Quality Assurance
Implement comprehensive quality assurance measures to verify that the study adheres strictly to the IRB-approved protocol, institutional policy, and all required regulations. Confirm that all study activities are executed as planned and that any deviations are addressed with precision and appropriateness.
- Participant Eligibility
As part of the essential research process steps, verify that potential study subjects meet all eligibility criteria and none of the ineligibility criteria before advancing with the research.
To maintain the highest standards of academic integrity and ethical conduct:
- Conduct research with unwavering honesty in all facets, including experimental design, data generation, and analysis, as well as the publication of results, as these are critical research process steps.
- Maintain a climate conducive to conducting research in strict accordance with good research practices, ensuring each step of the research process is meticulously observed.
- Provide appropriate supervision and training for researchers.
- Encourage open discussion of ideas and the widest dissemination of results possible.
- Keep clear and accurate records of research methods and results.
- Exercise a duty of care to all those involved in the research.
When collecting and assimilating data:
- Use professional online data analysis tools to streamline the process.
- Use metadata for context
- Assign codes or labels to facilitate grouping or comparison
- Convert data into different formats or scales for compatibility
- Organize documents in both the study participant and investigator's study regulatory files, creating a central repository for easy access and reference, as this organization is a pivotal step in the research process.
By adhering to these guidelines and upholding a commitment to ethical and rigorous research practices, you'll be well-equipped to conduct your research effectively and contribute meaningful insights to your field of study, thereby enhancing the integrity of the research process steps.
Step 6: Analyze and Interpret Data
Embarking on the research process steps, once you have gathered your research data, the subsequent critical phase is to delve into analysis and interpretation. This stage demands a meticulous examination of the data, spotting trends, and forging insightful conclusions that directly respond to your research question. Reflect on these tactics for a robust approach to data analysis and interpretation:
- Organize and Clean Your Data
A pivotal aspect of the research process steps is to start by structuring your data in an orderly and coherent fashion. This organizational task may encompass:
- Creating a spreadsheet or database to store your data
- Assigning codes or labels to facilitate grouping or comparison
- Cleaning the data by removing any errors, inconsistencies, or missing values
- Converting data into different formats or scales for compatibility
- Calculating measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode)
- Determining measures of variability (range, standard deviation)
- Creating frequency tables or histograms to visualize the distribution of your data
- Identifying any outliers or unusual patterns in your data
- Perform Inferential Analysis
Integral to the research process steps, you might engage in inferential analysis to evaluate hypotheses or extrapolate findings to a broader demographic, contingent on your research design and query. This analytical step may include:
- Selecting appropriate statistical tests (e.g., t-tests, ANOVA, regression analysis)
- As part of the research process steps, establishing a significance threshold (e.g., p < 0.05) is essential to gauge the likelihood of your results being a random occurrence rather than a significant finding.
- Interpreting the results of your statistical tests in the context of your research question
- Considering the practical significance of your findings, in addition to statistical significance
When interpreting your data, it's essential to:
- Look for relationships, patterns, and trends in your data
- Consider alternative explanations for your findings
- Acknowledge any limitations or potential biases in your research design or data collection
- Leverage data visualization techniques such as graphs, charts, and infographics to articulate your research findings with clarity and impact, thereby enhancing the communicative value of your data.
- Seek feedback from peers, mentors, or subject matter experts to validate your interpretations
It's important to recognize that data interpretation is a cyclical process that hinges on critical thinking, inventiveness, and the readiness to refine your conclusions with emerging insights. By tackling data analysis and interpretation with diligence and openness, you're setting the stage to derive meaningful and justifiable inferences from your research, in line with the research process steps.
Step 7: Present the Findings
After meticulous analysis and interpretation of your research findings, as dictated by the research process steps, the moment arrives to disseminate your insights. Effectively presenting your research is key to captivating your audience and conveying the importance of your findings. Employ these strategies to create an engaging and persuasive presentation:
- Organize Your Findings :
Use the PEEL method to structure your presentation:
- Point: Clearly state your main argument or finding
- Evidence: Present the data and analysis that support your point
- Explanation: Provide context and interpret the significance of your evidence
- Link: Connect your findings to the broader research question or field
- Tailor Your Message
Understanding your audience is crucial to effective communication. When presenting your research, it's important to tailor your message to their background, interests, and level of expertise, effectively employing user personas to guide your approach.
- Use clear, concise language and explain technical terms
- Highlight what makes your research unique and impactful
- Craft a compelling narrative with a clear structure and hook
- Share the big picture, emphasizing the significance of your findings
- Engage Your Audience : Make your presentation enjoyable and memorable by incorporating creative elements:
- Use visual aids, such as tables, charts, and graphs, to communicate your findings effectively
- To vividly convey your research journey, consider employing storytelling techniques, such as UX comics or storyboards, which can make complex information more accessible and engaging.
- Injecting humor and personality into your presentation can be a powerful tool for communication. Utilize funny messages or GIFs to lighten the mood, breaking up tension and refocusing attention, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of humor in communication.
By adhering to these strategies, you'll be well-prepared to present your research findings in a manner that's both clear and captivating. Ensure you follow research process steps such as citing your sources accurately and discussing the broader implications of your work, providing actionable recommendations, and delineating the subsequent phases for integrating your findings into broader practice or policy frameworks.
The research process is an intricate journey that demands meticulous planning, steadfast execution, and incisive analysis. By adhering to the fundamental research process steps outlined in this guide, from pinpointing your topic to showcasing your findings, you're setting yourself up for conducting research that's both effective and influential. Keep in mind that the research journey is iterative, often necessitating revisits to certain stages as fresh insights surface or unforeseen challenges emerge.
As you commence your research journey, seize the chance to contribute novel insights to your field and forge a positive global impact. By tackling your research with curiosity, integrity, and a dedication to excellence, you're paving the way towards attaining your research aspirations and making a substantial difference with your work, all while following the critical research process steps.
Sign up for more like this.
Basic Steps in the Research Process
The following steps outline a simple and effective strategy for writing a research paper. Depending on your familiarity with the topic and the challenges you encounter along the way, you may need to rearrange these steps.
Step 1: Identify and develop your topic
Selecting a topic can be the most challenging part of a research assignment. Since this is the very first step in writing a paper, it is vital that it be done correctly. Here are some tips for selecting a topic:
- Select a topic within the parameters set by the assignment. Many times your instructor will give you clear guidelines as to what you can and cannot write about. Failure to work within these guidelines may result in your proposed paper being deemed unacceptable by your instructor.
- Select a topic of personal interest to you and learn more about it. The research for and writing of a paper will be more enjoyable if you are writing about something that you find interesting.
- Select a topic for which you can find a manageable amount of information. Do a preliminary search of information sources to determine whether existing sources will meet your needs. If you find too much information, you may need to narrow your topic; if you find too little, you may need to broaden your topic.
- Be original. Your instructor reads hundreds of research papers every year, and many of them are on the same topics (topics in the news at the time, controversial issues, subjects for which there is ample and easily accessed information). Stand out from your classmates by selecting an interesting and off-the-beaten-path topic.
- Still can't come up with a topic to write about? See your instructor for advice.
Once you have identified your topic, it may help to state it as a question. For example, if you are interested in finding out about the epidemic of obesity in the American population, you might pose the question "What are the causes of obesity in America ?" By posing your subject as a question you can more easily identify the main concepts or keywords to be used in your research.
Step 2 : Do a preliminary search for information
Before beginning your research in earnest, do a preliminary search to determine whether there is enough information out there for your needs and to set the context of your research. Look up your keywords in the appropriate titles in the library's Reference collection (such as encyclopedias and dictionaries) and in other sources such as our catalog of books, periodical databases, and Internet search engines. Additional background information may be found in your lecture notes, textbooks, and reserve readings. You may find it necessary to adjust the focus of your topic in light of the resources available to you.
Step 3: Locate materials
With the direction of your research now clear to you, you can begin locating material on your topic. There are a number of places you can look for information:
If you are looking for books, do a subject search in One Search . A Keyword search can be performed if the subject search doesn't yield enough information. Print or write down the citation information (author, title,etc.) and the location (call number and collection) of the item(s). Note the circulation status. When you locate the book on the shelf, look at the books located nearby; similar items are always shelved in the same area. The Aleph catalog also indexes the library's audio-visual holdings.
Use the library's electronic periodical databases to find magazine and newspaper articles. Choose the databases and formats best suited to your particular topic; ask at the librarian at the Reference Desk if you need help figuring out which database best meets your needs. Many of the articles in the databases are available in full-text format.
Use search engines ( Google , Yahoo , etc.) and subject directories to locate materials on the Internet. Check the Internet Resources section of the NHCC Library web site for helpful subject links.
Step 4: Evaluate your sources
See the CARS Checklist for Information Quality for tips on evaluating the authority and quality of the information you have located. Your instructor expects that you will provide credible, truthful, and reliable information and you have every right to expect that the sources you use are providing the same. This step is especially important when using Internet resources, many of which are regarded as less than reliable.
Step 5: Make notes
Consult the resources you have chosen and note the information that will be useful in your paper. Be sure to document all the sources you consult, even if you there is a chance you may not use that particular source. The author, title, publisher, URL, and other information will be needed later when creating a bibliography.
Step 6: Write your paper
Begin by organizing the information you have collected. The next step is the rough draft, wherein you get your ideas on paper in an unfinished fashion. This step will help you organize your ideas and determine the form your final paper will take. After this, you will revise the draft as many times as you think necessary to create a final product to turn in to your instructor.
Step 7: Cite your sources properly
Give credit where credit is due; cite your sources.
Citing or documenting the sources used in your research serves two purposes: it gives proper credit to the authors of the materials used, and it allows those who are reading your work to duplicate your research and locate the sources that you have listed as references. The MLA and the APA Styles are two popular citation formats.
Failure to cite your sources properly is plagiarism. Plagiarism is avoidable!
Step 8: Proofread
The final step in the process is to proofread the paper you have created. Read through the text and check for any errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Make sure the sources you used are cited properly. Make sure the message that you want to get across to the reader has been thoroughly stated.
Additional research tips:
- Work from the general to the specific -- find background information first, then use more specific sources.
- Don't forget print sources -- many times print materials are more easily accessed and every bit as helpful as online resources.
- The library has books on the topic of writing research papers at call number area LB 2369.
- If you have questions about the assignment, ask your instructor.
- If you have any questions about finding information in the library, ask the librarian.
Contact Information
Craig larson.
Librarian 763-424-0733 [email protected] Zoom: myzoom Available by appointment
Get Started
Research Methodology
- Introduction to Research Methodology
- Research Approaches
- Concepts of Theory and Empiricism
- Characteristics of scientific method
- Understanding the Language of Research
11 Steps in Research Process
- Research Design
- Different Research Designs
- Compare and Contrast the Main Types of Research Designs
- Cross-sectional research design
- Qualitative and Quantitative Research
- Descriptive Research VS Qualitative Research
- Experimental Research VS Quantitative Research
- Sampling Design
- Probability VS Non-Probability Sampling
- 40 MCQ on Research Methodology
- MCQ on research Process
- MCQ on Research Design
- 18 MCQ on Quantitative Research
- 30 MCQ on Qualitative Research
- 45 MCQ on Sampling Methods
- 20 MCQ on Principles And Planning For Research
Research process refers to the systematic and organized series of steps taken to investigate and study a specific topic or problem in order to gain knowledge and find answers to questions. It is a methodical approach followed by researchers to collect, analyze, and interpret data to arrive at meaningful conclusions and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in a particular field.

The chart shows that the research process consists of several activities marked from I to VII. These activities are closely related and often overlap instead of following a strict order. Sometimes, the first step determines how the last step will be done. If certain important steps are not considered early on, it can cause serious problems and even stop the research from being completed.
It’s essential to understand that the steps involved in the research process are not completely separate from each other. They do not always follow a fixed order, and the researcher needs to be prepared for the requirements of the next steps at each stage of the research process.
Interpret data to arrive at meaningful conclusions and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in a particular field.
The research process typically involves the following key steps:
- Formulating the Research Problem: Identifying and defining the research question or problem that needs to be addressed.
- Literature Review: Conducting a thorough review of existing literature and research related to the topic to understand what has already been studied and discovered.
- Developing the Hypothesis: Creating a clear and testable statement that predicts the relationship between variables in the research.
- Research Design: Planning the overall structure and approach of the study, including selecting the research methods and data collection techniques.
- Sample Design: Determining the sample size and selecting the participants or subjects that will be part of the study.
- Data Collection: Gathering relevant data through various methods, such as surveys, interviews, experiments, or observations.
- Execution of the Project: Implementing the research plan and collecting the data as per the designed approach.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing the collected data using appropriate statistical or qualitative techniques to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Hypothesis Testing: Evaluating the hypothesis based on the analysis to determine whether it is supported or rejected.
- Generalizations and Interpretation: Making broader connections and interpretations of the findings in the context of the research problem.
- Conclusion and Recommendations: Summarizing the research results, drawing conclusions, and suggesting potential future research or practical implications.
Throughout the research process, researchers must maintain objectivity, rigor, and ethical considerations to ensure the validity and reliability of the results. Each step contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the research topic and the generation of new knowledge in the field.
15 Steps to Good Research
- Define and articulate a research question (formulate a research hypothesis). How to Write a Thesis Statement (Indiana University)
- Identify possible sources of information in many types and formats. Georgetown University Library's Research & Course Guides
- Judge the scope of the project.
- Reevaluate the research question based on the nature and extent of information available and the parameters of the research project.
- Select the most appropriate investigative methods (surveys, interviews, experiments) and research tools (periodical indexes, databases, websites).
- Plan the research project. Writing Anxiety (UNC-Chapel Hill) Strategies for Academic Writing (SUNY Empire State College)
- Retrieve information using a variety of methods (draw on a repertoire of skills).
- Refine the search strategy as necessary.
- Write and organize useful notes and keep track of sources. Taking Notes from Research Reading (University of Toronto) Use a citation manager: Zotero or Refworks
- Evaluate sources using appropriate criteria. Evaluating Internet Sources
- Synthesize, analyze and integrate information sources and prior knowledge. Georgetown University Writing Center
- Revise hypothesis as necessary.
- Use information effectively for a specific purpose.
- Understand such issues as plagiarism, ownership of information (implications of copyright to some extent), and costs of information. Georgetown University Honor Council Copyright Basics (Purdue University) How to Recognize Plagiarism: Tutorials and Tests from Indiana University
- Cite properly and give credit for sources of ideas. MLA Bibliographic Form (7th edition, 2009) MLA Bibliographic Form (8th edition, 2016) Turabian Bibliographic Form: Footnote/Endnote Turabian Bibliographic Form: Parenthetical Reference Use a citation manager: Zotero or Refworks
Adapted from the Association of Colleges and Research Libraries "Objectives for Information Literacy Instruction" , which are more complete and include outcomes. See also the broader "Information Literacy Competency Standards for Higher Education."

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The research process identifies the research problem, sets the research design and sample size, collects and analyzes the data, and reports on the findings. ... Eight steps research process is, in essence, part and parcel of a research proposal. It is an outline of the commitment that you intend to follow in executing a research study.
The research process is a structured, step-by-step approach that ensures accuracy, credibility, and thoroughness in exploring a research question. By following the outlined steps, researchers can build upon existing knowledge, make meaningful contributions to their fields, and communicate findings effectively.
Research Process Steps. The research process consists of a series of systematic procedures that a researcher must go through in order to generate knowledge that will be considered valuable by the project and focus on the relevant topic. To conduct effective research, you must understand the research process steps and follow them.
Step 2 - Designing the Research Project. This step focuses on creating a research plan or overall approach to how you will solve the issue or problem identified. A research plan or approach is a framework or blueprint for conducting a research project. It details the procedures necessary for obtaining the required information, and its purpose ...
Here is a step-by-step guide to writing your research project: Step 1: Define Your Research Question or Problem. Identify the Topic: Start with a broad area of interest and narrow it down to a specific, manageable topic. Formulate the Research Question: Turn your topic into a research question. For example, if your topic is climate change, a ...
This describes who the problem affects, why research is needed, and how your research project will contribute to solving it. >>Read more about defining a research problem. Step 3: Formulate research questions. Next, based on the problem statement, you need to write one or more research questions. These target exactly what you want to find out.
Step 4: Develop a Research Plan. Having formulated a precise research question, the ensuing phase involves developing a detailed research plan. This plan, integral to the research process steps, acts as a navigational guide for your project, keeping you organized, concentrated, and on a clear path to accomplishing your research objectives.
The following steps outline a simple and effective strategy for writing a research paper. Depending on your familiarity with the topic and the challenges you encounter along the way, you may need to rearrange these steps. Step 1: Identify and develop your topic. Selecting a topic can be the most challenging part of a research assignment.
his metadata provides an overview of the systematic and organized series of steps involved in conducting research. The process includes formulating the research problem, conducting a literature review, developing a hypothesis, planning the research design, determining the sample design, collecting data, executing the project, analyzing data, testing hypotheses, making generalizations and ...
Judge the scope of the project. Reevaluate the research question based on the nature and extent of information available and the parameters of the research project. Select the most appropriate investigative methods (surveys, interviews, experiments) and research tools (periodical indexes, databases, websites). Plan the research project.