- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

Empirical Research: Definition, Methods, Types & Steps
Empirical research is a way of learning through direct observation or experience. Instead of relying on theories or ideas alone, it gathers real-world data to understand how things work.
Researchers ask questions, conduct experiments, observe different situations, and carefully collect evidence to find answers. This method not only ensures that our beliefs are supported by facts but also reassures us that our understanding is based on solid evidence rather than mere assumptions.
In our everyday lives, we engage in informal empirical research whenever we try things and learn from the outcomes, making it an effective and relatable way to uncover the truth.
What is Empirical Research?
Empirical research depends on direct or indirect actual experience and observation as its primary source of knowledge. It focuses on collecting real-world data to answer specific research questions and solve practical problems. This method is widely used across various fields, as it helps professionals validate hypotheses with solid evidence rather than relying on assumptions.
In professional practices, empirical research is vital because it informs decisions with data-driven insights, ensuring that theories are tested and applicable in real-world scenarios.
In addition to advancing knowledge in current studies, empirical research sets a foundation for future studies. By answering specific research questions and testing new hypotheses, it continuously builds on previous findings and opens up new areas for exploration.
This empirical evidence can be gathered using quantitative market research and qualitative market research methods.
For example: A research is being conducted to find out if listening to happy music in the workplace while working may promote creativity? An experiment is conducted by using a music website survey on a set of audience who are exposed to happy music and another set who are not listening to music at all, and the subjects are then observed. The results derived from such a research will give empirical evidence if it does promote creativity or not.
Origin of Empirical Research
You must have heard the quote, “I will not believe it unless I see it.” This concept originated from the ancient empiricists, a fundamental understanding that:
- Powered the emergence of medieval science during the Renaissance period.
- Laid the foundation for modern science as we know it today.
The term “empirical” has its roots in Greek, derived from the word empirics , which means “experienced.”
In today’s world, empirical research refers to:
- The collection of data using evidence gathered through observation or experience.
- Observed and measured phenomena through experiments or by using calibrated scientific instruments.
- Reliance on previous studies and their methodology to design and validate new research.
All of these methods have one key factor in common: dependence on observation and experimentation to collect data, test hypotheses, and draw conclusions.
Empirical research can be categorized into:
- Quantitative research involves numerical data, statistical analysis, and the measurement of variables.
- Qualitative research focuses on non-numerical data and the interpretation of patterns and meanings.
In essence, empirical research relies on real-world evidence to form conclusions, distinguishing it from purely theoretical or speculative approaches.
Types And Methodologies of Empirical Research
Empirical research can be conducted and analysed using qualitative or quantitative methods.
- Quantitative research : Quantitative research methods are used to gather information through numerical data. It is used to quantify opinions, behaviors or other defined variables . These are predetermined and are in a more structured format. Some of the commonly used methods are survey, longitudinal studies, polls, etc
- Qualitative research: Qualitative research methods are used to gather non numerical data. It is used to find meanings, opinions, or the underlying reasons from its subjects. These methods are unstructured or semi structured. The sample size for such a research is usually small and it is a conversational type of method to provide more insight or in-depth information about the problem Some of the most popular forms of methods are focus groups, experiments, interviews, etc.
Data collected from these will need to be analysed. Empirical evidence can also be analysed either quantitatively and qualitatively. Using this, the researcher can answer empirical questions which have to be clearly defined and answerable with the findings he has got.
The type of research design used will vary depending on the field in which it is going to be used. Many of them might choose to do a collective research involving quantitative and qualitative method to better answer questions which cannot be studied in a laboratory setting.
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods aid in analyzing the empirical evidence gathered. By using these a researcher can find out if his hypothesis is supported or not.
1. Survey Research
Survey research generally involves a large audience to collect a large amount of data. This is a quantitative method having a predetermined set of closed questions which are pretty easy to answer. Because of the simplicity of such a method, high responses are achieved. It is one of the most commonly used methods for all kinds of research in today’s world.
Previously, surveys were taken face to face only with maybe a recorder. However, with advancement in technology and for ease, new mediums such as emails , or social media have emerged.
For example: Depletion of energy resources is a growing concern and hence there is a need for awareness about renewable energy. According to recent studies, fossil fuels still account for around 80% of energy consumption in the United States. Even though there is a rise in the use of green energy every year, there are certain parameters because of which the general population is still not opting for green energy.
In order to understand why, a survey can be conducted to gather opinions of the general population about green energy and the factors that influence their choice of switching to renewable energy. Such a survey can help institutions or governing bodies to promote appropriate awareness and incentive schemes to push the use of greener energy.
2. Experimental Research
In experimental research , an experiment is set up and a hypothesis is tested by creating a situation in which one of the variable is manipulated. This is also used to check cause and effect. It is tested to see what happens to the independent variable if the other one is removed or altered. The process for such a method is usually proposing a hypothesis, experimenting on it, analyzing the findings and reporting the findings to understand if it supports the theory or not.
For example: A particular product company is trying to find what is the reason for them to not be able to capture the market. So the organisation makes changes in each one of the processes like manufacturing, marketing, sales and operations. Through the experiment they understand that sales training directly impacts the market coverage for their product. If the person is trained well, then the product will have better coverage.
3. Correlational Research
Correlational research is used to find relation between two set of variables . Regression analysis is generally used to predict outcomes of such a method. It can be positive, negative or neutral correlation.
For example: Higher educated individuals will get higher paying jobs. This means higher education enables the individual to high paying job and less education will lead to lower paying jobs.
4. Longitudinal Study
Longitudinal study is used to understand the traits or behavior of a subject under observation after repeatedly testing the subject over a period of time. Data collected from such a method can be qualitative or quantitative in nature.
For example: A research to find out benefits of exercise. The target is asked to exercise everyday for a particular period of time and the results show higher endurance, stamina, and muscle growth. This supports the fact that exercise benefits an individual body.
5. Cross Sectional
Cross sectional study is an observational type of method, in which a set of audience is observed at a given point in time. In this type, the set of people are chosen in a fashion which depicts similarity in all the variables except the one which is being researched.
This type does not enable the researcher to establish a cause and effect relationship as it is not observed for a continuous time period. It is majorly used by healthcare sector or the retail industry.
For example: A medical study to find the prevalence of under-nutrition disorders in kids of a given population. This will involve looking at a wide range of parameters like age, ethnicity, location, incomes and social backgrounds. If a significant number of kids coming from poor families show under-nutrition disorders, the researcher can further investigate into it. Usually a cross sectional study is followed by a longitudinal study to find out the exact reason.
6. Causal-Comparative Research
This method is based on comparison. It is mainly used to find out cause-effect relationship between two variables or even multiple variables.
For example: A researcher measured the productivity of employees in a company which gave breaks to the employees during work and compared that to the employees of the company which did not give breaks at all.
Qualitative Research Methods
Some research questions need to be analysed qualitatively, as quantitative methods are not applicable there. In many cases, in-depth information is needed or a researcher may need to observe a target audience behavior, hence the results needed are in a descriptive analysis form. Qualitative research results will be descriptive rather than predictive. It enables the researcher to build or support theories for future potential quantitative research. In such a situation qualitative research methods are used to derive a conclusion to support the theory or hypothesis being studied.
1. Case Study
Case study method is used to find more information through carefully analyzing existing cases. It is very often used for business research or to gather empirical evidence for investigation purpose. It is a method to investigate a problem within its real life context through existing cases.
The researcher has to carefully analyse making sure the parameter and variables in the existing case are the same as to the case that is being investigated. Using the findings from the case study, conclusions can be drawn regarding the topic that is being studied.
For example: A report mentioning the solution provided by a company to its client. The challenges they faced during initiation and deployment, the findings of the case and solutions they offered for the problems. Such case studies are used by most companies as it forms an empirical evidence for the company to promote in order to get more business.
2. Observational Method
Observational method is a process to observe and gather data from its target. Since it is a qualitative method it is time consuming and very personal. It can be said that observational research method is a part of ethnographic research which is also used to gather empirical evidence. This is usually a qualitative form of research, however in some cases it can be quantitative as well depending on what is being studied.
For example: setting up a research to observe a particular animal in the rain-forests of amazon. Such a research usually take a lot of time as observation has to be done for a set amount of time to study patterns or behavior of the subject. Another example used widely nowadays is to observe people shopping in a mall to figure out buying behavior of consumers.
3. One-on-one Interview
Such a method is purely qualitative and one of the most widely used. The reason being it enables a researcher get precise meaningful data if the right questions are asked. It is a conversational method where in-depth data can be gathered depending on where the conversation leads.
For example: A one-on-one interview with the finance minister to gather data on financial policies of the country and its implications on the public.
4. Focus Groups
Focus groups are used when a researcher wants to find answers to why, what and how questions. A small group is generally chosen for such a method and it is not necessary to interact with the group in person. A moderator is generally needed in case the group is being addressed in person. This is widely used by product companies to collect data about their brands and the product.
For example: A mobile phone manufacturer wanting to have a feedback on the dimensions of one of their models which is yet to be launched. Such studies help the company meet the demand of the customer and position their model appropriately in the market.
5. Text Analysis
Text analysis method is a little new compared to the other types. Such a method is used to analyse social life by going through images or words used by the individual. In today’s world, with social media playing a major part of everyone’s life, such a method enables the research to follow the pattern that relates to his study.
For example: A lot of companies ask for feedback from the customer in detail mentioning how satisfied are they with their customer support team. Such data enables the researcher to take appropriate decisions to make their support team better.
Sometimes a combination of the methods is also needed for some questions that cannot be answered using only one type of method especially when a researcher needs to gain a complete understanding of complex subject matter.
We recently published a blog that talks about examples of qualitative data in education ; why don’t you check it out for more ideas?
Learn More: Data Collection Methods: Types & Examples
Steps of Conducting Empirical Research
Since empirical research is based on observation and capturing experiences, it is important to plan the steps to conduct the experiment and how to analyse it. This will enable the researcher to resolve problems or obstacles which can occur during the experiment.
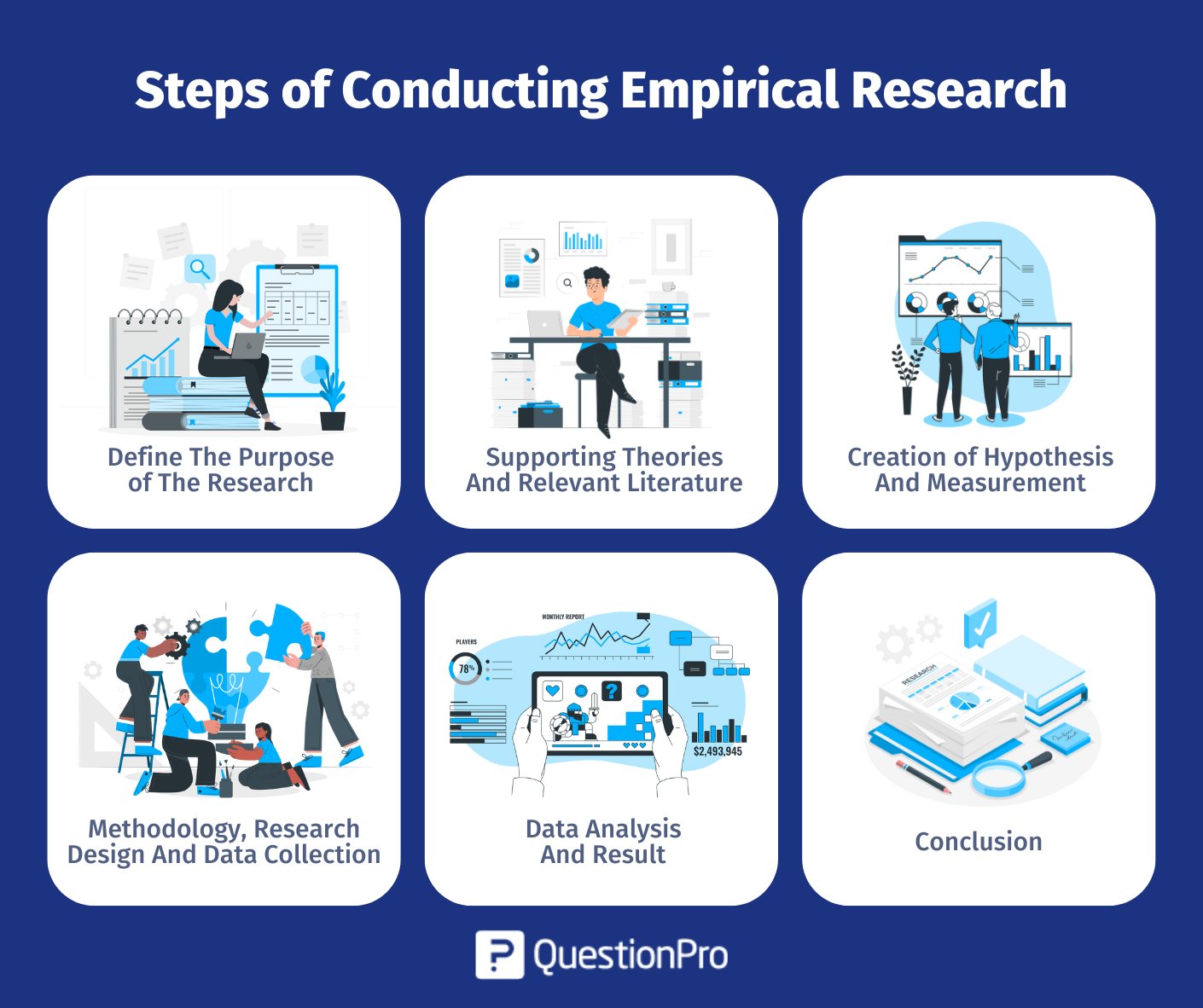
Step #1: Define The Purpose of The Research
This is the step where the researcher has to answer questions like what exactly do I want to find out? What is the problem statement? Are there any issues in terms of the availability of knowledge, data, time or resources. Will this research be more beneficial than what it will cost.
Before going ahead, a researcher has to clearly define his purpose for the research and set up a plan to carry out further tasks.
Step #2 : Supporting Theories And Relevant Literature
The researcher needs to find out if there are theories which can be linked to his research problem . He has to figure out if any theory can help him support his findings. All kind of relevant literature will help the researcher to find if there are others who have researched this before, or what are the problems faced during this research. The researcher will also have to set up assumptions and also find out if there is any history regarding his research problem
Step #3: Creation of Hypothesis And Measurement
Before beginning the actual research he needs to provide himself a working hypothesis or guess what will be the probable result. Researcher has to set up variables, decide the environment for the research and find out how can he relate between the variables.
Researcher will also need to define the units of measurements, tolerable degree for errors, and find out if the measurement chosen will be acceptable by others.
Step #4: Methodology, Research Design And Data Collection
In this step, the researcher has to define a strategy for conducting his research. He has to set up experiments to collect data which will enable him to propose the hypothesis. The researcher will decide whether he will need experimental or non experimental method for conducting the research. The type of research design will vary depending on the field in which the research is being conducted.
Last but not the least, the researcher will have to find out parameters that will affect the validity of the research design. Data collection will need to be done by choosing appropriate samples depending on the research question. To carry out the research, he can use one of the many sampling techniques. Once data collection is complete, researcher will have empirical data which needs to be analysed.
Step #5: Data Analysis And Result
Data analysis can be done in two ways, qualitatively and quantitatively. Researcher will need to find out what qualitative method or quantitative method will be needed or will he need a combination of both. Depending on the unit of analysis of his data, he will know if his hypothesis is supported or rejected. Analyzing this data is the most important part to support his hypothesis.
Step #6: Conclusion
A report will need to be made with the findings of the research. The researcher can give the theories and literature that support his research. He can make suggestions or recommendations for further research on his topic.
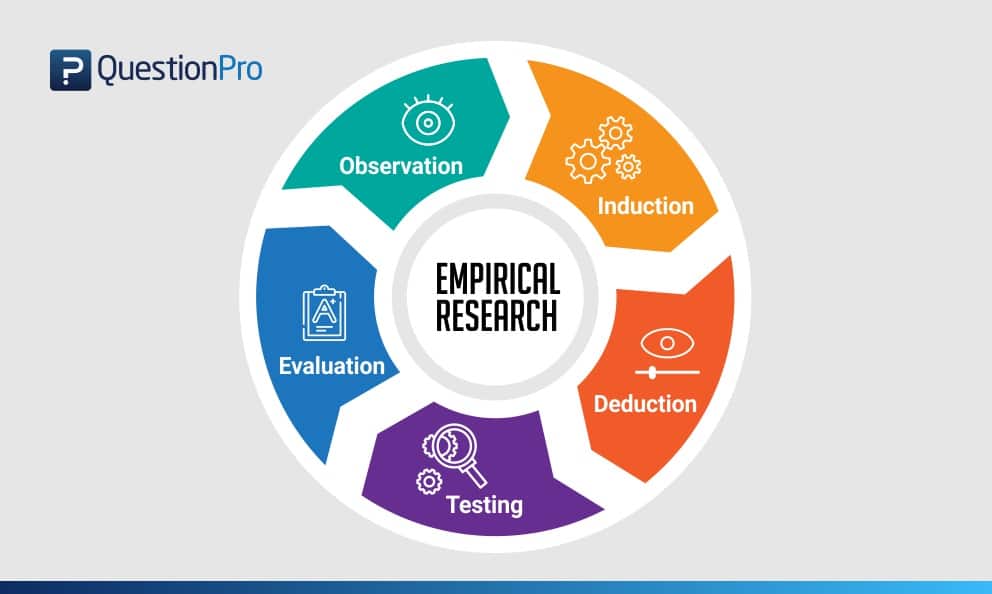
Empirical Research Methodology Cycle
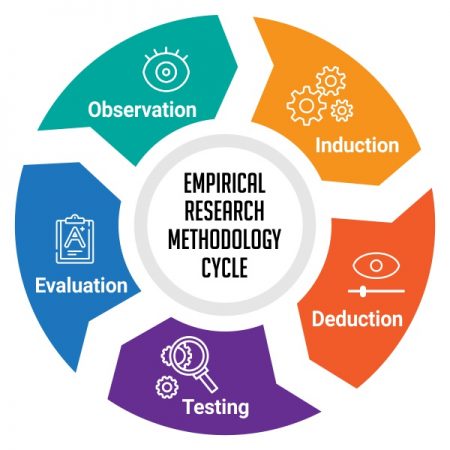
A.D. de Groot, a famous dutch psychologist and a chess expert conducted some of the most notable experiments using chess in the 1940’s. During his study, he came up with a cycle which is consistent and now widely used to conduct empirical research. It consists of 5 phases with each phase being as important as the next one.
The empirical cycle captures the process of coming up with hypothesis about how certain subjects work or behave and then testing these hypothesis against empirical data in a systematic and rigorous approach. It can be said that it characterizes the deductive approach to science. Following is the empirical cycle.
1. Observation
At this phase an idea is sparked for proposing a hypothesis. During this phase empirical data is gathered using observation. For example: a particular species of flower bloom in a different color only during a specific season.
2. Induction
Inductive reasoning is then carried out to form a general conclusion from the data gathered through observation. For example: As stated above it is observed that the species of flower blooms in a different color during a specific season. A researcher may ask a question “does the temperature in the season cause the color change in the flower?” He can assume that is the case, however it is a mere conjecture and hence an experiment needs to be set up to support this hypothesis. So he tags a few set of flowers kept at a different temperature and observes if they still change the color?
3. Deduction
This phase helps the researcher to deduce a conclusion out of his experiment. This has to be based on logic and rationality to come up with specific unbiased results.For example: In the experiment, if the tagged flowers in a different temperature environment do not change the color then it can be concluded that temperature plays a role in changing the color of the bloom.
This phase involves the researcher to return to empirical methods to put his hypothesis to the testing instruments. The researcher now needs to make sense of his data and hence needs to use statistical analysis plans to determine the temperature and bloom color relationship. If the researcher finds out that most flowers bloom a different color when exposed to the certain temperature and the others do not when the temperature is different, he has found support to his hypothesis. Please note this not proof but just a support to his hypothesis.
5. Evaluation
This phase is generally forgotten by most but is an important one to keep gaining knowledge. During this phase the researcher puts forth the data he has collected, the support argument and his conclusion. The researcher also states the limitations for the experiment and his hypothesis and suggests tips for others to pick it up and continue a more in-depth research for others in the future.
Pros and Cons of Empirical Research
As you may have noticed, empirical research has a lot to offer anyone who wants to conduct research and take advantage of its benefits. However, it is essential to consider not only the benefits but also the limitations and possible disadvantages you may encounter when using this methodology.
Below, we will explain both aspects a bit more so that you can consider them when conducting your research using this method.
Advantages of Empirical Research
There is a reason why empirical research is one of the most widely used method. There are a few advantages associated with it. Following are a few of them.
- It is used to authenticate traditional research through various experiments and observations.
- This research methodology makes the research being conducted more competent and authentic.
- It enables a researcher understand the dynamic changes that can happen and change his strategy accordingly.
- The level of control in such a research is high so the researcher can control multiple variables.
- It plays a vital role in increasing internal validity .
Disadvantages of Empirical Research
Even though empirical research makes the research more competent and authentic, it does have a few disadvantages. Following are a few of them.
- Such a research needs patience as it can be very time consuming. The researcher has to collect data from multiple sources and the parameters involved are quite a few, which will lead to a time consuming research.
- Most of the time, a researcher will need to conduct research at different locations or in different environments, this can lead to an expensive affair.
- There are a few rules in which experiments can be performed and hence permissions are needed. Many a times, it is very difficult to get certain permissions to carry out different methods of this research.
- Collection of data can be a problem sometimes, as it has to be collected from a variety of sources through different methods.
Empirical Research Vs Non-Empirical Research
Empirical and non-empirical research are two fundamental approaches in research methodology. Understanding their key differences helps researchers choose the appropriate method based on their research objectives.
Both empirical and non-empirical research offers valuable insights and contribute uniquely to knowledge. Together, they form a comprehensive approach to exploring, explaining, and expanding knowledge across disciplines.
Why is There a Need for Empirical Research?
Empirical research is important today because most people believe in something only when they can see, hear, or experience it. It is used to validate multiple hypotheses, derive knowledge, and increase human understanding, and it is continuing to do so to advance in various fields.
This often involves using testing instruments to ensure the accuracy and reliability of data collection, especially when it comes to complex variables.
In addition, research participants’ discussion often plays a key role in understanding the results and validating the findings within a theoretical framework that guides the entire study.
Qualitative methods are frequently used to gain deeper insights into participants’ perspectives, helping to contextualize empirical data. A literature review, or multiple literature reviews, also helps ground the research in existing knowledge, linking the new findings with past studies.
For example , pharmaceutical companies use empirical research to test specific drugs on controlled or random groups, using both qualitative methods and testing instruments to study cause and effect. This way, they prove certain theories they had proposed for the specific drug.
Such research is very important, as sometimes it can lead to finding a cure for a long-standing disease. In addition, the use of statistical data is essential for validating results and ensuring their reliability. Empirical research is useful in science, social sciences, business, and many other fields, like history, deriving knowledge through quantitative and qualitative methods.
Use QuestionPro Research Suite for Empirical Research
Using QuestionPro Research Suite for empirical research makes the process easier and more efficient. Here’s why:
01. User-Friendly Data Collection Tools
QuestionPro’s suite of tools, including surveys, polls, and questionnaires, are designed with user-friendliness in mind, making it a breeze to gather real-world data from diverse sources.
02. Highly Customizable
This lets you personalize surveys per your research requirements, ensuring the collected data is always relevant and valuable.
03. Real-Time Analytics
Get immediate feedback with QuestionPro real-time analytics to see trends and patterns in your data immediately
4. Even Better Data Management
The most efficient way of managing large sets of data is to keep the analysis and its outcomes faster and more reliable.
Overall, QuestionPro simplifies the empirical research process and allows you to focus more on data analysis and interpretation than manual collection and organization.
Conclusion About Empirical Research
Empirical research is a tool for understanding data and deducing its meaning. By focusing on what can be measured or experienced, we are better equipped to think critically and develop practical solutions.
When identifying empirical research, we focus on real-world data and its key characteristics, such as observation, experimentation, and evidence-based conclusions. The research process involves careful data collection, analysis, and the ability to communicate empirical research findings.
In doing so, we can make sense of the data and our feelings, leading to more informed decisions. Ultimately, empirical research enables us to transition from mere assumptions to solid evidence. Identifying patterns and validating hypotheses can improve outcomes in scientific and daily fields.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
Frequently Asked Questions( FAQs)
Empirical research is a type of study that relies on observation, experience, or experimentation to gather data. It involves collecting evidence through direct or indirect observation of real-world phenomena and analyzing that data to form conclusions, often using scientific methods such as experiments or surveys.
Examples of empirical research include: 1. Conducting experiments to test a scientific hypothesis. 2. Surveying individuals to gather opinions or behaviors. 3. Observing wildlife in their natural environment. 4. Measuring the effects of a treatment in a clinical trial. 5. Analyzing historical data to identify trends or patterns.
Empirical research relies on observation and data collection through experiments or real-world evidence, whether quantitative (numerical) or qualitative (non-numerical). Qualitative research , a subset of empirical research, focuses specifically on understanding patterns, behaviors, and experiences through non-numerical data like interviews, observations, or texts.
MORE LIKE THIS

QuestionPro Workforce Has All The Feels – Release of the New Sentiment Analysis
Dec 19, 2024

The Impact Of Synthetic Data On Modern Research

Companies are losing $ billions with gaps in market research – are you?
Dec 18, 2024

CultureAmp vs Qualtrics: The Best Employee Experience Platform
Dec 16, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Research Paper Topics

Anthropology Research Paper Topics
Argumentative research paper topics, art research paper topics, biology research paper topics, business research paper topics, career research paper topics, communication research paper topics, criminal justice research paper topics, economics research paper topics, education research paper topics, environmental research paper topics, ethics research paper topics, history research paper topics, law research paper topics, literature research paper topics, management research paper topics, marketing research paper topics, medical research paper topics, nursing research paper topics, persuasive research paper topics, philosophy research paper topics, political science research paper topics, psychology research paper topics, religion research paper topics, science research paper topics, sociology research paper topics, sports research paper topics, technology research paper topics, 1400 best research paper topics.
Choosing the right research paper topic is essential for academic success. A well-chosen topic aligns with recent developments, emerging trends, and future challenges within the field, ensuring relevance and originality. This comprehensive list provides 1400 research paper topics across 28 categories, covering a diverse range of disciplines—from sciences to humanities, technology to business, and more. Each category is designed to inspire students to engage deeply with their chosen subject, address real-world challenges, and contribute meaningfully to ongoing academic conversations.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Below, you will find introductory paragraphs and carefully curated topics for each category, offering ideas suitable for students at any academic level. Whether you are seeking fresh perspectives on current events or tackling long-term academic questions, these topics will serve as an excellent starting point.
Anthropology explores the complexities of human societies, cultures, and biological evolution. With today’s interconnected world, research in anthropology touches on a variety of critical issues, including globalization, cultural preservation, migration, and identity politics. These topics reflect the importance of understanding both ancient practices and modern transformations, offering opportunities to study the impact of social change across cultures.
- The role of technology in cultural identity formation
- Indigenous knowledge systems and environmental sustainability
- The impact of tourism on local cultures in developing nations
- Migration and cultural assimilation in the 21st century
- Globalization and the decline of endangered languages
- Cultural responses to climate change: A comparative study
- Medical anthropology: Traditional healing practices versus modern medicine
- The anthropology of social media: New forms of communication and community
- Urbanization and its impact on rural cultural traditions
- The ethics of anthropological fieldwork in indigenous communities
- Rituals and traditions in a globalized world
- The role of anthropology in public health policy development
- Gender roles in traditional versus modern societies
- Cross-cultural perspectives on mental health
- The influence of colonialism on contemporary cultural practices
- Anthropology and artificial intelligence: Understanding human behavior through data
- The rise of nationalism and its impact on cultural identities
- Evolutionary anthropology: Human adaptation to environmental changes
- The anthropology of aging: Cross-cultural attitudes towards the elderly
- Sacred spaces and their role in maintaining cultural heritage
- The commodification of cultural heritage: A study of museums and tourism
- Exploring family structures across different cultures
- The intersection of religion, politics, and culture
- Food and identity: Culinary traditions in diaspora communities
- Indigenous movements for land reclamation and sovereignty
- Cultural attitudes toward death and mourning practices
- The impact of digital technology on traditional art forms
- Cultural relativism and the challenges of ethical research
- The anthropology of conflict resolution in indigenous societies
- The effects of migration on kinship systems
- Cultural adaptation in post-conflict regions
- Language preservation efforts in the digital age
- The evolution of marriage practices across cultures
- Anthropology and climate justice: Cultural responses to environmental crises
- The role of festivals in preserving cultural heritage
- Understanding cultural hybridity in multicultural societies
- The anthropology of fashion: Clothing as cultural expression
- The social impact of anthropological research on policy-making
- Oral traditions and storytelling as cultural preservation tools
- The intersection of anthropology and education in multicultural societies
- Global media’s influence on cultural homogenization
- Cultural responses to pandemics: Lessons from history
- The role of folklore in modern identity politics
- The ethics of cultural appropriation in art and fashion
- Religious syncretism: Blending traditions in diverse societies
- The impact of displacement on indigenous communities
- Exploring cultural taboos across different societies
- The use of anthropology in corporate research and marketing
- Anthropological perspectives on human rights movements
- The anthropology of emerging rituals in digital spaces
See more Anthropology Research Paper Topics
Back to top
Argumentative research papers require students to take a clear position on controversial topics and defend their stance with strong evidence. These topics are designed to spark debate and critical thinking, reflecting ongoing societal debates and ethical dilemmas. From technology regulation to environmental activism, the following topics challenge students to engage with current events and formulate well-structured arguments.
- Should governments regulate social media platforms to prevent misinformation?
- Is universal basic income a sustainable solution to job displacement caused by automation?
- Should genetically modified organisms (GMOs) be banned in agriculture?
- Is artificial intelligence a threat to human jobs or an opportunity for innovation?
- Should countries impose stricter immigration policies to manage population growth?
- Is climate activism effective in shaping public policy?
- Should the death penalty be abolished worldwide?
- Should companies be required to offset their carbon emissions?
- Is online education as effective as traditional classroom learning?
- Should animal testing be banned in scientific research?
- Should cryptocurrencies replace traditional banking systems?
- Are video games promoting violence among youth?
- Should governments prioritize economic growth over environmental conservation?
- Is privacy a fundamental right in the digital age?
- Should athletes be allowed to protest during national anthems?
- Should space exploration be prioritized over addressing global poverty?
- Is cancel culture an effective tool for social justice or a threat to free speech?
- Should college education be free for all citizens?
- Is the use of surveillance technology justified for public safety?
- Should countries ban the production of single-use plastics?
- Are electric vehicles a sustainable solution for the future of transportation?
- Should genetically engineered babies be allowed?
- Is fast fashion harming the environment beyond repair?
- Should tech companies be broken up to prevent monopolies?
- Are standardized tests an accurate measure of student ability?
- Should individuals be legally required to vaccinate?
- Should governments ban the collection of personal data by tech companies?
- Is the influence of social media detrimental to mental health?
- Should celebrities be held accountable for promoting unhealthy products?
- Should national borders be open for refugees without restriction?
- Is the rise of remote work beneficial for society in the long run?
- Should students have the right to grade their teachers?
- Is capitalism responsible for growing economic inequality?
- Should voting be mandatory in democratic societies?
- Are influencer marketing practices ethical?
- Should governments censor offensive speech online?
- Should sports teams be penalized for political protests?
- Is homeschooling better than traditional education?
- Should nuclear energy be phased out in favor of renewable sources?
- Should social media influencers be regulated like traditional media?
- Should governments intervene in housing markets to control prices?
- Should fast food companies be held accountable for the obesity epidemic?
- Should students be taught coding from elementary school?
- Is artificial intelligence bias a significant issue for ethical AI development?
- Should athletes receive equal pay regardless of gender?
- Is cultural appropriation always harmful?
- Should governments subsidize the production of electric vehicles?
- Should schools eliminate homework?
- Should surveillance cameras be installed in public spaces?
- Is nationalism a threat to global cooperation?
See more Argumentative Research Paper Topics
The field of art continuously evolves, blending traditional forms with innovative mediums, including digital and immersive technologies. These topics explore the impact of modern movements, social changes, and the integration of technology in art creation, curation, and consumption. Students are encouraged to examine the role of art in shaping and reflecting contemporary culture while also considering future developments in artistic expression.
- The role of artificial intelligence in creating visual art
- NFTs and the future of digital art ownership
- Art as a tool for social activism: Case studies from recent movements
- The impact of virtual museums on art accessibility
- Environmental art: Promoting sustainability through artistic expression
- The influence of street art in urban identity formation
- Art therapy: Using creativity for mental health recovery
- Gender representation in contemporary visual arts
- The relationship between art and fashion in the digital age
- Censorship in art: Who decides what’s appropriate?
- The resurgence of abstract expressionism in modern art
- Art during pandemics: Exploring creative responses to crises
- The ethics of cultural appropriation in contemporary art
- The rise of interactive and installation art in exhibitions
- How social media has transformed the art world
- Postcolonial art: Reclaiming narratives through visual storytelling
- Exploring the role of photography in journalism and activism
- The connection between architecture and artistic movements
- Art as a medium for climate change awareness
- Exploring indigenous art in a globalized world
- The future of holographic art and immersive experiences
- AI-generated art: Creativity or computation?
- The relationship between art and consumerism in modern culture
- How public sculptures shape community identity
- Art markets and their influence on global art trends
- Exploring surrealism in contemporary media and advertising
- The role of feminist art in challenging stereotypes
- The impact of political art in authoritarian societies
- Comic art as a legitimate artistic medium
- Analyzing minimalist trends in modern design and art
- The role of digital galleries in democratizing art access
- Exploring art as a therapeutic practice in prisons
- How art education shapes creative thinking in children
- Exploring religious symbolism in contemporary artworks
- Pop art’s influence on modern aesthetics
- The use of augmented reality in modern art installations
- How environmental factors influence outdoor art installations
- Artistic responses to gentrification in urban areas
- The intersection of graffiti and high art
- The influence of Eastern aesthetics on contemporary Western art
- Art in video games: Creativity beyond traditional media
- The impact of generative art on traditional art criticism
- The evolution of digital painting techniques
- How art fosters empathy and cross-cultural understanding
- Exploring the role of color theory in modern visual arts
- Art and virtual reality: New frontiers in immersive storytelling
- The rise of eco-friendly materials in sculpture and installations
- The portrayal of marginalized groups in contemporary art
- Exploring the influence of cubism on modern design
- Art and the Anthropocene: Documenting environmental decline
Biology plays a crucial role in addressing the most pressing challenges of today, from climate change to healthcare innovations. These topics explore the frontiers of biological research, including genetics, biotechnology, and environmental conservation, offering students an opportunity to engage with the future of science and sustainability.
- CRISPR and its potential for genetic disease treatment
- The impact of microplastics on marine ecosystems
- Advances in synthetic biology and bioengineering
- The role of biodiversity in ecosystem stability
- Exploring the human microbiome and its health implications
- Genetic mutations and their impact on evolution
- Investigating the effects of climate change on plant physiology
- The role of biotechnology in sustainable agriculture
- The ethics of human cloning: Current debates and perspectives
- COVID-19’s long-term effects on the immune system
- Conservation biology: Protecting endangered species in urban areas
- The future of bioinformatics in medical research
- Epigenetics: How lifestyle choices influence gene expression
- Exploring the role of fungi in ecological restoration
- Stem cell research and its applications in regenerative medicine
- The impact of environmental toxins on human health
- Genetic engineering in agriculture: Benefits and risks
- Marine biology: Understanding coral bleaching and conservation strategies
- The role of gene therapy in treating rare diseases
- Studying the effects of pesticides on pollinators
- The future of personalized medicine through genomics
- Behavioral ecology: Exploring animal communication systems
- How invasive species disrupt native ecosystems
- Advances in plant biotechnology for food security
- Exploring the genetics of aging and longevity
- The role of bacteria in waste decomposition and recycling
- The impact of antibiotic resistance on public health
- Exploring symbiotic relationships in nature
- Using biotechnology to create biofuels
- Exploring genetic diversity in wild populations
- The effects of urbanization on wildlife behavior
- Climate change and its impact on animal migration patterns
- How genetics informs the study of human ancestry
- The role of protein folding in neurodegenerative diseases
- Exploring photosynthesis for renewable energy solutions
- Investigating the effects of plastic pollution on marine organisms
- Biotechnology and the future of pharmaceuticals
- The impact of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity
- Exploring the science behind gene editing ethics
- The role of algae in carbon sequestration
- The future of vaccines: Innovations in immunology
- Animal behavior and its relevance to conservation efforts
- The role of viruses in shaping evolutionary history
- The use of DNA barcoding in wildlife conservation
- Exploring the genetics of rare hereditary diseases
- The impact of diet on the gut microbiome
- Investigating the biology of circadian rhythms
- How biotechnology addresses the challenges of climate change
- Exploring emerging zoonotic diseases and their prevention
- The potential of biomimicry in technological innovation
The business landscape is rapidly evolving due to digital transformation, global competition, and shifting consumer behavior. These topics reflect the latest trends, challenges, and innovations in business, providing students with ideas to explore how companies adapt to changes and how new business models shape the future.
- The role of artificial intelligence in business decision-making
- Digital transformation and its impact on customer experience
- Exploring corporate social responsibility trends post-pandemic
- Remote work: Productivity challenges and solutions
- The influence of globalization on small businesses
- The rise of sustainable business practices and green marketing
- Exploring blockchain applications in supply chain management
- The impact of e-commerce on traditional retail stores
- Social entrepreneurship: Business models for social good
- The future of work: Trends in employee engagement
- Exploring the gig economy: Benefits and drawbacks
- Business ethics in the age of digital surveillance
- The impact of automation on the labor market
- How businesses adapt to changing consumer behavior
- The role of innovation in business growth strategies
- Exploring financial technologies and their impact on banking
- The effects of brand loyalty in competitive markets
- The role of leadership in organizational success
- Exploring mergers and acquisitions: Trends and challenges
- Diversity and inclusion in the modern workplace
- How companies respond to economic recessions
- The impact of data analytics on marketing strategies
- Exploring the future of virtual business meetings
- The influence of social media on brand reputation
- How companies integrate artificial intelligence in marketing
- Exploring the future of corporate governance
- The role of emotional intelligence in business leadership
- Business strategies for entering emerging markets
- How businesses navigate environmental regulations
- Exploring the future of fintech startups
- The impact of personalized marketing on consumer loyalty
- Exploring leadership trends in remote team management
- The future of business education: Trends in MBA programs
- How businesses manage cybersecurity risks
- Exploring trends in business sustainability reporting
- The role of social media influencers in marketing
- Exploring the rise of niche markets in global commerce
- The future of retail: Trends in experiential shopping
- How companies balance innovation with tradition
- Exploring the ethics of targeted advertising
- Business strategies in response to inflation
- The rise of subscription-based business models
- Exploring trends in financial literacy education
- The role of blockchain in securing business transactions
- The impact of climate change on business operations
- How companies manage crises through public relations
- Exploring trends in consumer finance solutions
- The impact of hybrid work models on business culture
- Business strategies for sustainable development
- The future of entrepreneurship in a digital economy
See more Business Research Paper Topics
Career-related research is essential in understanding how individuals navigate the modern workforce, develop professionally, and adapt to new technologies. With rapid changes in the job market, including automation and evolving employee expectations, these topics reflect current career challenges, trends, and opportunities, offering students a way to explore future career paths and strategies for professional development.
- The impact of automation on future careers
- Remote work: Changing dynamics in employee productivity and engagement
- Career adaptability: How professionals navigate job transitions
- The role of personal branding in career success
- The gig economy: Opportunities and challenges for professionals
- Mentorship programs and their influence on career development
- Gender inequality in leadership roles: Progress and challenges
- The importance of lifelong learning in a fast-changing job market
- Exploring the impact of artificial intelligence on job displacement
- The rise of digital nomad careers: Trends and future directions
- Strategies for maintaining work-life balance in demanding careers
- Career satisfaction: How employees find meaning in their work
- How organizational culture influences employee retention
- Career development in multicultural environments
- The role of internships in shaping career opportunities
- Exploring the future of careers in environmental sustainability
- The impact of professional certifications on career growth
- Networking strategies for building long-term professional relationships
- The role of emotional intelligence in career success
- Exploring career pathways in the creative industries
- How digital transformation reshapes traditional career models
- The influence of diversity and inclusion policies on career progression
- Career resilience: Strategies for coping with setbacks
- The impact of mentorship programs on minority groups
- Exploring entrepreneurial careers in the digital economy
- The future of career counseling in educational institutions
- The role of professional associations in career development
- How remote work affects employee promotions and career growth
- Exploring second-career opportunities for mid-life professionals
- The relationship between mental health and career performance
- Strategies for career success in competitive industries
- Exploring job satisfaction trends in different sectors
- The impact of technology on creative career paths
- Career mobility: How employees navigate international opportunities
- Strategies for re-skilling in a changing job market
- The role of work experience in securing high-paying jobs
- The influence of AI on recruiting and career development
- How internships prepare students for future careers
- The impact of flexible work schedules on career satisfaction
- Exploring gender differences in career aspirations
- The role of social media in shaping modern career paths
- Strategies for managing career burnout
- How companies support employee career growth through training
- Exploring future careers in the renewable energy sector
- The impact of generational differences on career expectations
- Career pathways in non-traditional sectors
- The importance of self-assessment tools in career planning
- How global economic trends influence job opportunities
- The rise of portfolio careers: Managing multiple roles
- Exploring the benefits and challenges of freelance careers
See more Career Research Paper Topics
In today’s digital age, communication plays a critical role in shaping personal, professional, and social interactions. This category focuses on trends such as digital communication platforms, misinformation, media influence, and intercultural communication. These topics encourage students to explore the evolving nature of communication and its impact on individuals, organizations, and societies.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion
- Digital communication and its impact on personal relationships
- The rise of misinformation: Combating fake news in the digital era
- How virtual communication affects teamwork and collaboration
- Intercultural communication in a globalized world
- The influence of mass media on political campaigns
- Crisis communication strategies in times of public emergencies
- The impact of AI chatbots on customer service communication
- Communication ethics in the era of digital marketing
- Exploring the role of body language in virtual meetings
- The effectiveness of storytelling in advertising campaigns
- The evolution of corporate communication strategies
- How cultural differences shape communication styles
- Social media influencers and their impact on consumer behavior
- The role of podcasts in modern media consumption
- Exploring visual communication trends in digital content
- Communication challenges in hybrid work environments
- The influence of memes on political discourse
- The rise of personal blogs and vlogs in digital communication
- Communication strategies for managing brand crises
- The role of emojis in modern written communication
- How digital media shapes public discourse
- The impact of mobile communication on social interaction
- Exploring non-verbal communication across cultures
- Communication strategies for promoting mental health awareness
- The ethics of targeted advertising in social media
- How media coverage shapes public perception of climate change
- The role of virtual reality in immersive storytelling
- Communication strategies in corporate social responsibility initiatives
- How political leaders use communication to shape public policy
- Exploring trends in influencer-brand partnerships
- The impact of video conferencing on business communication
- The role of media in shaping cultural identities
- The effectiveness of social media campaigns for social change
- The influence of communication technologies on education
- Exploring AI-generated content and its implications for journalism
- Communication strategies for building trust in organizations
- The role of communication in resolving workplace conflicts
- Exploring trends in communication research methodologies
- How humor influences online communication
- The impact of language barriers on international communication
- Communication strategies for engaging Gen Z audiences
- The role of media in promoting gender equality
- How virtual influencers are changing digital marketing
- Communication ethics in political campaigns
- The use of storytelling in nonprofit communication
- Exploring trends in digital content creation
- The impact of communication on employee engagement
- Media framing and its influence on public perception
- Communication strategies for enhancing brand loyalty
See more Communication Research Paper Topics
The field of criminal justice continuously evolves with societal changes, advancements in technology, and legal reforms. These topics reflect recent developments in policing, forensic science, correctional systems, and criminal law. Students can explore the intersection of technology, social justice, and public safety while examining future challenges and reforms needed in criminal justice systems worldwide.
- The impact of body-worn cameras on police accountability
- Cybercrime and the challenges of international law enforcement
- The role of artificial intelligence in crime prevention
- Police reforms in response to public protests
- The ethics of predictive policing technologies
- Exploring racial disparities in sentencing
- The impact of mental health on criminal behavior
- Juvenile justice: Trends and challenges in rehabilitation
- The influence of restorative justice on reducing recidivism
- The role of forensic science in cold case investigations
- Cyberbullying and legal consequences in the digital age
- The effectiveness of prison education programs
- How drug policies impact incarceration rates
- The role of community policing in urban crime prevention
- Gender differences in criminal behavior and sentencing
- Human trafficking: Prevention strategies and legal responses
- The rise of white-collar crime in the digital economy
- The effectiveness of parole programs in reducing reoffending
- How media portrayal influences public perception of crime
- The use of facial recognition technology in law enforcement
- Police use of force: Legal and ethical considerations
- The role of victim advocacy groups in criminal justice reform
- Exploring wrongful convictions and the role of DNA evidence
- The future of rehabilitation programs in prisons
- The impact of prison overcrowding on inmate behavior
- Exploring international cooperation in combating organized crime
- Hate crimes: Trends and prevention strategies
- The role of social services in juvenile crime prevention
- Mental health courts: An alternative to incarceration
- The impact of immigration policies on crime and policing
- The rise of financial fraud and cybersecurity measures
- The role of plea bargains in the criminal justice system
- The future of autonomous drones in law enforcement
- Exploring trends in sentencing reform
- The impact of the opioid crisis on the criminal justice system
- The role of ethics in forensic science investigations
- How social media aids in criminal investigations
- The effectiveness of domestic violence intervention programs
- The impact of privatized prisons on inmate outcomes
- Exploring restorative justice practices in schools
- How technology is reshaping forensic investigations
- The influence of cultural diversity on policing strategies
- The role of international courts in prosecuting war crimes
- Exploring trends in anti-human trafficking legislation
- How prison labor programs affect rehabilitation efforts
- The role of public opinion in shaping criminal justice policy
- Analyzing the effectiveness of zero-tolerance policies
- The future of policing in smart cities
- The impact of social inequality on crime rates
- How climate change may influence crime trends
See more Criminal Justice Research Paper Topics
Economics is a vital field that shapes policies and decisions affecting nations, industries, and individuals. These topics address emerging trends, including cryptocurrency, global trade dynamics, inflation, and sustainable development. Students can explore the economic implications of technological change, environmental policies, and financial innovations to understand their impact on global and local economies.
- The role of cryptocurrency in the global economy
- The impact of inflation on consumer behavior
- The economics of renewable energy adoption
- How trade wars affect global supply chains
- Behavioral economics: Understanding irrational consumer choices
- The impact of automation on unemployment rates
- Exploring the relationship between education and economic growth
- The future of work: Economic implications of remote work
- Economic policies for combating climate change
- The rise of digital currencies: Central bank responses
- The effects of financial literacy on personal savings
- The impact of urbanization on regional economic development
- Exploring economic inequality in developing countries
- The role of foreign aid in sustainable development
- How e-commerce reshapes retail economics
- The economics of healthcare in aging populations
- The impact of environmental policies on business competitiveness
- Exploring the future of global tourism post-pandemic
- The role of government intervention during economic recessions
- The economics of food security and agricultural innovation
- How technological innovation drives economic growth
- Exploring trends in consumer debt management
- The role of women in economic development
- The economics of urban mobility and public transportation
- The impact of geopolitical conflicts on global markets
- Circular economy: A sustainable approach to production
- The relationship between taxation policies and business investment
- The role of microfinance in poverty reduction
- Exploring economic challenges in post-conflict regions
- How demographic shifts affect national economies
- The economics of green technologies and investments
- The impact of inflation targeting on financial markets
- How globalization shapes regional economic policies
- The rise of fintech and its impact on banking systems
- Exploring trends in labor market flexibility
- The effects of climate-related risks on economic stability
- The impact of minimum wage policies on employment
- The role of tourism in economic recovery
- The influence of foreign exchange rates on exports
- Exploring the economics of mental health initiatives
- How trade agreements influence economic growth
- The future of gig economy jobs: Economic implications
- Exploring trends in public debt management
- The impact of automation on income distribution
- The economics of corporate social responsibility
- How blockchain technology transforms financial systems
- Exploring the impact of pandemics on global trade
- The role of venture capital in fostering innovation
- The influence of environmental regulations on small businesses
- How economic policies address wealth inequality
See more Economics Research Paper Topics
Education is undergoing a transformation with the rise of digital learning, evolving teaching strategies, and a growing focus on inclusivity. These topics reflect recent trends, challenges, and innovations in education. Students can explore themes such as online education, the future of teaching, education policy, and the role of technology in shaping learning environments.
- The effectiveness of online learning compared to traditional classrooms
- Exploring the impact of AI tools on personalized education
- How inclusive education improves student outcomes
- The role of technology in reducing educational inequality
- The future of hybrid learning models
- How teacher professional development influences student success
- The impact of parental involvement on academic achievement
- The effectiveness of early childhood education programs
- How gamification enhances student engagement
- Exploring trends in STEM education for girls
- The role of mental health support in student performance
- The impact of standardized testing on learning outcomes
- Exploring the role of digital literacy in the 21st century
- How educational policies affect marginalized communities
- The influence of multicultural education on social integration
- The future of lifelong learning and adult education
- The role of mobile devices in modern classrooms
- How collaborative learning promotes critical thinking
- Exploring trends in homeschooling
- The impact of flipped classrooms on student engagement
- The role of social-emotional learning in education
- The influence of school leadership on teacher motivation
- Exploring the future of bilingual education
- How curriculum design shapes learning experiences
- The role of assessment in promoting deeper learning
- Exploring the impact of digital textbooks on learning outcomes
- The future of vocational education and training
- How school funding influences student achievement
- The role of AI in automating administrative tasks in education
- Exploring the relationship between arts education and creativity
- The impact of environmental education on student awareness
- How virtual field trips enhance learning
- Exploring trends in special education
- The role of community involvement in school success
- How edtech startups are transforming education
- Exploring trends in higher education enrollment
- The impact of teacher-student relationships on learning outcomes
- How classroom design affects student engagement
- The role of peer mentoring in student retention
- Exploring the future of open educational resources
- How school policies address bullying and harassment
- The influence of artificial intelligence on education policy
- Exploring trends in education equity and access
- The role of experiential learning in career preparation
- How digital tools support formative assessment
- The impact of leadership training on school improvement
- Exploring the benefits of outdoor education programs
- The influence of global education initiatives on national policies
- The role of mindfulness practices in student well-being
- How virtual reality shapes future learning experiences
See more Education Research Paper Topics
Environmental research is becoming more critical than ever as climate change, biodiversity loss, and sustainability challenges demand innovative solutions. These topics reflect the intersection of science, policy, and activism, providing students with opportunities to explore current environmental challenges and propose future directions for sustainable development.
- The impact of climate change on coastal ecosystems
- Exploring the effectiveness of carbon offset programs
- The role of environmental activism in shaping policy
- Sustainable urban development: Challenges and solutions
- The effects of deforestation on biodiversity loss
- How plastic pollution affects marine wildlife
- Renewable energy adoption: Trends and challenges
- The future of electric vehicles in reducing emissions
- How sustainable agriculture can combat food insecurity
- Exploring the environmental impact of fast fashion
- The role of green technologies in mitigating climate change
- Environmental justice: Addressing inequalities in pollution exposure
- The effectiveness of global climate agreements
- Exploring the rise of eco-tourism
- How extreme weather events influence public policy
- The role of forests in carbon sequestration
- Exploring the future of hydrogen energy
- How wildlife conservation efforts address habitat loss
- The role of indigenous knowledge in environmental conservation
- Exploring trends in green architecture and design
- The impact of microplastics on human health
- How recycling programs influence consumer behavior
- Environmental education: Raising awareness in schools
- The relationship between air quality and public health
- Exploring the economics of sustainable energy
- The impact of invasive species on ecosystems
- The role of environmental laws in protecting biodiversity
- Exploring sustainable solutions for water scarcity
- How urban green spaces promote mental well-being
- Environmental ethics: Balancing development and conservation
- The impact of oil spills on marine ecosystems
- Exploring the future of sustainable packaging
- How climate change affects global food production
- The role of technology in wildlife monitoring
- Exploring trends in circular economy practices
- The impact of melting glaciers on global sea levels
- How environmental journalism shapes public opinion
- The effectiveness of environmental NGOs in policy advocacy
- Exploring trends in zero-waste lifestyles
- The role of artificial intelligence in environmental research
- How environmental policies affect economic growth
- Exploring trends in sustainable business practices
- How urban sprawl contributes to environmental degradation
- The future of organic farming and its environmental impact
- The role of renewable energy in addressing energy poverty
- The environmental consequences of mining operations
- Exploring trends in marine conservation strategies
- How air pollution influences climate patterns
- The impact of industrial agriculture on soil health
- Exploring environmental challenges in developing countries
See more Environmental Research Paper Topics
Ethics plays a crucial role in guiding individual behavior, corporate practices, and public policies. In today’s interconnected and technologically advanced world, ethical challenges have become more complex, requiring thoughtful solutions. These topics encourage students to engage with dilemmas in areas such as technology, medicine, business, and environmental practices, exploring how ethics shape decisions and societal norms.
- The ethics of artificial intelligence in decision-making
- Privacy versus security: Balancing individual rights and public safety
- The ethics of gene editing in humans
- Ethical dilemmas in environmental conservation policies
- The role of ethics in corporate social responsibility
- Exploring the ethics of autonomous vehicles
- The impact of digital surveillance on personal privacy
- How ethical theories guide medical practices
- The ethics of social media influencers and advertising
- Exploring the ethical implications of the gig economy
- The ethics of animal testing in scientific research
- Balancing profit and ethics in pharmaceutical industries
- The role of ethics in climate activism
- Exploring the ethics of online data collection
- The impact of whistleblowing on corporate ethics
- The ethics of global inequality and wealth distribution
- Exploring the role of ethics in artificial intelligence governance
- The ethics of vaccine mandates
- How ethical considerations shape genetic research
- The role of ethics in space exploration
- The impact of biased algorithms on social justice
- Exploring ethical dilemmas in journalism
- The ethics of cancel culture and public shaming
- How ethics influence healthcare policies
- Exploring the ethics of self-driving cars
- The ethics of digital content creation and copyright
- How cultural values influence ethical decisions
- The role of ethics in environmental sustainability
- The ethics of targeted advertising on social media
- Exploring ethical challenges in mental health treatment
- How technology companies address ethical concerns
- The ethics of organ transplantation and donation
- Exploring trends in business ethics
- The role of ethics in scientific research practices
- The ethics of using AI in law enforcement
- How ethics guide the development of biotechnology
- Exploring ethical challenges in climate change mitigation
- The ethics of medical trials on vulnerable populations
- The role of ethics in leadership and governance
- How ethics shape global public health policies
- The impact of religious ethics on modern policies
- Exploring the ethics of war and conflict
- The ethics of marketing unhealthy products to children
- How ethical frameworks shape policy decisions
- The ethics of human enhancement technologies
- Exploring ethical concerns in cryptocurrency
- How ethics influence environmental reporting
- The role of ethics in artificial general intelligence research
- The ethics of remote work policies
- Exploring the role of ethics in disaster management
See more Ethics Research Paper Topics
The study of history allows us to understand past events and their influence on present and future societies. These topics explore historical narratives, events, and movements from new perspectives, focusing on lesser-known histories, evolving interpretations, and the relevance of historical lessons in today’s world. Students can dive into diverse areas, including political movements, wars, revolutions, and social transformations, to uncover trends and insights applicable to modern challenges.
- The long-term impact of colonialism on global politics
- How pandemics shaped historical transformations
- The role of propaganda during World War II
- The impact of the Industrial Revolution on social classes
- Women’s suffrage movements across different cultures
- Exploring historical interpretations of the Cold War
- The influence of ancient trade routes on modern economies
- How revolutions shaped democratic movements worldwide
- The impact of migration on cultural evolution in history
- The role of religion in medieval political systems
- How the abolition of slavery transformed global economies
- Exploring indigenous resistance to colonization
- The impact of the Renaissance on European culture and science
- How historical treaties shaped current international relations
- The influence of African kingdoms on global trade networks
- The role of historical narratives in shaping national identities
- How climate changes influenced ancient civilizations
- The evolution of warfare strategies through history
- Exploring the role of art and literature in revolutions
- The global impact of the American Civil War
- How historical myths shape modern political ideologies
- The role of espionage in shaping World War I outcomes
- How the printing press revolutionized communication
- Exploring the consequences of decolonization in Africa
- The significance of historical monuments in modern debates
- How the Enlightenment shaped modern human rights ideals
- The role of women in the French Revolution
- How cultural exchanges shaped ancient empires
- The influence of historical pandemics on urban development
- The impact of the Transatlantic Slave Trade on global history
- How the Great Depression reshaped economic policies
- Exploring the cultural impact of the Silk Road
- The role of history in shaping environmental policies
- How ancient legal systems influenced modern law
- The impact of the fall of the Berlin Wall on global politics
- The evolution of human rights through historical events
- How art movements reflected political upheavals
- The role of maritime exploration in colonial expansion
- Exploring hidden histories of marginalized communities
- The impact of religious reforms on European politics
- How World War I influenced literature and arts
- The role of technology in shaping military history
- How historical events shaped climate policy negotiations
- Exploring historical narratives of indigenous people
- The impact of industrialization on environmental policies
- How ancient philosophies shaped governance systems
- The role of youth movements in shaping revolutions
- The significance of historical archives in modern research
- How global conflicts reshaped borders and nations
- The influence of historical diplomacy on contemporary politics
See more History Research Paper Topics
Legal studies explore the rules and systems that govern societies, balancing justice with evolving social and technological changes. These research topics address recent developments in legislation, emerging legal challenges, and future directions in law. Students can explore a variety of fields, including digital law, human rights, criminal justice reform, and environmental law, offering insights into how legal systems adapt to societal transformations.
- The impact of artificial intelligence on privacy laws
- Cybersecurity laws and the protection of personal data
- The evolution of international human rights law
- The role of environmental law in climate change mitigation
- How intellectual property laws influence innovation
- Exploring trends in corporate governance and business law
- The effectiveness of restorative justice programs
- The future of digital contracts and blockchain in law
- The impact of immigration policies on human rights
- Exploring gender equality in international law
- The role of the judiciary in shaping environmental policies
- The influence of public opinion on criminal law reforms
- How anti-discrimination laws promote workplace diversity
- Legal challenges in regulating social media platforms
- The impact of whistleblower protections on corporate ethics
- Exploring trends in cybercrime legislation
- The role of the law in protecting indigenous rights
- The effectiveness of international treaties on climate change
- Legal responses to pandemics: Balancing rights and safety
- The impact of technology on intellectual property disputes
- Exploring trends in family law reforms
- How trade laws influence global supply chains
- The role of law in combating financial fraud
- The impact of the gig economy on labor laws
- The evolution of constitutional law in emerging democracies
- How environmental regulations shape business strategies
- The role of the judiciary in protecting civil liberties
- Exploring trends in legal education and practice
- The impact of legal frameworks on sustainable development
- The effectiveness of anti-corruption laws in global governance
- How technology is reshaping dispute resolution mechanisms
- Exploring human rights issues in international criminal law
- The role of law in promoting social justice movements
- The legal challenges of regulating cryptocurrencies
- How family law adapts to modern relationships
- The role of law in addressing environmental justice
- The influence of public health laws on pandemic responses
- Exploring trends in employment law and remote work
- The future of intellectual property in the digital economy
- The impact of law on freedom of speech in the digital age
- The evolution of consumer protection laws
- How legal frameworks address climate migration
- The role of law in combating online hate speech
- Exploring trends in juvenile justice reforms
- How international law addresses global terrorism
- The impact of human rights law on refugee policies
- Exploring trends in contract law and e-commerce
- The role of law in managing digital identities
- How environmental law promotes biodiversity conservation
- The impact of data privacy regulations on global businesses
See more Law Research Paper Topics
The study of literature offers insights into human experiences, societal transformations, and cultural identities across time. These topics reflect emerging themes, new interpretations of classic texts, and the role of literature in addressing modern challenges. Students can explore the intersection of literature with social issues, digital storytelling, and new literary movements to gain a deeper understanding of how literature evolves in the contemporary world.
- Postcolonial themes in contemporary African literature
- Exploring mental health narratives in modern fiction
- The impact of climate change on literary genres
- The role of feminism in 21st-century literature
- Literary responses to the COVID-19 pandemic
- How digital storytelling reshapes traditional narratives
- The influence of migration on diaspora literature
- The role of graphic novels in modern literary studies
- Gender and identity in LGBTQ+ literature
- The revival of folklore in contemporary fiction
- Dystopian literature: Reflections on social and political issues
- Literary adaptations: Challenges and opportunities in cinema
- The role of memory in autobiographical writing
- Exploring environmental themes in eco-literature
- How artificial intelligence is portrayed in speculative fiction
- The influence of digital culture on literary styles
- The evolution of detective fiction in modern literature
- Representation of marginalized communities in young adult fiction
- The role of mythological motifs in fantasy literature
- How modern poetry reflects societal anxieties
- The impact of war on literary movements
- The role of magical realism in Latin American literature
- Exploring intertextuality in contemporary fiction
- How literature influences social justice movements
- Narratives of resistance in indigenous literature
- The impact of book censorship on literary creativity
- The role of humor in satirical literature
- Exploring mental illness in gothic literature
- How literature reflects shifting cultural identities
- The influence of folklore in children’s literature
- Literary portrayals of climate disasters
- The role of language in postcolonial literature
- Representation of trauma in Holocaust literature
- The impact of technology on reading habits
- The role of spirituality in contemporary literature
- Exploring themes of exile in diaspora poetry
- How digital platforms foster new literary communities
- The influence of historical fiction on public memory
- The future of literature in the age of artificial intelligence
- Narratives of redemption in modern literary works
- The role of literature in addressing environmental activism
- The significance of unreliable narrators in contemporary fiction
- Exploring the intersection of art and literature
- The evolution of romance tropes in popular fiction
- Literary responses to political revolutions
- Exploring gender dynamics in Shakespearean plays
- The role of translation in promoting world literature
- How novels shape national identities
- The use of non-linear narratives in modern literature
- The role of dystopian fiction in shaping public discourse
See more Literature Research Paper Topics
Management research focuses on understanding how organizations operate and how leadership practices evolve in response to new challenges. These topics explore contemporary trends in management, including digital transformation, leadership development, sustainability practices, and the impact of globalization. Students can investigate the ways in which businesses manage change, foster innovation, and promote diversity to remain competitive in dynamic environments.
- Leadership strategies for remote team management
- The role of emotional intelligence in leadership development
- How digital transformation reshapes management practices
- Managing organizational change during economic crises
- The impact of diversity and inclusion on team performance
- Exploring sustainable management practices in businesses
- The role of big data analytics in decision-making
- Managing employee well-being in hybrid work environments
- The influence of artificial intelligence on managerial roles
- How ethical leadership impacts organizational culture
- The future of talent management in the digital economy
- Exploring trends in crisis management strategies
- The role of innovation management in competitive markets
- How leadership styles evolve with changing workforce dynamics
- Exploring the impact of globalization on management practices
- The role of corporate social responsibility in business success
- How performance management systems drive employee engagement
- The effectiveness of agile management practices
- The role of technology in project management
- Exploring trends in leadership training programs
- How businesses manage cross-cultural teams
- The impact of emotional labor on managerial effectiveness
- How data-driven insights shape strategic planning
- The role of mentorship programs in leadership development
- Exploring trends in organizational behavior research
- Managing innovation in the technology sector
- How companies foster employee loyalty in competitive markets
- The influence of remote work on leadership strategies
- Exploring sustainable supply chain management practices
- The role of communication in managing change
- How leadership influences company reputation
- The impact of digital collaboration tools on teamwork
- Exploring trends in executive coaching and leadership development
- The role of ethics in strategic management decisions
- Managing conflict in diverse work environments
- How emotional intelligence shapes leadership effectiveness
- The impact of leadership styles on employee retention
- Exploring trends in succession planning strategies
- The role of social media in shaping corporate leadership
- How businesses manage innovation in uncertain markets
- The influence of cultural differences on management practices
- Exploring trends in corporate governance models
- How digital platforms transform customer relationship management
- The role of leadership in promoting sustainability initiatives
- Managing burnout in leadership positions
- The impact of leadership on organizational resilience
- Exploring trends in workplace mentoring programs
- The role of leadership in fostering innovation cultures
- How companies balance profitability and sustainability
- The future of management education in a digital world
See more Management Research Paper Topics
Marketing is evolving rapidly with the integration of new technologies, data analytics, and shifting consumer behaviors. These topics reflect current trends in digital marketing, social media strategies, sustainable branding, and personalization. Students can explore how businesses leverage marketing innovations to stay competitive, build brand loyalty, and address global challenges like sustainability and consumer privacy.
- The impact of influencer marketing on consumer behavior
- How personalized advertising drives customer engagement
- Social media marketing strategies for small businesses
- The role of data analytics in shaping marketing campaigns
- The rise of sustainable branding in consumer markets
- Exploring trends in experiential marketing
- How neuromarketing influences product design
- The impact of video content on brand visibility
- The future of augmented reality in retail marketing
- How AI shapes personalized marketing experiences
- The effectiveness of email marketing in digital strategies
- The role of emotional branding in customer retention
- How cultural values shape global marketing strategies
- Exploring trends in subscription-based business models
- The influence of mobile marketing on consumer behavior
- The impact of GDPR on digital marketing practices
- How brands use storytelling to connect with audiences
- The future of marketing in the metaverse
- The role of digital influencers in brand partnerships
- Exploring green marketing and consumer trust
- How viral marketing campaigns shape brand perception
- The impact of social commerce on consumer purchasing
- How companies manage online reputational crises
- The role of nostalgia marketing in brand loyalty
- Exploring the effectiveness of content marketing strategies
- How mobile apps enhance customer experience
- The impact of predictive analytics on marketing outcomes
- Exploring trends in cause-related marketing
- How user-generated content builds brand communities
- The role of SEO in digital marketing success
- The influence of cultural differences on advertising effectiveness
- Exploring trends in multi-channel marketing strategies
- How marketing automation enhances campaign efficiency
- The role of AI chatbots in customer service and engagement
- The impact of cross-border e-commerce on global marketing
- How brands balance personalization and privacy
- Exploring trends in brand activism
- The future of influencer marketing in niche markets
- How companies use gamification to enhance customer loyalty
- The impact of brand transparency on consumer trust
- How visual content drives engagement on social media
- The effectiveness of podcasts in brand storytelling
- The role of nostalgia in marketing campaigns
- How online reviews influence consumer purchase decisions
- Exploring the future of marketing analytics
- The role of local influencers in shaping brand perception
- How blockchain technology impacts marketing strategies
- Exploring trends in ethical advertising
- The influence of generational preferences on marketing campaigns
- How emotional AI shapes brand-customer interactions
Medical research plays a pivotal role in improving public health, developing innovative treatments, and advancing healthcare practices. These topics explore recent trends in medical science, such as personalized medicine, gene editing, and telehealth, along with emerging public health challenges. Students can investigate the future of healthcare and how advancements in medical technology influence patient outcomes.
- The role of personalized medicine in treating chronic diseases
- How telemedicine improves access to healthcare services
- The impact of artificial intelligence in medical diagnostics
- Exploring the future of gene therapy in disease prevention
- The role of wearable technology in monitoring health conditions
- How the microbiome influences mental and physical health
- The impact of nanotechnology on cancer treatment
- Exploring trends in robotic surgery techniques
- How healthcare policies address pandemic preparedness
- The role of CRISPR in curing genetic disorders
- Exploring advancements in regenerative medicine
- The impact of climate change on public health
- How digital health records improve patient care
- Exploring the future of vaccines and immunotherapy
- The role of 3D printing in prosthetics and implants
- How artificial intelligence predicts disease outbreaks
- Exploring trends in mental health treatment innovations
- The impact of telehealth on patient-doctor relationships
- How virtual reality is used in medical training
- The role of genetics in personalized cancer treatments
- How lifestyle interventions prevent cardiovascular diseases
- Exploring the ethics of human genome editing
- The impact of wearable devices on patient adherence
- How big data analytics improve public health policies
- The role of blockchain in securing patient data
- Exploring trends in pediatric healthcare
- The impact of remote monitoring on chronic disease management
- How AI-powered tools enhance clinical decision-making
- Exploring trends in global healthcare innovations
- The role of nutrition in preventing non-communicable diseases
- How mobile health apps improve patient engagement
- Exploring new trends in mental health therapies
- How virtual assistants aid in healthcare delivery
- The role of public health campaigns in disease prevention
- The impact of genetic testing on preventive care
- Exploring trends in fertility treatments
- How telemedicine transforms rural healthcare
- The future of precision medicine in oncology
- Exploring trends in emergency medicine
- How artificial organs revolutionize healthcare
- The role of AI in detecting rare diseases
- Exploring the impact of lifestyle medicine
- The future of clinical trials in personalized medicine
- The role of genomics in infectious disease control
- Exploring advancements in palliative care
- How smart technologies shape patient care
- The impact of public health surveillance on disease control
- The ethics of artificial womb technology
- Exploring trends in virtual healthcare services
See more Medical Research Paper Topics
Nursing research focuses on improving patient care, advancing healthcare practices, and addressing public health challenges. With the rise of telehealth, mental health awareness, and personalized care, these topics reflect current trends and the future of nursing. Students can explore issues such as nurse burnout, patient safety, leadership in healthcare, and innovative practices that enhance patient outcomes.
- The role of telehealth in nursing practice
- Nurse burnout: Causes and prevention strategies
- How nurse leadership influences patient outcomes
- The impact of technology on nursing care delivery
- The role of nurses in mental health crisis interventions
- How cultural competence improves nursing care
- The future of nursing education: Trends and challenges
- Exploring the role of advanced practice nurses in primary care
- The impact of staffing ratios on patient safety
- How nursing research influences healthcare policies
- Exploring trends in pediatric nursing care
- How nurses manage chronic disease patients remotely
- The role of emotional intelligence in nursing practice
- How nursing addresses health disparities in marginalized communities
- The impact of COVID-19 on nursing practices
- Exploring the ethics of end-of-life care in nursing
- How technology enhances nursing education and training
- The role of nurse-patient communication in improving care
- Exploring mental health support for healthcare workers
- The impact of evidence-based practice on nursing care
- The role of nurses in promoting public health campaigns
- How interdisciplinary collaboration improves patient care
- Exploring trends in neonatal nursing
- How simulation-based learning improves nursing skills
- The role of nurses in managing pandemic response efforts
- How nursing addresses the opioid crisis
- Exploring the impact of artificial intelligence on nursing
- The future of nurse-led clinics
- How nursing supports aging populations
- Exploring nurse advocacy in healthcare reform
- The impact of mobile health apps on patient monitoring
- How mindfulness practices benefit nurses and patients
- The role of community health nurses in disease prevention
- Exploring the future of nursing informatics
- How leadership training empowers nurses
- The role of school nurses in promoting child health
- Exploring trends in geriatric nursing care
- How telehealth impacts patient-nurse relationships
- The impact of team-based care on nursing workflows
- Exploring trends in nursing research methodologies
- The role of technology in managing nurse workloads
- Exploring holistic care practices in nursing
- How public health nurses address vaccine hesitancy
- The impact of leadership styles on nursing teams
- Exploring gender diversity in the nursing profession
- How nurses support patients with chronic pain
- The role of nursing in addressing healthcare inequities
- Exploring the challenges of remote nursing care
- How virtual simulations enhance nursing education
- The impact of self-care practices on nurse well-being
See more Nursing Research Paper Topics
Persuasive research papers challenge students to argue a position on controversial issues, supporting their viewpoint with evidence and reasoning. These topics reflect modern debates surrounding ethics, technology, social policies, and environmental concerns. Students are encouraged to take a stance on pressing issues, developing skills in critical thinking and argumentation.
- Should social media platforms be regulated?
- Is universal healthcare a right or a privilege?
- Should animal testing be banned globally?
- Is climate activism effective in driving policy changes?
- Should voting be mandatory in democratic nations?
- Is remote work the future of employment?
- Should companies adopt a four-day workweek?
- Is censorship ever justified in modern media?
- Should genetically modified foods be labeled?
- Is free college education sustainable?
- Should plastic production be banned?
- Is cryptocurrency the future of finance?
- Should countries impose carbon taxes to combat climate change?
- Is cancel culture harmful to free speech?
- Should students have more control over their curriculum?
- Is the gig economy good for workers?
- Should there be stricter regulations on AI development?
- Are electric vehicles the best solution for reducing emissions?
- Should employers monitor remote workers?
- Is surveillance technology necessary for public safety?
- Should governments subsidize renewable energy?
- Are standardized tests effective in assessing student abilities?
- Should childhood vaccinations be mandatory?
- Is fast fashion unethical?
- Should governments ban the sale of junk food?
- Is space exploration worth the investment?
- Should violent video games be regulated?
- Is social media harmful to teenagers?
- Should athletes be paid equally regardless of gender?
- Is homeschooling better than public education?
- Should college athletes be paid?
- Should fossil fuel companies be held accountable for climate change?
- Is virtual reality the future of education?
- Should smartphones be banned in schools?
- Are electric scooters an environmentally friendly alternative?
- Should the death penalty be abolished?
- Is online privacy a fundamental right?
- Should zoos be banned?
- Is it ethical to use animals for medical research?
- Should junk food advertising be restricted?
- Are cryptocurrencies more secure than traditional currencies?
- Should governments ban single-use plastics?
- Is artificial intelligence a threat to human jobs?
- Should museums return cultural artifacts to their countries of origin?
- Are reality TV shows harmful to society?
- Should fast food chains be taxed for contributing to obesity?
- Should influencers disclose sponsored content?
- Is homeschooling the solution to modern education challenges?
- Should countries open their borders to refugees?
Philosophy encourages deep reflection on human existence, ethics, knowledge, and reality. These topics explore how philosophical thought evolves in response to contemporary issues such as artificial intelligence, climate change, and social justice. Students can engage with classical philosophical theories, emerging ideas, and interdisciplinary approaches to develop critical perspectives on modern challenges.
- The ethics of artificial intelligence: A philosophical inquiry
- Existentialism and mental health: Finding meaning in modern life
- The role of philosophy in addressing climate change
- The nature of consciousness: Debates in philosophy of mind
- Exploring free will in the age of neuroscience
- How utilitarianism shapes public policy
- The philosophical implications of virtual reality
- The concept of justice in contemporary society
- Philosophical reflections on cancel culture
- The role of philosophy in education reform
- Nietzsche’s influence on modern self-help movements
- The impact of feminist philosophy on social justice movements
- The philosophy of happiness: Ancient vs. modern perspectives
- Moral dilemmas in medical ethics
- The philosophical roots of environmental activism
- The relevance of Stoicism in today’s world
- How Eastern philosophy shapes Western mindfulness practices
- The ethics of genetic engineering
- The role of philosophy in shaping leadership theories
- Exploring nihilism in modern culture
- The philosophy of art: Defining creativity and beauty
- Is reality a simulation? Exploring philosophical arguments
- The impact of social contract theory on modern politics
- The ethics of consumerism in a capitalist society
- Philosophical reflections on the nature of time
- The role of philosophy in promoting mental well-being
- The relationship between philosophy and religion
- Philosophical debates on identity and the self
- The concept of the common good in political philosophy
- Exploring philosophical approaches to multiculturalism
- The nature of knowledge: Classical vs. postmodern theories
- The role of philosophy in shaping artificial consciousness
- How existentialist thought addresses loneliness
- The impact of philosophical skepticism on scientific inquiry
- Ethical considerations in space exploration
- The relationship between language and thought
- How philosophy informs environmental justice
- The influence of Kantian ethics in modern debates
- Exploring the philosophy of human rights
- The role of philosophy in addressing inequality
- The concept of authenticity in existential philosophy
- How philosophy shapes contemporary political ideologies
- Philosophical reflections on life after death
- The role of philosophy in defining freedom
- Exploring the ethics of surveillance in modern society
- The concept of truth in post-truth politics
- The philosophy of love: Ancient and contemporary perspectives
- Exploring the meaning of life in modern philosophy
- How philosophical inquiry addresses mental health stigma
- The role of philosophy in shaping social movements
See more Philosophy Research Paper Topics
Political science examines power structures, governance, and public policies that shape societies and global relations. These topics reflect ongoing debates, emerging trends, and future challenges in domestic and international politics. Students can explore issues such as globalization, populism, public policy, and political ideologies to understand the complexities of modern governance and political dynamics.
- The impact of populism on democratic institutions
- Exploring the role of social media in election campaigns
- The influence of international organizations on global governance
- How nationalism shapes contemporary politics
- The impact of COVID-19 on public policy
- Exploring the rise of authoritarianism in the 21st century
- The role of youth movements in political change
- How political ideologies shape economic policies
- The influence of fake news on public opinion
- The future of diplomacy in a digital world
- The role of political parties in shaping climate policy
- Exploring the impact of electoral reforms
- The influence of migration on political stability
- The impact of international trade agreements on sovereignty
- How political campaigns use data analytics
- The future of global cooperation in addressing pandemics
- The impact of gender equality policies on governance
- How governments manage public trust during crises
- Exploring trends in public administration reform
- The role of international law in conflict resolution
- The influence of political leadership on economic recovery
- How governments address misinformation in elections
- The impact of political polarization on policy-making
- Exploring the relationship between religion and politics
- The future of the United Nations in global governance
- How climate change shapes geopolitical conflicts
- The impact of military alliances on global security
- Exploring the ethics of political lobbying
- The role of political movements in human rights advocacy
- How governments manage economic inequality
- The future of electoral democracy
- Exploring trends in political participation among youth
- How governments address cybersecurity threats
- The impact of urbanization on political governance
- Exploring the rise of environmental political movements
- The role of transparency in public administration
- How international sanctions impact political regimes
- The influence of political ideologies on education policy
- Exploring trends in voter behavior research
- The impact of digital platforms on public policy debates
- How political protests shape government responses
- The role of think tanks in shaping public policy
- Exploring the relationship between media and political power
- How technology shapes political accountability
- The influence of political ideologies on healthcare policies
- The role of non-state actors in global governance
- How international conflicts reshape alliances
- Exploring the future of populism in global politics
- The impact of regional integration on national sovereignty
- How political ideologies evolve in response to crises
See more Political Science Research Paper Topics
Psychology explores human thoughts, behaviors, emotions, and mental processes, offering insights into individual and social functioning. These topics reflect the latest trends, emerging research areas, and challenges in mental health, neuroscience, cognitive psychology, and social behavior. Students can engage with current psychological issues such as the impact of technology, mental health stigma, and new therapeutic approaches.
- The psychological impact of social media on youth
- Exploring new trends in cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
- The role of virtual reality in mental health treatment
- The impact of mindfulness practices on emotional regulation
- Exploring the psychology of decision-making under uncertainty
- The effects of remote work on employee well-being
- The role of neuroplasticity in learning and memory
- How trauma shapes personality development
- Exploring the relationship between sleep and mental health
- The impact of parenting styles on child development
- The role of emotional intelligence in workplace success
- How mental health stigma affects help-seeking behavior
- The influence of video games on cognitive skills
- Exploring gender differences in emotional processing
- The impact of mindfulness on reducing anxiety and depression
- How the brain processes addiction: A neuroscientific perspective
- The effects of chronic stress on physical health
- The role of group therapy in addiction recovery
- Exploring the psychological aspects of consumer behavior
- How childhood trauma impacts adult relationships
- The impact of pet ownership on mental well-being
- The role of attachment theory in modern relationships
- How personality traits influence career choices
- Exploring new approaches to treating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- The effects of social isolation on cognitive functioning
- How cognitive biases shape political opinions
- Exploring the impact of music therapy on mental health
- The role of psychological resilience in coping with adversity
- How technology influences human attention span
- The effects of exercise on mental health and well-being
- Exploring trends in adolescent mental health interventions
- How gratitude practices improve psychological well-being
- The role of therapy animals in mental health care
- Exploring the connection between art therapy and trauma recovery
- The impact of cultural differences on emotional expression
- How social support systems influence mental health recovery
- The role of parenting in emotional development
- How neuroimaging enhances understanding of mental disorders
- The influence of childhood bullying on adult mental health
- Exploring trends in online therapy and counseling
- The role of genetics in mental health disorders
- How interpersonal relationships shape self-esteem
- Exploring the psychology of procrastination
- The impact of humor on psychological resilience
- How gender stereotypes affect mental health outcomes
- The role of empathy in conflict resolution
- Exploring the psychological effects of climate anxiety
- The influence of diet on cognitive performance
- How mindfulness reduces workplace stress
- Exploring the psychology of motivation in education
See more Psychology Research Paper Topics
Religious studies offer a deep exploration of spiritual beliefs, practices, and traditions, along with their impact on culture, politics, and individual behavior. These topics reflect emerging trends in interfaith dialogue, secularization, and the role of religion in addressing modern societal challenges. Students can explore religion’s influence on ethics, public policy, and personal identity, focusing on how spirituality evolves in a globalized world.
- The impact of secularization on modern societies
- Exploring the role of religion in promoting mental well-being
- How religious pluralism fosters interfaith dialogue
- The influence of religious beliefs on environmental ethics
- The role of faith communities during public health crises
- Exploring the impact of globalization on religious practices
- The rise of spiritual but not religious (SBNR) movements
- How religion shapes ethical decision-making in politics
- The role of pilgrimage in religious identity formation
- Exploring the impact of digital technology on religious practices
- The influence of religious leaders on social justice movements
- How interfaith marriages shape family dynamics
- Exploring trends in religious education
- The impact of religion on gender roles
- How spirituality influences recovery from addiction
- The role of religious rituals in fostering community bonds
- Exploring the relationship between science and religion
- How religious narratives shape national identities
- The impact of atheism and agnosticism on religious discourse
- The role of religion in addressing mental health stigma
- Exploring trends in youth participation in religious communities
- How religion influences moral development in children
- The impact of religious festivals on cultural identity
- Exploring the ethics of religious proselytism
- How religious beliefs influence end-of-life decisions
- The role of religion in conflict resolution
- Exploring the impact of religious art and symbolism
- How religious institutions address environmental challenges
- The role of women in shaping modern religious practices
- Exploring religious responses to climate change
- The influence of mysticism on contemporary spirituality
- The impact of religious freedom on global politics
- Exploring trends in online religious communities
- How religion shapes responses to migration
- The role of prayer in stress management
- Exploring the future of religion in the digital age
- The relationship between religion and economic development
- How theology informs human rights debates
- Exploring trends in new religious movements
- The role of religion in fostering forgiveness and reconciliation
- How religious teachings influence healthcare decisions
- The impact of religious identity on political activism
- Exploring the relationship between religion and education
- The influence of religious texts on legal systems
- How religious diversity shapes public policy
- The role of spirituality in coping with grief
- Exploring the impact of religion on cultural tourism
- The role of religious charities in humanitarian efforts
- How religious beliefs shape environmental stewardship
- Exploring trends in feminist theology
See more Religion Research Paper Topics
Scientific research drives innovation and provides solutions to some of the most pressing global challenges, from climate change to space exploration. These topics reflect cutting-edge advancements and emerging trends in various scientific fields. Students can explore areas such as genetics, physics, environmental science, and space studies, engaging with how science shapes the future of humanity and the planet.
- The role of CRISPR in genetic engineering
- How quantum computing will transform technology
- Exploring the potential of fusion energy as a sustainable solution
- How artificial intelligence contributes to scientific discovery
- Exploring the future of personalized medicine
- The role of nanotechnology in cancer treatment
- The effects of climate change on global biodiversity
- The potential of space mining for resource extraction
- How renewable energy technologies evolve
- The role of big data in scientific research
- How advances in neuroscience explain consciousness
- The future of robotics in healthcare
- The impact of extreme weather on agricultural systems
- How machine learning accelerates drug discovery
- Exploring trends in renewable energy storage solutions
- The role of space exploration in understanding Earth’s climate
- How microbiomes affect human health
- The potential of artificial photosynthesis in clean energy
- Exploring new discoveries in particle physics
- How advances in astronomy redefine our understanding of the universe
- The impact of deforestation on the carbon cycle
- How wearable technology monitors health conditions
- How gene editing could eliminate hereditary diseases
- Exploring the ethics of artificial intelligence in scientific research
- The effects of ocean acidification on marine species
- The impact of space debris on future space missions
- How gravitational waves expand our understanding of the cosmos
- The role of stem cell research in regenerative medicine
- Exploring trends in climate engineering
- How smart materials are revolutionizing construction
- The impact of virtual labs on science education
- How renewable technologies transform transportation
- The future of 3D printing in scientific research
- How CRISPR technology addresses food security challenges
- The impact of dark matter research on cosmology
- The potential of hydroponics for urban agriculture
- How climate models predict future environmental scenarios
- The role of citizen science in biodiversity monitoring
- The influence of artificial intelligence on astronomy
- How nanomaterials enhance solar cell efficiency
- The impact of extreme environments on human biology
- The role of science in mitigating environmental disasters
- Exploring the future of gene drives in controlling invasive species
- How atmospheric chemistry influences climate change
- The potential of algae as a biofuel source
- How advances in optics improve medical imaging
- The future of wearable biosensors in healthcare
- Exploring the relationship between science and society
See more Science Research Paper Topics
Sociology examines social behavior, structures, and changes within societies. These topics focus on contemporary social issues such as inequality, technology, globalization, and cultural transformations. Students can explore the ways societies adapt to change and the challenges they face, addressing social trends and future developments in areas such as urbanization, education, and social movements.
- The impact of social media on interpersonal relationships
- How technology influences social mobility
- Exploring the rise of gig economy jobs in modern society
- The impact of remote work on social structures
- How globalization affects cultural identities
- Exploring gender roles in contemporary societies
- The role of education in reducing social inequality
- How urbanization shapes social behavior
- The influence of digital activism on social movements
- How family dynamics evolve in multicultural societies
- The sociology of mental health stigma
- How cultural diversity shapes workplace dynamics
- The impact of migration on community cohesion
- Exploring the role of religion in modern society
- How media representation affects social norms
- The impact of climate change on social inequality
- Exploring trends in youth subcultures
- The role of social capital in community development
- How automation reshapes labor markets
- Exploring the future of rural communities
- How social policies address homelessness
- The sociology of aging populations
- The impact of consumer culture on identity
- How gender stereotypes influence career choices
- The role of social networks in shaping political opinions
- Exploring the impact of cancel culture on social behavior
- How sports influence social integration
- The sociology of mental health in urban settings
- Exploring the future of education in digital societies
- The role of public spaces in fostering social interaction
- How poverty shapes health outcomes
- Exploring the impact of immigration policies on families
- The influence of online communities on social identity
- The sociology of crime and punishment
- How environmental changes impact social policies
- The role of cultural heritage in urban development
- Exploring trends in social entrepreneurship
- The impact of the pandemic on social cohesion
- How digital communication changes family dynamics
- The sociology of body image in social media
- Exploring trends in community-based mental health initiatives
- How art influences social change
- The role of volunteerism in community development
- How peer influence shapes adolescent behavior
- The impact of cultural festivals on community identity
- Exploring the future of online dating
- The sociology of economic inequality
- How urban planning addresses social segregation
- The role of religion in promoting social justice
- Exploring the impact of AI on social behavior
See more Sociology Research Paper Topics
Sports are integral to culture, society, and health, reflecting broader social trends and issues. These topics explore how sports intersect with technology, psychology, economics, and social behavior. Students can investigate the challenges athletes face, the impact of sports on mental health, and the role of sports in promoting social change.
- The impact of mental health initiatives in sports
- Exploring the rise of esports and its future
- The role of technology in improving athletic performance
- How gender equality evolves in professional sports
- The influence of sports sponsorship on brand loyalty
- The impact of sports on youth development
- Exploring trends in injury prevention technologies
- How social media reshapes fan engagement
- The role of sports in promoting national identity
- Exploring the future of virtual sports
- The impact of coaching styles on team dynamics
- How athletes cope with retirement
- The role of sports psychology in performance enhancement
- Exploring trends in wearable fitness technology
- The influence of climate change on outdoor sports
- How sports foster social inclusion
- The impact of doping scandals on sports governance
- Exploring the economics of mega-sporting events
- The role of athletes in social justice movements
- How data analytics shape coaching strategies
- The future of sports betting and its regulation
- Exploring the impact of fan behavior on team performance
- The role of nutrition in athletic success
- How female athletes challenge stereotypes
- The influence of sports media on public perception
- Exploring trends in adaptive sports for disabled athletes
- The impact of sports on community development
- How sports address mental health stigma
- Exploring trends in high-performance training methods
- The impact of COVID-19 on professional sports
- How youth sports programs promote physical health
- The role of sports in reducing social inequality
- Exploring trends in athlete branding and marketing
- The influence of international competitions on diplomacy
- How wearable technology monitors player health
- The impact of fan culture on sports organizations
- Exploring the role of ethics in sports management
- How virtual reality enhances athlete training
- The role of biomechanics in preventing sports injuries
- How sports leagues address mental health
- Exploring trends in athlete activism
- The influence of technology on referee decisions
- The impact of diversity initiatives in sports organizations
- How sports promote environmental sustainability
- Exploring trends in high-altitude training
- The role of sports tourism in economic development
- How sponsorships shape athlete careers
- Exploring trends in sports law and governance
- The impact of age on athletic performance
- The future of mixed-gender sports
Technology is a driving force behind social, economic, and cultural transformations, impacting every aspect of modern life. These topics explore the latest advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, digital transformation, and the ethical challenges that accompany technological progress. Students can engage with cutting-edge research to examine how technology shapes the present and redefines the future.
- The role of artificial intelligence in healthcare innovation
- Exploring the future of blockchain beyond cryptocurrency
- How autonomous vehicles will change urban transportation
- The impact of cybersecurity threats on national security
- Exploring trends in quantum computing research
- The ethics of AI in decision-making processes
- How the Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming smart cities
- The influence of 5G technology on communication systems
- How augmented reality (AR) enhances education and training
- The role of big data analytics in personalized marketing
- Exploring trends in cloud computing security
- How technology shapes the future of remote work
- The impact of digital twins on industrial processes
- The role of robotics in supply chain optimization
- How virtual reality (VR) transforms healthcare treatments
- Exploring trends in wearable technology
- The future of space exploration with private sector involvement
- How artificial intelligence impacts financial markets
- The role of technology in tackling climate change
- Exploring the ethics of facial recognition systems
- The impact of social media algorithms on public discourse
- How digital currencies are reshaping the global economy
- The role of AI in combating cybercrime
- How self-driving cars will impact urban planning
- The influence of automation on job displacement
- Exploring trends in digital transformation across industries
- The impact of artificial intelligence on education systems
- The future of cybersecurity in the metaverse
- How technology addresses global healthcare disparities
- Exploring the risks of deepfake technology
- The role of machine learning in environmental monitoring
- How blockchain ensures data transparency and security
- The future of human-computer interaction
- Exploring trends in bioinformatics and genomics
- The ethics of AI in warfare
- How smart homes improve energy efficiency
- The impact of cryptocurrency on financial regulation
- Exploring trends in edge computing
- The role of open-source technology in innovation
- How technology influences consumer privacy
- The future of biometric authentication systems
- Exploring the use of drones in disaster management
- The impact of virtual workplaces on productivity
- The influence of technology on creative industries
- Exploring trends in AI-driven healthcare diagnostics
- How robotics shapes the future of agriculture
- The role of technology in mental health interventions
- How quantum computing will revolutionize encryption
- The impact of technology on cultural preservation
- Exploring the future of artificial general intelligence (AGI)
See more Technology Research Paper Topics
This collection of 1400 research paper topics across 28 categories provides students with diverse ideas to inspire engaging and impactful research. Each topic reflects current issues, emerging trends, and future developments, ensuring that students can explore timely questions relevant to their academic and career aspirations. Whether delving into psychology, economics, technology, or environmental studies, these topics offer an excellent starting point for any research journey. For further support, students can leverage iResearchNet’s professional writing services to develop their chosen topics into high-quality, well-researched papers.
What is the Key to a Perfect Topic for a Research Paper?
The key to a perfect topic includes three main secrets: interest, precision, and innovation.
It is impossible to do something great if you have no interest in what you are doing. For this reason, make sure you choose the topic that drives you. If you are bored by what you investigate, do not expect that your paper will be exciting. Right now, spend some minutes or even hours thinking about what interests you. Jot down all your preferences in life, science, politics, social issues etc. It will help you get the idea what you can write about.
After realizing what drives you, narrow this general idea to a more specific one. A research paper is not about beating around the bush. You will need clear facts and data. You will have to provide evidence to your ideas. You will need to be precise, specific and convincing.
Finally, the idea of any research is that it should be surprising and distinctive. Think what makes your perspective and approach special. What is the novelty of your research?
Use Technology
If you are still stuck, use technology. Today we have an opportunity to make our lives easier with a bit of technology used. You can find paper topic generators online. This software will examine the category you want to investigate and the keywords from your research. Within several seconds, this program generates paper topics, so you can try it yourself. It can help you get started with your assignment.
100% Effective Advice
We will now give you advice that is 100% effective when picking the topic. Firstly, forget about what others may think about your topic. This is your topic and this is your perception of the world. Stay personal and let your personal style get you the top grades. Secondly, never decide on the topic before analyzing the background for your research. By this we mean, investigate the topic before you start the research proper. It happens quite often that students choose the topic and later they realize there is no data or information to use. That is why conduct some research beforehand. Thirdly, read other researchers’ papers on the topic you want to write about. It will help you get the idea of the investigation. Moreover, it will help you understand whether you truly want to write a paper on this topic. Finally, when you have picked the topic, started your research, make sure you dedicate your time and energy. If you want to get high results, you need to study every little details of your research.
Examine Different Ideas
People often come up with genius ideas after analyzing thousands of other people’s ideas. This is how our brain works. That is why you can analyze other people’s ideas for research paper topics and think up your own. If you have never written any paper of that kind, it will help you understand the gist of this assignment, the style and the requirements. By comparing different topics, you can motivate yourself and get inspired with these ideas. Luckily, you have come to the right place. Here is our list of top 100 research paper topics.
What Makes a Good Topic for a Research Paper?
A good research paper topic is the one that is successful and manageable in your particular case. A successful research paper poses an interesting question you can actually answer. Just as important, it poses a question you can answer within the time available. The question should be one that interests you and deserves exploration. It might be an empirical question or a theoretical puzzle. In some fields, it might be a practical problem or policy issue. Whatever the question is, you need to mark off its boundaries clearly and intelligently so you can complete the research paper and not get lost in the woods. That means your topic should be manageable as well as interesting and important.
A topic is manageable if you can:
- Master the relevant literature
- Collect and analyze the necessary data
- Answer the key questions you have posed
- Do it all within the time available, with the skills you have
A topic is important if it:
- Touches directly on major theoretical issues and debates, or
- Addresses substantive topics of great interest in your field
Ideally, your topic can do both, engaging theoretical and substantive issues. In elementary education, for example, parents, teachers, scholars, and public officials all debate the effectiveness of charter schools, the impact of vouchers, and the value of different reading programs. A research paper on any of these would resonate within the university and well beyond it. Still, as you approach such topics, you need to limit the scope of your investigation so you can finish your research and writing on time. After all, to be a good research paper, it first has to be a completed one. A successful research paper poses an interesting question you can actually answer within the time available for the project. Some problems are simply too grand, too sweeping to master within the time limits. Some are too minor to interest you or anybody else.
The solution, however, is not to find a lukewarm bowl of porridge, a bland compromise. Nor is it to abandon your interest in larger, more profound issues such as the relationship between school organization and educational achievement or between immigration and poverty. Rather, the solution is to select a well-defined topic that is closely linked to some larger issue and then explore that link. Your research paper will succeed if you nail a well-defined topic. It will rise to excellence if you probe that topic deeply and show how it illuminates wider issues. The best theses deal with important issues, framed in manageable ways. The goal is to select a well-defined topic that is closely linked to some larger issue and can illuminate it.
You can begin your project with either a large issue or a narrowly defined topic, depending on your interests and the ideas you have generated. Whichever way you start, the goals are the same: to connect the two in meaningful ways and to explore your specific topic in depth.
Of course, the choice of a particular research paper topic depends on the course you’re taking. Our site can offer you the following research paper topics and example research papers:
Moving from a Research Paper Idea to a Research Paper Topic
Let’s begin as most students actually do, by going from a “big issue” to a more manageable research paper topic. Suppose you start with a big question such as, “Why has the United States fought so many wars since 1945?” That’s certainly a big, important question. Unfortunately, it’s too complex and sprawling to cover well in a research paper. Working with your professor or instructor, you could zero in on a related but feasible research topic, such as “Why did the Johnson administration choose to escalate the U.S. war in Vietnam?” By choosing this topic, your research paper can focus on a specific war and, within that, on a few crucial years in the mid-1960s.
You can draw on major works covering all aspects of the Vietnam War and the Johnson administration’s decision making. You have access to policy memos that were once stamped top secret. These primary documents have now been declassified, published by the State Department, and made available to research libraries. Many are readily available on the Web. You can also take advantage of top-quality secondary sources (that is, books and articles based on primary documents, interviews, and other research data).
Drawing on these primary and secondary sources, you can uncover and critique the reasons behind U.S. military escalation. As you answer this well-defined question about Vietnam, you can (and you should) return to the larger themes that interest you, namely, “What does the escalation in Southeast Asia tell us about the global projection of U.S. military power since 1945?” As one of America’s largest military engagements since World War II, the war in Vietnam should tell us a great deal about the more general question.
The goal here is to pick a good case to study, one that is compelling in its own right and speaks to the larger issue. It need not be a typical example, but it does need to illuminate the larger question. Some cases are better than others precisely because they illuminate larger issues. That’s why choosing the best cases makes such a difference in your research paper.
Since you are interested in why the United States has fought so often since 1945, you probably shouldn’t focus on U.S. invasions of Grenada, Haiti, or Panama in the past two decades. Why? Because the United States has launched numerous military actions against small, weak states in the Caribbean for more than a century. That is important in its own right, but it doesn’t say much about what has changed so dramatically since 1945. The real change since 1945 is the projection of U.S. power far beyond the Western Hemisphere, to Europe and Asia. You cannot explain this change—or any change, for that matter—by looking at something that remains constant.
In this case, to analyze the larger pattern of U.S. war fighting and the shift it represents, you need to pick examples of distant conflicts, such as Korea, Vietnam, Kosovo, Afghanistan, or Iraq. That’s the noteworthy change since 1945: U.S. military intervention outside the Western Hemisphere. The United States has fought frequently in such areas since World War II but rarely before then. Alternatively, you could use statistics covering many cases of U.S. intervention around the world, perhaps supplemented with some telling cases studies.
Students in the humanities want to explore their own big ideas, and they, too, need to focus their research. In English literature, their big issue might be “masculinity” or, to narrow the range a bit, “masculinity in Jewish American literature.” Important as these issues are, they are too vast for anyone to read all the major novels plus all the relevant criticism and then frame a comprehensive research paper.
If you don’t narrow these sprawling topics and focus your work, you can only skim the surface. Skimming the surface is not what you want to do in a research paper. You want to understand your subject in depth and convey that understanding to your readers.
That does not mean you have to abandon your interest in major themes. It means you have to restrict their scope in sensible ways. To do that, you need to think about which aspects of masculinity really interest you and then find works that deal with them.
You may realize your central concern is how masculinity is defined in response to strong women. That focus would still leave you considerable flexibility, depending on your academic background and what you love to read. That might be anything from a reconsideration of Macbeth to an analysis of early twentieth-century American novels, where men must cope with women in assertive new roles. Perhaps you are interested in another aspect of masculinity: the different ways it is defined within the same culture at the same moment. That would lead you to novelists who explore these differences in their characters, perhaps contrasting men who come from different backgrounds, work in different jobs, or simply differ emotionally. Again, you would have considerable flexibility in choosing specific writers.
Connecting a Specific Research Paper Topic to a Bigger Idea
Not all students begin their research paper concerned with big issues such as masculinity or American wars over the past half century. Some start with very specific topics in mind. One example might be the decision to create NAFTA, the North American Free Trade Agreement encompassing Canada, the United States, and Mexico. Perhaps you are interested in NAFTA because you discussed it in a course, heard about it in a political campaign, or saw its effects firsthand on local workers, companies, and consumers. It intrigues you, and you would like to study it in a research paper. The challenge is to go from this clear-cut subject to a larger theme that will frame your paper.
Why do you even need to figure out a larger theme? Because NAFTA bears on several major topics, and you cannot explore all of them. Your challenge—and your opportunity—is to figure out which one captures your imagination.
One way to think about that is to finish this sentence: “For me, NAFTA is a case of ___________.” If you are mainly interested in negotiations between big and small countries, then your answer is, “For me, NAFTA is a case of a large country like the United States bargaining with a smaller neighbor.” Your answer would be different if you are mainly interested in decision making within the United States, Mexico, or Canada. In that case, you might say, “NAFTA seems to be a case where a strong U.S. president pushed a trade policy through Congress.” Perhaps you are more concerned with the role played by business lobbies. “For me, NAFTA is a case of undue corporate influence over foreign economic policy.” Or you could be interested in the role of trade unions, environmental groups, or public opinion.
The NAFTA decision is related to all these big issues and more. You cannot cover them all. There is not enough time, and even if there were, the resulting paper would be too diffuse, too scattershot. To make an impact, throw a rock, not a handful of pebbles.
Choosing one of these large issues will shape your research paper on NAFTA. If you are interested in U.S. decision making, for example, you might study the lobbying process or perhaps the differences between Democrats and Republicans. If you are interested in diplomacy, you would focus on negotiations between the United States, Canada, and Mexico. Either would make an interesting research paper, but they are different topics.
Although the subject matter and analysis are decidedly different in the humanities, many of the same considerations still apply to topic selection. In English or comparative literature, for example, you may be attracted to a very specific topic such as several poems by William Wordsworth. You are not trying, as a social scientist would, to test some generalizations that apply across time or space. Rather, you want to analyze these specific poems, uncover their multiple meanings, trace their allusions, and understand their form and beauty.
As part of the research paper, however, you may wish to say something bigger, something that goes beyond these particular poems. That might be about Wordsworth’s larger body of work. Are these poems representative or unusual? Do they break with his previous work or anticipate work yet to come? You may wish to comment on Wordsworth’s close ties to his fellow “Lake Poets,” Coleridge and Southey, underscoring some similarities in their work. Do they use language in shared ways? Do they use similar metaphors or explore similar themes? You may even wish to show how these particular poems are properly understood as part of the wider Romantic movement in literature and the arts. Any of these would connect the specific poems to larger themes.
How to Refine Your Research Paper Topic
One of your professor’s or instructor’s most valuable contributions to the success of your research paper is to help you refine your topic. She can help you select the best cases for detailed study or the best data and statistical techniques. S/he can help you find cases that shed light on larger questions, have good data available, and are discussed in a rich secondary literature. She may know valuable troves of documents to explore. That’s why it is so important to bring these issues up in early meetings. These discussions with your instructor are crucial in moving from a big but ill-defined idea to a smart, feasible topic.Some colleges supplement this advising process by offering special workshops and tutorial support for students. These are great resources, and you should take full advantage of them. They can improve your project in at least two ways.
First, tutors and workshop leaders are usually quite adept at helping you focus and shape your topic. That’s what they do best. Even if they are relatively new teachers, they have been writing research papers themselves for many years. They know how to do it well and how to avoid common mistakes. To craft their own papers, they have learned how to narrow their topics, gather data, interpret sources, and evaluate conjectures. They know how to use appropriate methods and how to mine the academic literature. In all these ways, they can assist you with their own hard-won experience. To avoid any confusion, just make sure your instructor knows what advice you are getting from workshop leaders and tutors. You want everyone to be pulling in the same direction.
Second, you will benefit enormously from batting around your research paper in workshops. The more you speak about your subject, the better you will understand it yourself. The better you understand it, the clearer your research and writing will be. You will learn about your project as you present your ideas; you will learn more as you listen to others discuss your work; and you will learn still more as you respond to their suggestions. Although you should do that in sessions with your instructor, you will also profit from doing it in workshops and tutorial sessions.
Secrets to Keep in Mind when Writing a Research Paper
As a bonus, we have prepared several secrets for you to make your paper perfect. Firstly, always write your paper from scratch. Do not copy the already existing materials, as it can lead to unsatisfactory mark or even expulsion. Secondly, start your research early; do not put off investigating the topic. The earlier you start, the easier it will be to meet the deadline. Thirdly, plan your work and create an outline for your task. A planned work will help you be systematic. Plus, it will help you avoid writer’s block, as you always have an outline to follow. Another secret is following all the requirements. A research paper is an academic assignment, so all these structural and formatting standards are important. Finally, make sure you proofread and edit your task. Check your paper for grammar and spelling mistakes, examine your choice of vocabulary. If it seems too much, you can always ask our professional editors and they will check the paper for you. A mistakes-free paper is essential to get high results.
Custom Research Paper Writing Service
At iResearchNet, we understand that writing a high-quality research paper can be both time-consuming and challenging. Whether students are grappling with tight deadlines, complex topics, or the pressure to meet academic standards, our custom research paper writing services are here to help. We provide expert assistance at every stage of the research process, from topic selection to final editing, ensuring students submit papers that meet the highest academic standards. Our services are designed to offer flexibility, precision, and support, enabling students to focus on their studies while we handle the complexities of academic writing.
- Expert Degree-Holding Writers: Our team consists of experienced writers with advanced degrees in various fields. They bring subject matter expertise to each project, ensuring that research papers meet academic expectations.
- Custom Written Works: Every research paper is crafted from scratch according to the client’s specific requirements, guaranteeing originality and adherence to the highest academic standards.
- In-Depth Research on Every Topic: We conduct thorough research using the latest academic sources, ensuring that each paper reflects current developments, emerging trends, and future directions in the chosen field.
- Custom Formatting: Our writers are proficient in all major citation styles and formatting guidelines, ensuring that papers are correctly structured and properly referenced.
- Top Quality and Originality: We prioritize quality, delivering well-researched, well-structured, and plagiarism-free papers. Each project undergoes multiple rounds of quality checks before submission.
- Customized Solutions Based on Your Needs: We tailor our services to meet individual academic requirements, providing personalized solutions that align with students’ expectations and goals.
- Flexible Pricing Plans: Our pricing structure is designed to accommodate students with varying budgets, offering competitive rates and discounts without compromising on quality.
- Timely Delivery Guaranteed: We understand the importance of deadlines. Our team ensures that every research paper is delivered on time, even under tight schedules.
- 24/7 Customer Support: Our support team is available around the clock to address any questions or concerns. Whether students need assistance with placing an order or tracking their progress, we are here to help.
- Absolute Privacy and Confidentiality We value our clients’ privacy and guarantee that all personal information and order details remain confidential.
- Easy Order Tracking System: Our user-friendly order tracking system allows students to monitor the progress of their papers and communicate directly with their assigned writer.
- Money-Back Guarantee: We are committed to customer satisfaction. If students are not satisfied with the final product, we offer a money-back guarantee for peace of mind.
With iResearchNet’s custom research paper writing services, students can confidently tackle any academic challenge. Whether you need help selecting a topic, conducting research, or formatting your paper, our team of expert writers is ready to assist. We combine in-depth knowledge, personalized service, and reliable support to deliver top-quality papers that meet the highest academic standards. Trust iResearchNet to make your academic journey smoother, one research paper at a time.
- ABM Thesis Topics
- Accounting and Finance Thesis Topics
- Business Thesis Topics
- Computer Science Thesis Topics
- Economics Thesis Topics
- Education Thesis Topics
- Engineering Thesis Topics
- Environmental Studies Thesis Topics
- Finance Thesis Topics
- Health Thesis Topics
- Information Technology Thesis Topics
- Law Thesis Topics
- Literature Thesis Topics
- Management Thesis Topics
- Marketing Thesis Topics
- MBA Thesis Topics
- Media and Communication Thesis Topics
- Nursing Thesis Topics
- Philosophy Thesis Topics
- Political Science Thesis Topics
- Psychology Thesis Topics
- Science Thesis Topics
- STEM Thesis Topics
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

What is Empirical Research? Definition, Methods, Examples
Appinio Research · 09.02.2024 · 36min read

Ever wondered how we gather the facts, unveil hidden truths, and make informed decisions in a world filled with questions? Empirical research holds the key.
In this guide, we'll delve deep into the art and science of empirical research, unraveling its methods, mysteries, and manifold applications. From defining the core principles to mastering data analysis and reporting findings, we're here to equip you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the empirical landscape.
What is Empirical Research?
Empirical research is the cornerstone of scientific inquiry, providing a systematic and structured approach to investigating the world around us. It is the process of gathering and analyzing empirical or observable data to test hypotheses, answer research questions, or gain insights into various phenomena. This form of research relies on evidence derived from direct observation or experimentation, allowing researchers to draw conclusions based on real-world data rather than purely theoretical or speculative reasoning.
Characteristics of Empirical Research
Empirical research is characterized by several key features:
- Observation and Measurement : It involves the systematic observation or measurement of variables, events, or behaviors.
- Data Collection : Researchers collect data through various methods, such as surveys, experiments, observations, or interviews.
- Testable Hypotheses : Empirical research often starts with testable hypotheses that are evaluated using collected data.
- Quantitative or Qualitative Data : Data can be quantitative (numerical) or qualitative (non-numerical), depending on the research design.
- Statistical Analysis : Quantitative data often undergo statistical analysis to determine patterns , relationships, or significance.
- Objectivity and Replicability : Empirical research strives for objectivity, minimizing researcher bias . It should be replicable, allowing other researchers to conduct the same study to verify results.
- Conclusions and Generalizations : Empirical research generates findings based on data and aims to make generalizations about larger populations or phenomena.
Importance of Empirical Research
Empirical research plays a pivotal role in advancing knowledge across various disciplines. Its importance extends to academia, industry, and society as a whole. Here are several reasons why empirical research is essential:
- Evidence-Based Knowledge : Empirical research provides a solid foundation of evidence-based knowledge. It enables us to test hypotheses, confirm or refute theories, and build a robust understanding of the world.
- Scientific Progress : In the scientific community, empirical research fuels progress by expanding the boundaries of existing knowledge. It contributes to the development of theories and the formulation of new research questions.
- Problem Solving : Empirical research is instrumental in addressing real-world problems and challenges. It offers insights and data-driven solutions to complex issues in fields like healthcare, economics, and environmental science.
- Informed Decision-Making : In policymaking, business, and healthcare, empirical research informs decision-makers by providing data-driven insights. It guides strategies, investments, and policies for optimal outcomes.
- Quality Assurance : Empirical research is essential for quality assurance and validation in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and technology. It ensures that products and processes meet established standards.
- Continuous Improvement : Businesses and organizations use empirical research to evaluate performance, customer satisfaction , and product effectiveness. This data-driven approach fosters continuous improvement and innovation.
- Human Advancement : Empirical research in fields like medicine and psychology contributes to the betterment of human health and well-being. It leads to medical breakthroughs, improved therapies, and enhanced psychological interventions.
- Critical Thinking and Problem Solving : Engaging in empirical research fosters critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and a deep appreciation for evidence-based decision-making.
Empirical research empowers us to explore, understand, and improve the world around us. It forms the bedrock of scientific inquiry and drives progress in countless domains, shaping our understanding of both the natural and social sciences.
How to Conduct Empirical Research?
So, you've decided to dive into the world of empirical research. Let's begin by exploring the crucial steps involved in getting started with your research project.
1. Select a Research Topic
Selecting the right research topic is the cornerstone of a successful empirical study. It's essential to choose a topic that not only piques your interest but also aligns with your research goals and objectives. Here's how to go about it:
- Identify Your Interests : Start by reflecting on your passions and interests. What topics fascinate you the most? Your enthusiasm will be your driving force throughout the research process.
- Brainstorm Ideas : Engage in brainstorming sessions to generate potential research topics. Consider the questions you've always wanted to answer or the issues that intrigue you.
- Relevance and Significance : Assess the relevance and significance of your chosen topic. Does it contribute to existing knowledge? Is it a pressing issue in your field of study or the broader community?
- Feasibility : Evaluate the feasibility of your research topic. Do you have access to the necessary resources, data, and participants (if applicable)?
2. Formulate Research Questions
Once you've narrowed down your research topic, the next step is to formulate clear and precise research questions . These questions will guide your entire research process and shape your study's direction. To create effective research questions:
- Specificity : Ensure that your research questions are specific and focused. Vague or overly broad questions can lead to inconclusive results.
- Relevance : Your research questions should directly relate to your chosen topic. They should address gaps in knowledge or contribute to solving a particular problem.
- Testability : Ensure that your questions are testable through empirical methods. You should be able to gather data and analyze it to answer these questions.
- Avoid Bias : Craft your questions in a way that avoids leading or biased language. Maintain neutrality to uphold the integrity of your research.
3. Review Existing Literature
Before you embark on your empirical research journey, it's essential to immerse yourself in the existing body of literature related to your chosen topic. This step, often referred to as a literature review, serves several purposes:
- Contextualization : Understand the historical context and current state of research in your field. What have previous studies found, and what questions remain unanswered?
- Identifying Gaps : Identify gaps or areas where existing research falls short. These gaps will help you formulate meaningful research questions and hypotheses.
- Theory Development : If your study is theoretical, consider how existing theories apply to your topic. If it's empirical, understand how previous studies have approached data collection and analysis.
- Methodological Insights : Learn from the methodologies employed in previous research. What methods were successful, and what challenges did researchers face?
4. Define Variables
Variables are fundamental components of empirical research. They are the factors or characteristics that can change or be manipulated during your study. Properly defining and categorizing variables is crucial for the clarity and validity of your research. Here's what you need to know:
- Independent Variables : These are the variables that you, as the researcher, manipulate or control. They are the "cause" in cause-and-effect relationships.
- Dependent Variables : Dependent variables are the outcomes or responses that you measure or observe. They are the "effect" influenced by changes in independent variables.
- Operational Definitions : To ensure consistency and clarity, provide operational definitions for your variables. Specify how you will measure or manipulate each variable.
- Control Variables : In some studies, controlling for other variables that may influence your dependent variable is essential. These are known as control variables.
Understanding these foundational aspects of empirical research will set a solid foundation for the rest of your journey. Now that you've grasped the essentials of getting started, let's delve deeper into the intricacies of research design.

Empirical Research Design
Now that you've selected your research topic, formulated research questions, and defined your variables, it's time to delve into the heart of your empirical research journey – research design . This pivotal step determines how you will collect data and what methods you'll employ to answer your research questions. Let's explore the various facets of research design in detail.
Types of Empirical Research
Empirical research can take on several forms, each with its own unique approach and methodologies. Understanding the different types of empirical research will help you choose the most suitable design for your study. Here are some common types:
- Experimental Research : In this type, researchers manipulate one or more independent variables to observe their impact on dependent variables. It's highly controlled and often conducted in a laboratory setting.
- Observational Research : Observational research involves the systematic observation of subjects or phenomena without intervention. Researchers are passive observers, documenting behaviors, events, or patterns.
- Survey Research : Surveys are used to collect data through structured questionnaires or interviews. This method is efficient for gathering information from a large number of participants.
- Case Study Research : Case studies focus on in-depth exploration of one or a few cases. Researchers gather detailed information through various sources such as interviews, documents, and observations.
- Qualitative Research : Qualitative research aims to understand behaviors, experiences, and opinions in depth. It often involves open-ended questions, interviews, and thematic analysis.
- Quantitative Research : Quantitative research collects numerical data and relies on statistical analysis to draw conclusions. It involves structured questionnaires, experiments, and surveys.
Your choice of research type should align with your research questions and objectives. Experimental research, for example, is ideal for testing cause-and-effect relationships, while qualitative research is more suitable for exploring complex phenomena.
Experimental Design
Experimental research is a systematic approach to studying causal relationships. It's characterized by the manipulation of one or more independent variables while controlling for other factors. Here are some key aspects of experimental design:
- Control and Experimental Groups : Participants are randomly assigned to either a control group or an experimental group. The independent variable is manipulated for the experimental group but not for the control group.
- Randomization : Randomization is crucial to eliminate bias in group assignment. It ensures that each participant has an equal chance of being in either group.
- Hypothesis Testing : Experimental research often involves hypothesis testing. Researchers formulate hypotheses about the expected effects of the independent variable and use statistical analysis to test these hypotheses.
Observational Design
Observational research entails careful and systematic observation of subjects or phenomena. It's advantageous when you want to understand natural behaviors or events. Key aspects of observational design include:
- Participant Observation : Researchers immerse themselves in the environment they are studying. They become part of the group being observed, allowing for a deep understanding of behaviors.
- Non-Participant Observation : In non-participant observation, researchers remain separate from the subjects. They observe and document behaviors without direct involvement.
- Data Collection Methods : Observational research can involve various data collection methods, such as field notes, video recordings, photographs, or coding of observed behaviors.
Survey Design
Surveys are a popular choice for collecting data from a large number of participants. Effective survey design is essential to ensure the validity and reliability of your data. Consider the following:
- Questionnaire Design : Create clear and concise questions that are easy for participants to understand. Avoid leading or biased questions.
- Sampling Methods : Decide on the appropriate sampling method for your study, whether it's random, stratified, or convenience sampling.
- Data Collection Tools : Choose the right tools for data collection, whether it's paper surveys, online questionnaires, or face-to-face interviews.
Case Study Design
Case studies are an in-depth exploration of one or a few cases to gain a deep understanding of a particular phenomenon. Key aspects of case study design include:
- Single Case vs. Multiple Case Studies : Decide whether you'll focus on a single case or multiple cases. Single case studies are intensive and allow for detailed examination, while multiple case studies provide comparative insights.
- Data Collection Methods : Gather data through interviews, observations, document analysis, or a combination of these methods.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
In empirical research, you'll often encounter the distinction between qualitative and quantitative research . Here's a closer look at these two approaches:
- Qualitative Research : Qualitative research seeks an in-depth understanding of human behavior, experiences, and perspectives. It involves open-ended questions, interviews, and the analysis of textual or narrative data. Qualitative research is exploratory and often used when the research question is complex and requires a nuanced understanding.
- Quantitative Research : Quantitative research collects numerical data and employs statistical analysis to draw conclusions. It involves structured questionnaires, experiments, and surveys. Quantitative research is ideal for testing hypotheses and establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
Understanding the various research design options is crucial in determining the most appropriate approach for your study. Your choice should align with your research questions, objectives, and the nature of the phenomenon you're investigating.
Data Collection for Empirical Research
Now that you've established your research design, it's time to roll up your sleeves and collect the data that will fuel your empirical research. Effective data collection is essential for obtaining accurate and reliable results.
Sampling Methods
Sampling methods are critical in empirical research, as they determine the subset of individuals or elements from your target population that you will study. Here are some standard sampling methods:
- Random Sampling : Random sampling ensures that every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. It minimizes bias and is often used in quantitative research.
- Stratified Sampling : Stratified sampling involves dividing the population into subgroups or strata based on specific characteristics (e.g., age, gender, location). Samples are then randomly selected from each stratum, ensuring representation of all subgroups.
- Convenience Sampling : Convenience sampling involves selecting participants who are readily available or easily accessible. While it's convenient, it may introduce bias and limit the generalizability of results.
- Snowball Sampling : Snowball sampling is instrumental when studying hard-to-reach or hidden populations. One participant leads you to another, creating a "snowball" effect. This method is common in qualitative research.
- Purposive Sampling : In purposive sampling, researchers deliberately select participants who meet specific criteria relevant to their research questions. It's often used in qualitative studies to gather in-depth information.
The choice of sampling method depends on the nature of your research, available resources, and the degree of precision required. It's crucial to carefully consider your sampling strategy to ensure that your sample accurately represents your target population.
Data Collection Instruments
Data collection instruments are the tools you use to gather information from your participants or sources. These instruments should be designed to capture the data you need accurately. Here are some popular data collection instruments:
- Questionnaires : Questionnaires consist of structured questions with predefined response options. When designing questionnaires, consider the clarity of questions, the order of questions, and the response format (e.g., Likert scale , multiple-choice).
- Interviews : Interviews involve direct communication between the researcher and participants. They can be structured (with predetermined questions) or unstructured (open-ended). Effective interviews require active listening and probing for deeper insights.
- Observations : Observations entail systematically and objectively recording behaviors, events, or phenomena. Researchers must establish clear criteria for what to observe, how to record observations, and when to observe.
- Surveys : Surveys are a common data collection instrument for quantitative research. They can be administered through various means, including online surveys, paper surveys, and telephone surveys.
- Documents and Archives : In some cases, data may be collected from existing documents, records, or archives. Ensure that the sources are reliable, relevant, and properly documented.
To streamline your process and gather insights with precision and efficiency, consider leveraging innovative tools like Appinio . With Appinio's intuitive platform, you can harness the power of real-time consumer data to inform your research decisions effectively. Whether you're conducting surveys, interviews, or observations, Appinio empowers you to define your target audience, collect data from diverse demographics, and analyze results seamlessly.
By incorporating Appinio into your data collection toolkit, you can unlock a world of possibilities and elevate the impact of your empirical research. Ready to revolutionize your approach to data collection?
Book a Demo
Data Collection Procedures
Data collection procedures outline the step-by-step process for gathering data. These procedures should be meticulously planned and executed to maintain the integrity of your research.
- Training : If you have a research team, ensure that they are trained in data collection methods and protocols. Consistency in data collection is crucial.
- Pilot Testing : Before launching your data collection, conduct a pilot test with a small group to identify any potential problems with your instruments or procedures. Make necessary adjustments based on feedback.
- Data Recording : Establish a systematic method for recording data. This may include timestamps, codes, or identifiers for each data point.
- Data Security : Safeguard the confidentiality and security of collected data. Ensure that only authorized individuals have access to the data.
- Data Storage : Properly organize and store your data in a secure location, whether in physical or digital form. Back up data to prevent loss.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are paramount in empirical research, as they ensure the well-being and rights of participants are protected.
- Informed Consent : Obtain informed consent from participants, providing clear information about the research purpose, procedures, risks, and their right to withdraw at any time.
- Privacy and Confidentiality : Protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants. Ensure that data is anonymized and sensitive information is kept confidential.
- Beneficence : Ensure that your research benefits participants and society while minimizing harm. Consider the potential risks and benefits of your study.
- Honesty and Integrity : Conduct research with honesty and integrity. Report findings accurately and transparently, even if they are not what you expected.
- Respect for Participants : Treat participants with respect, dignity, and sensitivity to cultural differences. Avoid any form of coercion or manipulation.
- Institutional Review Board (IRB) : If required, seek approval from an IRB or ethics committee before conducting your research, particularly when working with human participants.
Adhering to ethical guidelines is not only essential for the ethical conduct of research but also crucial for the credibility and validity of your study. Ethical research practices build trust between researchers and participants and contribute to the advancement of knowledge with integrity.
With a solid understanding of data collection, including sampling methods, instruments, procedures, and ethical considerations, you are now well-equipped to gather the data needed to answer your research questions.
Empirical Research Data Analysis
Now comes the exciting phase of data analysis, where the raw data you've diligently collected starts to yield insights and answers to your research questions. We will explore the various aspects of data analysis, from preparing your data to drawing meaningful conclusions through statistics and visualization.
Data Preparation
Data preparation is the crucial first step in data analysis. It involves cleaning, organizing, and transforming your raw data into a format that is ready for analysis. Effective data preparation ensures the accuracy and reliability of your results.
- Data Cleaning : Identify and rectify errors, missing values, and inconsistencies in your dataset. This may involve correcting typos, removing outliers, and imputing missing data.
- Data Coding : Assign numerical values or codes to categorical variables to make them suitable for statistical analysis. For example, converting "Yes" and "No" to 1 and 0.
- Data Transformation : Transform variables as needed to meet the assumptions of the statistical tests you plan to use. Common transformations include logarithmic or square root transformations.
- Data Integration : If your data comes from multiple sources, integrate it into a unified dataset, ensuring that variables match and align.
- Data Documentation : Maintain clear documentation of all data preparation steps, as well as the rationale behind each decision. This transparency is essential for replicability.
Effective data preparation lays the foundation for accurate and meaningful analysis. It allows you to trust the results that will follow in the subsequent stages.
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics help you summarize and make sense of your data by providing a clear overview of its key characteristics. These statistics are essential for understanding the central tendencies, variability, and distribution of your variables. Descriptive statistics include:
- Measures of Central Tendency : These include the mean (average), median (middle value), and mode (most frequent value). They help you understand the typical or central value of your data.
- Measures of Dispersion : Measures like the range, variance, and standard deviation provide insights into the spread or variability of your data points.
- Frequency Distributions : Creating frequency distributions or histograms allows you to visualize the distribution of your data across different values or categories.
Descriptive statistics provide the initial insights needed to understand your data's basic characteristics, which can inform further analysis.
Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics take your analysis to the next level by allowing you to make inferences or predictions about a larger population based on your sample data. These methods help you test hypotheses and draw meaningful conclusions. Key concepts in inferential statistics include:
- Hypothesis Testing : Hypothesis tests (e.g., t-tests , chi-squared tests ) help you determine whether observed differences or associations in your data are statistically significant or occurred by chance.
- Confidence Intervals : Confidence intervals provide a range within which population parameters (e.g., population mean) are likely to fall based on your sample data.
- Regression Analysis : Regression models (linear, logistic, etc.) help you explore relationships between variables and make predictions.
- Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) : ANOVA tests are used to compare means between multiple groups, allowing you to assess whether differences are statistically significant.
Chi-Square Calculator :
t-Test Calculator :
One-way ANOVA Calculator :
Inferential statistics are powerful tools for drawing conclusions from your data and assessing the generalizability of your findings to the broader population.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis is employed when working with non-numerical data, such as text, interviews, or open-ended survey responses. It focuses on understanding the underlying themes, patterns, and meanings within qualitative data. Qualitative analysis techniques include:
- Thematic Analysis : Identifying and analyzing recurring themes or patterns within textual data.
- Content Analysis : Categorizing and coding qualitative data to extract meaningful insights.
- Grounded Theory : Developing theories or frameworks based on emergent themes from the data.
- Narrative Analysis : Examining the structure and content of narratives to uncover meaning.
Qualitative data analysis provides a rich and nuanced understanding of complex phenomena and human experiences.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is the art of representing data graphically to make complex information more understandable and accessible. Effective data visualization can reveal patterns, trends, and outliers in your data. Common types of data visualization include:
- Bar Charts and Histograms : Used to display the distribution of categorical data or discrete data .
- Line Charts : Ideal for showing trends and changes in data over time.
- Scatter Plots : Visualize relationships and correlations between two variables.
- Pie Charts : Display the composition of a whole in terms of its parts.
- Heatmaps : Depict patterns and relationships in multidimensional data through color-coding.
- Box Plots : Provide a summary of the data distribution, including outliers.
- Interactive Dashboards : Create dynamic visualizations that allow users to explore data interactively.
Data visualization not only enhances your understanding of the data but also serves as a powerful communication tool to convey your findings to others.
As you embark on the data analysis phase of your empirical research, remember that the specific methods and techniques you choose will depend on your research questions, data type, and objectives. Effective data analysis transforms raw data into valuable insights, bringing you closer to the answers you seek.
How to Report Empirical Research Results?
At this stage, you get to share your empirical research findings with the world. Effective reporting and presentation of your results are crucial for communicating your research's impact and insights.
1. Write the Research Paper
Writing a research paper is the culmination of your empirical research journey. It's where you synthesize your findings, provide context, and contribute to the body of knowledge in your field.
- Title and Abstract : Craft a clear and concise title that reflects your research's essence. The abstract should provide a brief summary of your research objectives, methods, findings, and implications.
- Introduction : In the introduction, introduce your research topic, state your research questions or hypotheses, and explain the significance of your study. Provide context by discussing relevant literature.
- Methods : Describe your research design, data collection methods, and sampling procedures. Be precise and transparent, allowing readers to understand how you conducted your study.
- Results : Present your findings in a clear and organized manner. Use tables, graphs, and statistical analyses to support your results. Avoid interpreting your findings in this section; focus on the presentation of raw data.
- Discussion : Interpret your findings and discuss their implications. Relate your results to your research questions and the existing literature. Address any limitations of your study and suggest avenues for future research.
- Conclusion : Summarize the key points of your research and its significance. Restate your main findings and their implications.
- References : Cite all sources used in your research following a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Ensure accuracy and consistency in your citations.
- Appendices : Include any supplementary material, such as questionnaires, data coding sheets, or additional analyses, in the appendices.
Writing a research paper is a skill that improves with practice. Ensure clarity, coherence, and conciseness in your writing to make your research accessible to a broader audience.
2. Create Visuals and Tables
Visuals and tables are powerful tools for presenting complex data in an accessible and understandable manner.
- Clarity : Ensure that your visuals and tables are clear and easy to interpret. Use descriptive titles and labels.
- Consistency : Maintain consistency in formatting, such as font size and style, across all visuals and tables.
- Appropriateness : Choose the most suitable visual representation for your data. Bar charts, line graphs, and scatter plots work well for different types of data.
- Simplicity : Avoid clutter and unnecessary details. Focus on conveying the main points.
- Accessibility : Make sure your visuals and tables are accessible to a broad audience, including those with visual impairments.
- Captions : Include informative captions that explain the significance of each visual or table.
Compelling visuals and tables enhance the reader's understanding of your research and can be the key to conveying complex information efficiently.
3. Interpret Findings
Interpreting your findings is where you bridge the gap between data and meaning. It's your opportunity to provide context, discuss implications, and offer insights. When interpreting your findings:
- Relate to Research Questions : Discuss how your findings directly address your research questions or hypotheses.
- Compare with Literature : Analyze how your results align with or deviate from previous research in your field. What insights can you draw from these comparisons?
- Discuss Limitations : Be transparent about the limitations of your study. Address any constraints, biases, or potential sources of error.
- Practical Implications : Explore the real-world implications of your findings. How can they be applied or inform decision-making?
- Future Research Directions : Suggest areas for future research based on the gaps or unanswered questions that emerged from your study.
Interpreting findings goes beyond simply presenting data; it's about weaving a narrative that helps readers grasp the significance of your research in the broader context.
With your research paper written, structured, and enriched with visuals, and your findings expertly interpreted, you are now prepared to communicate your research effectively. Sharing your insights and contributing to the body of knowledge in your field is a significant accomplishment in empirical research.
Examples of Empirical Research
To solidify your understanding of empirical research, let's delve into some real-world examples across different fields. These examples will illustrate how empirical research is applied to gather data, analyze findings, and draw conclusions.
Social Sciences
In the realm of social sciences, consider a sociological study exploring the impact of socioeconomic status on educational attainment. Researchers gather data from a diverse group of individuals, including their family backgrounds, income levels, and academic achievements.
Through statistical analysis, they can identify correlations and trends, revealing whether individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds are less likely to attain higher levels of education. This empirical research helps shed light on societal inequalities and informs policymakers on potential interventions to address disparities in educational access.
Environmental Science
Environmental scientists often employ empirical research to assess the effects of environmental changes. For instance, researchers studying the impact of climate change on wildlife might collect data on animal populations, weather patterns, and habitat conditions over an extended period.
By analyzing this empirical data, they can identify correlations between climate fluctuations and changes in wildlife behavior, migration patterns, or population sizes. This empirical research is crucial for understanding the ecological consequences of climate change and informing conservation efforts.
Business and Economics
In the business world, empirical research is essential for making data-driven decisions. Consider a market research study conducted by a business seeking to launch a new product. They collect data through surveys , focus groups , and consumer behavior analysis.
By examining this empirical data, the company can gauge consumer preferences, demand, and potential market size. Empirical research in business helps guide product development, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns, increasing the likelihood of a successful product launch.
Psychological studies frequently rely on empirical research to understand human behavior and cognition. For instance, a psychologist interested in examining the impact of stress on memory might design an experiment. Participants are exposed to stress-inducing situations, and their memory performance is assessed through various tasks.
By analyzing the data collected, the psychologist can determine whether stress has a significant effect on memory recall. This empirical research contributes to our understanding of the complex interplay between psychological factors and cognitive processes.
These examples highlight the versatility and applicability of empirical research across diverse fields. Whether in medicine, social sciences, environmental science, business, or psychology, empirical research serves as a fundamental tool for gaining insights, testing hypotheses, and driving advancements in knowledge and practice.
Conclusion for Empirical Research
Empirical research is a powerful tool for gaining insights, testing hypotheses, and making informed decisions. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you've learned how to select research topics, collect data, analyze findings, and effectively communicate your research to the world. Remember, empirical research is a journey of discovery, and each step you take brings you closer to a deeper understanding of the world around you. Whether you're a scientist, a student, or someone curious about the process, the principles of empirical research empower you to explore, learn, and contribute to the ever-expanding realm of knowledge.
How to Collect Data for Empirical Research?
Introducing Appinio , the real-time market research platform revolutionizing how companies gather consumer insights for their empirical research endeavors. With Appinio, you can conduct your own market research in minutes, gaining valuable data to fuel your data-driven decisions.
Appinio is more than just a market research platform; it's a catalyst for transforming the way you approach empirical research, making it exciting, intuitive, and seamlessly integrated into your decision-making process.
Here's why Appinio is the go-to solution for empirical research:
- From Questions to Insights in Minutes : With Appinio's streamlined process, you can go from formulating your research questions to obtaining actionable insights in a matter of minutes, saving you time and effort.
- Intuitive Platform for Everyone : No need for a PhD in research; Appinio's platform is designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, ensuring that anyone can navigate and utilize it effectively.
- Rapid Response Times : With an average field time of under 23 minutes for 1,000 respondents, Appinio delivers rapid results, allowing you to gather data swiftly and efficiently.
- Global Reach with Targeted Precision : With access to over 90 countries and the ability to define target groups based on 1200+ characteristics, Appinio empowers you to reach your desired audience with precision and ease.
Get free access to the platform!
Get facts and figures 🧠
Want to see more data insights? Our free reports are just the right thing for you!
Wait, there's more

04.11.2024 | 5min read
Trustly uses Appinio’s insights to revolutionize utility bill payments

19.09.2024 | 9min read
Track Your Customer Retention & Brand Metrics for Post-Holiday Success

16.09.2024 | 10min read
Creative Checkup – Optimize Advertising Slogans & Creatives for ROI

- Ask a Librarian
Research: Overview & Approaches
- Getting Started with Undergraduate Research
- Planning & Getting Started
- Building Your Knowledge Base
- Locating Sources
- Reading Scholarly Articles
- Creating a Literature Review
- Productivity & Organizing Research
- Scholarly and Professional Relationships
Introduction to Empirical Research
Databases for finding empirical research, google scholar, examples of empirical research, sources and further reading.
- Interpretive Research
- Action-Based Research
- Creative & Experimental Approaches
- Technical Support
Your Librarian

This brief video listed above introduces empirical research, questions and methods used in this research approach, provides some tips to locating empirical research studies.
- Engineering Village (Compendex & INSPEC Combined) This information database covers the fields of physics, electronics, computing, control engineering and information technology with technical and scientific journals and conference proceedings.
- Proquest Statistical Insight This database includes statistical information produced by U.S. Federal agencies, States, private organizations, and major intergovernmental organizations.
- Study on radiation transfer in human skin for cosmetics
- Long-Term Mobile Phone Use and the Risk of Vestibular Schwannoma: A Danish Nationwide Cohort Study
- Emissions Impacts and Benefits of Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles and Vehicle-to-Grid Services
- Review of design considerations and technological challenges for successful development and deployment of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles
- Endocrine disrupters and human health: could oestrogenic chemicals in body care cosmetics adversely affect breast cancer incidence in women?
- << Previous: Scholarly and Professional Relationships
- Next: Interpretive Research >>
- Last Updated: Dec 10, 2024 3:25 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.purdue.edu/research_approaches

Up to 65% off on all yearly plans! 🎁 Start fresh with a yearly plan. Now 65% off! ❄️ 🏷️
- Form Builder
- Survey Maker
- AI Form Generator
- AI Survey Tool
- AI Quiz Maker
- Store Builder
- WordPress Plugin
HubSpot CRM
Google Sheets
Google Analytics
Microsoft Excel
- Popular Forms
- Job Application Form Template
- Rental Application Form Template
- Hotel Accommodation Form Template
- Online Registration Form Template
- Employment Application Form Template
- Application Forms
- Booking Forms
- Consent Forms
- Contact Forms
- Donation Forms
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys
- Employee Satisfaction Surveys
- Evaluation Surveys
- Feedback Surveys
- Market Research Surveys
- Personality Quiz Template
- Geography Quiz Template
- Math Quiz Template
- Science Quiz Template
- Vocabulary Quiz Template
Try without registration Quick Start
Read engaging stories, how-to guides, learn about forms.app features.
Inspirational ready-to-use templates for getting started fast and powerful.
Spot-on guides on how to use forms.app and make the most out of it.
See the technical measures we take and learn how we keep your data safe and secure.
- Integrations
- Help Center
- Sign In Sign Up Free
- What is empirical research: Methods, types & examples
Defne Çobanoğlu
Having opinions on matters based on observation is okay sometimes. Same as having theories on the subject you want to solve. However, some theories need to be tested. Just like Robert Oppenheimer says, “Theory will take you only so far .”
In that case, when you have your research question ready and you want to make sure it is correct, the next step would be experimentation. Because only then you can test your ideas and collect tangible information. Now, let us start with the empirical research definition:
- What is empirical research?
Empirical research is a research type where the aim of the study is based on finding concrete and provable evidence . The researcher using this method to draw conclusions can use both quantitative and qualitative methods. Different than theoretical research, empirical research uses scientific experimentation and investigation.
Using experimentation makes sense when you need to have tangible evidence to act on whatever you are planning to do. As the researcher, you can be a marketer who is planning on creating a new ad for the target audience, or you can be an educator who wants the best for the students. No matter how big or small, data gathered from the real world using this research helps break down the question at hand.
- When to use empirical research?
Empirical research methods are used when the researcher needs to gather data analysis on direct, observable, and measurable data. Research findings are a great way to make grounded ideas. Here are some situations when one may need to do empirical research:
1. When quantitative or qualitative data is needed
There are times when a researcher, marketer, or producer needs to gather data on specific research questions to make an informed decision. And the concrete data gathered in the research process gives a good starting point.
2. When you need to test a hypothesis
When you have a hypothesis on a subject, you can test the hypothesis through observation or experiment. Making a planned study is a great way to collect information and test whether or not your hypothesis is correct.
3. When you want to establish causality
Experimental research is a good way to explore whether or not there is any correlation between two variables. Researchers usually establish causality by changing a variable and observing if the independent variable changes accordingly.
- Types of empirical research
The aim of empirical research is to collect information about a subject from the people by doing experimentation and other data collection methods. However, the methods and data collected are divided into two groups: one collects numerical data, and the other one collects opinion-like data. Let us see the difference between these two types:
Quantitative research
Quantitative research methods are used to collect data in a numerical way. Therefore, the results gathered by these methods will be numbers, statistics, charts, etc. The results can be used to quantify behaviors, opinions, and other variables. Quantitative research methods are surveys, questionnaires, and experimental research.
Qualitiative research
Qualitative research methods are not used to collect numerical answers, instead, they are used to collect the participants’ reasons, opinions, and other meaningful aspects. Qualitative research methods include case studies, observations, interviews, focus groups, and text analysis.
- 5 steps to conduct empirical research

Necessary steps for empirical research
When you want to collect direct and concrete data on a subject, empirical research is a great way to go. And, just like every other project and research, it is best to have a clear structure in mind. This is even more important in studies that may take a long time, such as experiments that take years. Let us look at a clear plan on how to do empirical research:
1. Define the research question
The very first step of every study is to have the question you will explore ready. Because you do not want to change your mind in the middle of the study after investing and spending time on the experimentation.
2. Go through relevant literature
This is the step where you sit down and do a desk research where you gather relevant data and see if other researchers have tried to explore similar research questions. If so, you can see how well they were able to answer the question or what kind of difficulties they faced during the research process.
3. Decide on the methodology
Once you are done going through the relevant literature, you can decide on which method or methods you can use. The appropriate methods are observation, experimentation, surveys, interviews, focus groups, etc.
4. Do data analysis
When you get to this step, it means you have successfully gathered enough data to make a data analysis. Now, all you need to do is look at the data you collected and make an informed analysis.
5. Conclusion
This is the last step, where you are finished with the experimentation and data analysis process. Now, it is time to decide what to do with this information. You can publish a paper and make informed decisions about whatever your goal is.
- Empirical research methodologies

Some essential methodologies to conduct empirical research
The aim of this type of research is to explore brand-new evidence and facts. Therefore, the methods should be primary and gathered in real life, directly from the people. There is more than one method for this goal, and it is up to the researcher to use which one(s). Let us see the methods of empirical research:
- Observation
The method of observation is a great way to collect information on people without the effect of interference. The researcher can choose the appropriate area, time, or situation and observe the people and their interactions with one another. The researcher can be just an outside observer or can be a participant as an observer or a full participant.
- Experimentation
The experimentation process can be done in the real world by intervening in some elements to unify the environment for all participants. This method can also be done in a laboratory environment. The experimentation process is good for being able to change the variables according to the aim of the study.
The case study method is done by making an in-depth analysis of already existing cases. When the parameters and variables are similar to the research question at hand, it is wise to go through what was researched before.
- Focus groups
The case study method is done by using a group of individuals or multiple groups and using their opinions, characteristics, and responses. The scientists gather the data from this group and generalize it to the whole population.
Surveys are an effective way to gather data directly from people. It is a systematic approach to collecting information. If it is done in an online setting as an online survey , it would be even easier to reach out to people and ask their opinions in open-ended or close-ended questions.
Interviews are similar to surveys as you are using questions to collect information and opinions of the people. Unlike a survey, this process is done face-to-face, as a phone call, or as a video call.
- Advantages of empirical research
Empirical research is effective for many reasons, and helps researchers from numerous fields. Here are some advantages of empirical research to have in mind for your next research:
- Empirical research improves the internal validity of the study.
- Empirical evidence gathered from the study is used to authenticate the research question.
- Collecting provable evidence is important for the success of the study.
- The researcher is able to make informed decisions based on the data collected using empirical research.
- Disadvantages of empirical research
After learning about the positive aspects of empirical research, it is time to mention the negative aspects. Because this type may not be suitable for everyone and the researcher should be mindful of the disadvantages of empirical research. Here are the disadvantages of empirical research:
- As it is similar to other research types, a case study where experimentation is included will be time-consuming no matter what. It has more steps and variables than concluding a secondary research.
- There are a lot of variables that need to be controlled and considered. Therefore, it may be a challenging task to be mindful of all the details.
- Doing evidence-based research can be expensive if you need to complete it on a large scale.
- When you are conducting an experiment, you may need some waivers and permissions.
- Frequently asked questions about empirical research
Empirical research is one of the many research types, and there may be some questions in mind about its similarities and differences to other research types.
Is empirical research qualitative or quantitative?
The data collected by empirical research can be qualitative, quantitative, or a mix of both. It is up to the aim of researcher to what kind of data is needed and searched for.
Is empirical research the same as quantitative research?
As quantitative research heavily relies on data collection methods of observation and experimentation, it is, in nature, an empirical study. Some professors may even use the terms interchangeably. However, that does not mean that empirical research is only a quantitative one.
What is the difference between theoretical and empirical research?
Empirical studies are based on data collection to prove theories or answer questions, and it is done by using methods such as observation and experimentation. Therefore, empirical research relies on finding evidence that backs up theories. On the other hand, theoretical research relies on theorizing on empirical research data and trying to make connections and correlations.
What is the difference between conceptual and empirical research?
Conceptual research is about thoughts and ideas and does not involve any kind of experimentation. Empirical research, on the other hand, works with provable data and hard evidence.
What is the difference between empirical vs applied research?
Some scientists may use these two terms interchangeably however, there is a difference between them. Applied research involves applying theories to solve real-life problems. On the other hand, empirical research involves the obtaining and analysis of data to test hypotheses and theories.
- Final words
Empirical research is a good means when the goal of your study is to find concrete data to go with. You may need to do empirical research when you need to test a theory, establish causality, or need qualitative/quantitative data. For example, you are a scientist and want to know if certain colors have an effect on people’s moods, or you are a marketer and want to test your theory on ad places on websites.
In both scenarios, you can collect information by using empirical research methods and make informed decisions afterward. These are just the two of empirical research examples. This research type can be applied to many areas of work life and social sciences. Lastly, for all your research needs, you can visit forms.app to use its many useful features and over 1000 form and survey templates!
Defne is a content writer at forms.app. She is also a translator specializing in literary translation. Defne loves reading, writing, and translating professionally and as a hobby. Her expertise lies in survey research, research methodologies, content writing, and translation.
- Form Features
- Data Collection
Table of Contents
Related posts.

8 Creative web surveys to take inspiration from when building your online store
35 Great questions to ask in a quality of life questionnaire
Şeyma Beyazçiçek

Employment forms: Types, examples, and best practices
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
What Is Empirical Research? Definition And Tips For Students

So what is an empirical research article? What does empirical research entail? What are good examples of empirical research topics? These are common questions most students find themselves asking whenever a research paper instructs them to read and analyze empirical articles or evidence to answer a particular question. Such questions also arise when it comes to graduation papers and many students just ask writers to help. If this points out your current dilemma, then you are in good company because below is a well-detailed guide on all you need to know about empirical research.
Definition of Empirical Research
Empirical research is a type of research whose findings or conclusions are mainly drawn from empirical or verifiable evidence rather than rationality.
Simply put, empirical research is any research whose findings are based on observable or experimentation evidence rather than through reasoning or logic alone. For instance, if a scientist wants to find out whether soft music promotes sleep, he or she will find a group of people and divide them into two groups.
The first group will be in a space with soft music while the second one will be in an area with no music at all for observation. Once the experiment is over, the results or conclusion drawn from it will be termed as empirical evidence whether or not soft music promotes sleep.
The Objectives of Empirical Research
There is more to empirical research than just observations. In fact, these observations will be useless if the scientist does not turn them into testable questions. So, now that you know what empirical research entails, what are the objectives? Well, the main reason why you’ll be asked to conduct such research is so you can use the findings drawn from your observations to answer well-defined questions that go with or against a particular hypothesis.
In the earlier mentioned example, for instance, the hypothesis would be “soft music promotes sleep.” Thus, the aim of carrying out empirical research, in this case, would be to come up with conclusions that either accept or reject the hypotheses.
Now to achieve this, you can either use quantitative or qualitative methodologies. Here is a breakdown of what each of the mentioned entails
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative empirical research methods are often used to collect information and draw conclusions through numerical data. Quantitative methods are usually predetermined and are set in a more structured format. Some good examples include
- Longitudinal studies
- Cross-sectional studies
- Experimental research
- Causal comparative research
The above techniques are often more effective for physics or medicine.
Qualitative Methods
Qualitative empirical research methods, on the other hand, are used to gather non-numerical data. They are mainly unstructured or semi-structured and are used to find meaning or underlying reasons for a particular phenomenon. In other words, they are used to provide more insight into the problem being researched. So, is qualitative research empirical? The short answer to that is yes. It is indeed empirical but more appropriate in finding answers to social science-related questions.
Types of Empirical Research
Note, there is a difference between methodologies and types of empirical research. Methodologies are the earlier mentioned quantitative and qualitative, and they refer to the methods used to conduct or analyze data. But when it comes to types of empirical research, it can be either experimental or non-experimental.
In experimental research, a particular intervention is often used to drive a hypothesized changed in the variables of interest. In non-experimental empirical research, however, the subjects of the study are simply observed without any form of intervention. This is why it’s also referred to as informal research.
How to Identify Empirical Research Articles
Now that you know the types of empirical research as well as methodologies, how do you distinguish an empirical research paper from a regular research paper? Well, as with any other research question, empirical research questions usually have features that can help you identify them as shown below
Empirical Research Article Format
The easiest way to identify an empirical research article is through its unique format. It’s usually divided into these sections
- The Title. It offers an overview of the research and also includes the author(s) who conducted it
- An abstract. It provides a very brief yet comprehensive summary of the empirical research study. It’s usually a paragraph long.
- The Introduction. Here the author provides background information on the research problem. For instance, they talk about similar studies and explain why the research was conducted in the first place.
- The MethodsIn this section, the author offers a detailed description of all methods used to conduct the empirical research study. In some articles, it may be titled methodology.
- The Results. Here the author provides the answer to the research question.
- DiscussionThe author will then go on to give a detailed discussion of the data obtained or the results found above. They may also compare the results of their empirical research study to the results obtained by other empirical studies on similar topics.
- ReferencesHere as you may have guessed, the author lists citations of any journal articles, studies, or books mentioned or used in coming up with the results.
Keywords Used in an Empirical Research Paper
Other than the format, you can also identify an empirical research paper based on the phrases used within it. Some of the must-have keywords include:
- Measure or measurements
- Qualitative and quantitative research
- Sample size
- Methodology
- Original study or research study
Empirical Research Examples
Some of the empirical questions you could come across in empirical research include:
- According to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, at which level are, leaders need level?
- The lop-sided sales of illegal guns among licensed handgun retailers.
- Freeway truck travel-time prediction for seamless freight planning using GPS data.
- Use empirical research to explain the entrepreneurial mindset concerning cognition and motivation.
- Are meta-analysis reviews theoretical or empirical research?
Theoretical vs. Empirical Research
Unlike empirical research, which is based on valid or observational evidence, theoretical research is more logical than observational. It is a logical exploration of a system of assumptions and involves defining how a particular system and its environment behave without the analysis of concrete data.
Therefore, theoretical research can be classified as non-empirical data as it is conducted without data. It is essential as it offers anyone conducting research a place to start. For instance, saying soft music promotes sleep gives the researcher a hypothesis to base their research proposal on and an easy way to start. However, theoretical data is only useful if empirical research is conducted.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Canvas | University | Ask a Librarian
- Library Homepage
- Arrendale Library
Empirical & Non-Empirical Research
- Empirical Research
Introduction: What is Empirical Research?
Quantitative methods, qualitative methods.
- Quantitative vs. Qualitative
- Reference Works for Social Sciences Research
- What is Non-Empirical Research?
- Contact Us!
Call us at 706-776-0111
Chat with a Librarian
Send Us Email
Library Hours
Empirical research is based on phenomena that can be observed and measured. Empirical research derives knowledge from actual experience rather than from theory or belief.
Key characteristics of empirical research include:
- Specific research questions to be answered;
- Definitions of the population, behavior, or phenomena being studied;
- Description of the methodology or research design used to study this population or phenomena, including selection criteria, controls, and testing instruments (such as surveys);
- Two basic research processes or methods in empirical research: quantitative methods and qualitative methods (see the rest of the guide for more about these methods).
(based on the original from the Connelly LIbrary of LaSalle University)

Empirical Research: Qualitative vs. Quantitative
Learn about common types of journal articles that use APA Style, including empirical studies; meta-analyses; literature reviews; and replication, theoretical, and methodological articles.
Academic Writer
© 2024 American Psychological Association.
- More about Academic Writer ...
Quantitative Research
A quantitative research project is characterized by having a population about which the researcher wants to draw conclusions, but it is not possible to collect data on the entire population.
- For an observational study, it is necessary to select a proper, statistical random sample and to use methods of statistical inference to draw conclusions about the population.
- For an experimental study, it is necessary to have a random assignment of subjects to experimental and control groups in order to use methods of statistical inference.
Statistical methods are used in all three stages of a quantitative research project.
For observational studies, the data are collected using statistical sampling theory. Then, the sample data are analyzed using descriptive statistical analysis. Finally, generalizations are made from the sample data to the entire population using statistical inference.
For experimental studies, the subjects are allocated to experimental and control group using randomizing methods. Then, the experimental data are analyzed using descriptive statistical analysis. Finally, just as for observational data, generalizations are made to a larger population.
Iversen, G. (2004). Quantitative research . In M. Lewis-Beck, A. Bryman, & T. Liao (Eds.), Encyclopedia of social science research methods . (pp. 897-898). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc.
Qualitative Research
What makes a work deserving of the label qualitative research is the demonstrable effort to produce richly and relevantly detailed descriptions and particularized interpretations of people and the social, linguistic, material, and other practices and events that shape and are shaped by them.
Qualitative research typically includes, but is not limited to, discerning the perspectives of these people, or what is often referred to as the actor’s point of view. Although both philosophically and methodologically a highly diverse entity, qualitative research is marked by certain defining imperatives that include its case (as opposed to its variable) orientation, sensitivity to cultural and historical context, and reflexivity.
In its many guises, qualitative research is a form of empirical inquiry that typically entails some form of purposive sampling for information-rich cases; in-depth interviews and open-ended interviews, lengthy participant/field observations, and/or document or artifact study; and techniques for analysis and interpretation of data that move beyond the data generated and their surface appearances.
Sandelowski, M. (2004). Qualitative research . In M. Lewis-Beck, A. Bryman, & T. Liao (Eds.), Encyclopedia of social science research methods . (pp. 893-894). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc.
- Next: Quantitative vs. Qualitative >>
- Last Updated: Dec 17, 2024 10:08 AM
- URL: https://library.piedmont.edu/empirical-research
- Ebooks & Online Video
- New Materials
- Renew Checkouts
- Faculty Resources
- Friends of the Library
- Library Services
- Our Mission
- Library History
- Ask a Librarian!
- Making Citations
- Working Online
Arrendale Library Piedmont University 706-776-0111
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Empirical Paper Writing From A To Z

When asked to write an empirical paper, many learners don’t know where to start. That’s because most students don’t know much about this paper. Perhaps, you came across this article after searching for the meaning of this paper online. Well, you’ve come to the right place because this article will explain everything you want to know about this paper.
What is an Empirical Paper?
Importance of an empirical paper, how to write an empirical research paper, interesting empirical research topics to consider, useful tips and insights.
In most cases, humans decide based on evidence. Thus, most people decide based on what they can prove as valid or measure. When presented with plausible alternatives, most individuals tilt towards choices that have been proven effective. Empirical research adopts a similar approach.
In this study, researchers arrive at results by testing their empirical evidence. And they test the available evidence using quantitative and qualitative observation methods, as determined by the research nature. Perhaps, you’re torn between a theoretical paper vs. empirical paper. Just like the name suggests, a theoretical paper is largely based on theories. On the other hand, a paper whose basis is empirical research is largely based on evidence. Ideally, the features and methodology of empirical research set it apart from the other study approaches. Therefore, researchers must understand what constitutes this study.
An empirical research paper is a write-up that is based on verifiable evidence. Ideally, the conclusion of this paper is arrived at after analyzing verifiable evidence. In simple terms, it’s a paper that solely depends on evidence acquired via scientific methods of gathering data or observation.
Researchers can conduct empirical research using quantitative or qualitative observation methods, based on their data sample. That is non-numerical data or quantifiable data. As hinted, this is what differentiates empirical papers from theoretical papers. Ideally, theoretical papers depend on pre-conceived notions regarding research variables. On the other hand, empirical research entails engaging in a scientific investigation and measuring the experimental probability of those variables.
Perhaps, you’re wondering why you should engage in a scientific investigation to write this paper. Well, empirical research is very common because it’s used to perform systematic investigations. Researchers use this method to validate different research hypotheses in fields like law, anthropology, and medicine. Based on the empirical paper definition, this task is important for the following reasons:
- Authenticating traditional research via observations and experiments
- Providing more authentic and competent findings
- Understanding the dynamic changes that happen over time
- Studying rules, institutions, and procedures to understand their operations
- Testing and validating multiple hypotheses to improve human knowledge
- To study human cultures and behavioral patterns
For your paper to serve its purpose effectively, it should be carefully and thoroughly researched. All information included in your paper should be factual and supported with evidence.
As hinted, the basis of your paper should be verifiable research. Therefore, you must conduct extensive research before you write your paper.
Preparation
Start by preparing to write your paper. This step requires you to do several things as follows.
- Select a topic : Start by choosing a topic for your paper. Pick a topic you’re comfortable researching and writing about. Make sure that your topic is not too broad or too narrow. That’s because you won’t cover a too broad topic exhaustively. And if your topic is too narrow, you won’t meet the specified word count for your paper.
- Research the topic : Gather as much information as possible about the topic. Take your time to analyze the information and understand different aspects of your topic. That way, you will know the best angle to take when writing your paper.
Before you proceed to actual writing, you can find and read an APA empirical paper sample to understand what the educator expects from you.
Actual Writing
Now that you have the topic and information that you need to write the paper, you can proceed to the actual writing step. Here’s a guide on how to write an empirical paper.
- Write the title page : This page should summarize your main point, question, or findings that you will present in the paper. It should also include your institutional affiliations and name. Make the title informative, professional, and interesting. That’s because the title is the first thing your readers will see.
- Write the abstract : In empirical research papers, the abstract can be written after completing the paper. That’s because it’s a paragraph that summarizes the paper for the readers. When writing this section, explain your research question briefly. You can also explain research methods, samples, and conclusions briefly.
- Write the introduction : When writing the introduction of empirical paper, include the research problem and then tell your readers why it’s important. Also, provide background information about your topic. Your introduction should explain specific hypotheses while demonstrating how your chosen research design corresponds with them.
- Methodology : In this section, describe the research methods you used to conduct your research. If writing an APA paper, label subsections like participants, sampling procedures, sample size, and study design. Don’t skip this section because you can easily some of the research methods.
- Results : Perhaps, this is the most important part of an empirical research paper structure. Here, you include statistics and data analysis. Report your findings consistently if you mention them in other sections. That way, your readers can easily follow and understand your findings.
- Discussion : Restate your study findings in this section using plain terms. Also, explain how your research findings relate to your hypotheses. Ideally, interpret results in this section while discussing their implications. And this should include practical and theoretical consequences . If you encountered research limitations, acknowledge them in this section.
- Reference : Use the APA guidelines to compose the reference section of your paper. This is an important part of the paper because it provides additional information on your topic.
The order of parts in empirical paper may vary but these are the most important sections of this write-up.
Proofreading
Once you’ve written your paper, take your time to go through it correcting all typo, spelling, grammatical, and factual errors. That’s because you could have brilliant ideas and findings but minor errors can damage the quality of your paper.
One of the most challenging parts of the process of writing this paper is choosing a topic. That’s because learners want to choose topics they will be comfortable researching and writing about. They also want unique topics that will impress educators to award them good grades. If struggling to find a topic for your paper, consider these ideas.
- An empirical analysis of foreign exchange management in developing economies
- An empirical analysis of liquidity problem in commercial banks
- How capital structure affects profitability- Empirical analysis of selected companies
- An empirical analysis of the effect of multi-national oil companies on an economy
- Conflicts management in financial institutions- Empirical analysis of the staff
- An empirical analysis of the impact of monetary policies on a country’s economy
- Impact of currency depreciation on a country’s economy- Empirical analysis
- An empirical analysis of the effect of political institutions on the development and economic growth
- How religion affects social development- Empirical analysis
- Effects of policies, institutions, and events on a society
You can pick any of these empirical paper topics, research extensively, and analyze your findings to compose a winning paper. Nevertheless, make sure only relevant and evidence-backed information goes into your paper.
Follow these tips and insights to write a brilliant paper:
- Check your educator’s guidelines and follow all the instructions, including word count and formatting.
- Create your empirical research paper outline to come up with a properly organized paper with logically flowing ideas.
- Be concise and clear by including important information only.
- Use headings and subheadings to make your paper easy to read.
- Cite multiple credible sources in your paper.
- Include figures and tables to convey information if you find it hard to discuss using paragraphs.
- Get our thesis writing help if you’re got stuck.
Always remember that your paper should be based on research. And the evidence in your paper should be verifiable. You can gather empirical evidence using qualitative and quantitative research methods. The above guidelines and tips should help you come up with a winning paper. However, follow the instructions provided by your educator when writing this paper. If unable to complete this assignment even with these tips and guidelines, get and read a good empirical research paper example first. That way, you will know the kind of information and presentation the educator expects from you.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Nov 19, 2024 · Definition of Empirical Research: Empirical research is based on verifiable evidence derived from observation and experimentation, aiming to understand how the world works. Origins: The concept of empirical research dates back to ancient Greek medical practitioners who relied on observed phenomena rather than dogmatic principles.
Examples of Empirical Research Questions 1. What is the effect of working during high school (or college) on GPA? a. Variations on this topic (e.g., what is the effect of alcohol or drug use on GPA?) 2. Do gun control laws reduce violent crimes? 3. Are police officers compensated for working in higher-risk environments? 4.
01. What is meant by empirical research? Empirical research is a type of study that relies on observation, experience, or experimentation to gather data. It involves collecting evidence through direct or indirect observation of real-world phenomena and analyzing that data to form conclusions, often using scientific methods such as experiments ...
This collection of 1400 research paper topics across 28 categories provides students with diverse ideas to inspire engaging and impactful research. Each topic reflects current issues, emerging trends, and future developments, ensuring that students can explore timely questions relevant to their academic and career aspirations.
Feb 9, 2024 · This empirical research is crucial for understanding the ecological consequences of climate change and informing conservation efforts. Business and Economics. In the business world, empirical research is essential for making data-driven decisions. Consider a market research study conducted by a business seeking to launch a new product.
Dec 10, 2024 · This book introduces readers to methods and strategies for research and provides them with enough knowledge to become discerning, confident consumers of research in writing. Topics covered include: library research, empirical methodology, quantitative research, experimental research, surveys, focus groups, ethnographies, and much more.
Nov 2, 2023 · Empirical research is a research type where the aim of the study is based on finding concrete and provable evidence. The researcher using this method to draw conclusions can use both quantitative and qualitative methods. Different than theoretical research, empirical research uses scientific experimentation and investigation.
Empirical research is a type of research whose findings or conclusions are mainly drawn from empirical or verifiable evidence rather than rationality. Simply put, empirical research is any research whose findings are based on observable or experimentation evidence rather than through reasoning or logic alone.
6 days ago · Empirical research is based on phenomena that can be observed and measured. Empirical research derives knowledge from actual experience rather than from theory or belief. Key characteristics of empirical research include: Specific research questions to be answered; Definitions of the population, behavior, or phenomena being studied;
An empirical analysis of the effect of political institutions on the development and economic growth; How religion affects social development- Empirical analysis; Effects of policies, institutions, and events on a society; You can pick any of these empirical paper topics, research extensively, and analyze your findings to compose a winning paper.