

Essay on Photosynthesis
Students are often asked to write an essay on Photosynthesis in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Photosynthesis
What is photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is how plants make their own food using sunlight. It happens in the leaves of plants. Tiny parts inside the leaves, called chloroplasts, use sunlight to turn water and carbon dioxide from the air into sugar and oxygen. The sugar is food for the plant.
The Ingredients
The main things needed for photosynthesis are sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Roots soak up water from the soil. Leaves take in carbon dioxide from the air. Then, using sunlight, plants create food and release oxygen.
The Process
In the chloroplasts, sunlight energy is changed into chemical energy. This energy turns water and carbon dioxide into glucose, a type of sugar. Oxygen is made too, which goes into the air for us to breathe.
Why It’s Important
Photosynthesis is vital for life on Earth. It gives us food and oxygen. Without it, there would be no plants, and without plants, animals and people would not survive. It also helps take in carbon dioxide, which is good for the Earth.
250 Words Essay on Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants, algae, and some bacteria to turn sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food and oxygen. Think of it like a recipe that plants use to make their own food. This happens in the leaves of plants, which have a green substance called chlorophyll.
Why is Photosynthesis Important?
This process is very important because it is the main way plants make food for themselves and for us, too. Without photosynthesis, plants could not grow, and without plants, animals and humans would not have oxygen to breathe or food to eat.
How Photosynthesis Works
Photosynthesis happens in two main stages. In the first stage, the plant captures sunlight with its leaves. The sunlight gives the plant energy to split water inside its leaves into hydrogen and oxygen. The oxygen is released into the air, and the hydrogen is used in the next stage.
In the second stage, the plant mixes the hydrogen with carbon dioxide from the air to make glucose, which is a type of sugar that plants use for energy. This energy helps the plant to grow, make flowers, and produce seeds.
The Cycle of Life
Photosynthesis is a key part of the cycle of life on Earth. By making food and oxygen, plants support life for all creatures. When animals eat plants, they get the energy from the plants, and when animals breathe, they use the oxygen that plants release. It’s a beautiful cycle that keeps the planet alive.
500 Words Essay on Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants, algae, and some bacteria to turn sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food and oxygen. This happens in the green parts of plants, mainly the leaves. The green color comes from chlorophyll, a special substance in the leaves that captures sunlight.
The Ingredients of Photosynthesis
To make their food, plants need three main things: sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Sunlight is the energy plants use to create their food. They get water from the ground through their roots. Carbon dioxide, a gas found in the air, is taken in through tiny holes in the leaves called stomata.
The Photosynthesis Recipe
When sunlight hits the leaves, the chlorophyll captures it and starts the food-making process. The energy from the sunlight turns water and carbon dioxide into glucose, a type of sugar that plants use for energy, and oxygen, which is released into the air. This process is like a recipe that plants follow to make their own food.
The Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is very important for life on Earth. It gives us oxygen, which we need to breathe. Plants use the glucose they make for growth and to build other important substances like cellulose, which they use to make their cell walls. Without photosynthesis, there would be no food for animals or people, and no oxygen to breathe.
The Benefits to the Environment
Photosynthesis also helps the environment. Plants take in carbon dioxide, which is a gas that can make the Earth warmer when there is too much of it in the air. By using carbon dioxide to make food, plants help keep the air clean and the Earth’s temperature just right.
Photosynthesis and the Food Chain
All living things need energy to survive, and this energy usually comes from food. Plants are at the bottom of the food chain because they can make their own food using photosynthesis. Animals that eat plants get energy from the glucose in the plants. Then, animals that eat other animals get this energy too. So, photosynthesis is the start of the food chain that feeds almost every living thing on Earth.
Photosynthesis in Our Lives
Photosynthesis affects our lives in many ways. It gives us fruits, vegetables, and grains to eat. Trees and plants also give us wood, paper, and other materials. Plus, they provide shade and help make the air fresh and clean.
In conclusion, photosynthesis is a vital process that allows plants to make food and oxygen using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. It is the foundation of the food chain and has a big impact on the environment and our lives. Understanding photosynthesis helps us appreciate how important plants are and why we need to take care of them and the environment they live in.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Gender Equality And Women’s Empowerment
- Essay on Gender Equality And Sustainable Development
- Essay on Exciting Cricket Match
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The Process of Photosynthesis
Introduction.
Photosynthesis is fundamental to the energy flow process in living organisms. “Plants are the primary producers and they make use of sunlight to produce sugars for energy production.” (Govindjee, 1997, p. 45) Excess nutrients are stored and the plants are eaten up by herbivores and omnivores which rely on the energy stored in the plant cells to keep alive. The herbivores are subsequently consumed by the omnivores and carnivores; this process continues from one living organism to another creating a food chain that sustains life on earth.
Problem statement
The energy flow process is fundamental to the sustenance of life on earth. For survival, each organism requires nutrition; the nutrition is sourced from another organism as food substrates except for the green plants which manufacture their food using sunlight and minerals. Many types of research have been conducted and reveal that the process of photosynthesis is the main process that sustains life. This experimental study is designed to ascertain how the process of photosynthesis leads to energy production and how it is affected by variation in light intensity and wavelength.
Relevance of the question
This study is essential for a proper understanding of the role of plants as primary producers in the food chain process.
Literature review
The photosynthesis process occurs primarily in the leaves with little taking place in the stem for some plants. The main parts of the leaf in which are involved in the process include; “the upper and lower epidermis, the mesophyll, the vascular bundles and the stomates.” (Photosynthesis, 2000) The epidermis lacks chlorophyll and therefore photosynthesis does not occur there, the epidermis only acts to protect the internal part of the leaf. “The stomates are tiny holes in the epidermis through which gaseous exchange takes place.” (Photosynthesis, 2000, para.2)
Through the stomates, Co2 enters, and O2 leaves. “The vascular bundles constitute the plants transport system through which water and other nutrients are moved around the plant.” (Photosynthesis, 2000, para.2)

Chlorophyll is composed of the outer and inner membranes, “there is also an inter membrane space stroma and thylakoids which are stacked in grana. The chlorophyll is normally built in the membrane of the thylakoids.” (Photosynthesis, 2000, para.3)

Thus, photosynthesis is the main process in which the “radiant light energy is absorbed by the chloroplast’s pigment, chlorophyll and converted into chemical energy in the molecular form of ATP and NADH.” (Photosynthesis, 2000) The energy is then utilized in driving the Calvin cycle in the production of three-carbon sugars. The three-carbon sugars are subsequently converted to various types of carbohydrates.
According to Govindjee, it is currently possible to carry out photolysis in the laboratory. The reaction was first performed by Robert Hill in 1937 and thus became known as the Hill Reaction. The Hill Reaction requires only intact isolated chloroplasts rather than the entire intact plant cell. However, since isolated chloroplasts do not reduce carbon dioxide directly, it is essential to provide a hydrogen acceptor for the reduction process and permit electron transport to take place. The hydrogen acceptor that was chosen for this experiment is the synthetic compound 2,6-dichlorophenol-indophenol or DPIP , which is blue in the oxidized form and colorless when reduced. As indicated above, the source of hydrogen for the reduction in water. This hydrogen can reduce DPIP and turn it from a blue substance to a colorless one.
Oxygen is also formed, but it is not monitored in this experiment. The change in color of the DPIP solution, which is directly proportional to the number of hydrogen produced in the Hill Reaction, can be assayed using colorimetric spectrophotometry. The more hydrogen produced, the more DPIP that is reduced and the more colorless the solution containing DPIP becomes. Therefore, the course of this reaction can be assessed by the bleaching of the artificial hydrogen acceptor. (1997, p. 144))
Light + CO2 + 2H2O → n (CH2O) + H2O + O2
The experiment entailed the use of both boiled and fresh chloroplast suspension. The boiled chloroplast was used as a control and photosynthetic activities were monitored in the fresh chloroplast. The results were measured using a spectrophotometer and tabulated. The same procedure was repeated with variations in the light intensity and wavelength.
- Spectrophotometer
- Spectrophotometer cuvettes
- Phosphate buffer (pH6.5)
- Chloroplast suspension
- Sodium hydrosulfite
- Distilled water
- Wrapping foil
- Digital timer
- DPIP solution
The source of hydrogen for the reduction in water. This hydrogen can reduce DPIP and turn it from a blue substance to a colorless one. Oxygen is also formed, but it is not monitored in this experiment. The change in color of the DPIP solution, which is directly proportional to the number of hydrogen produced in the Hill Reaction, can be assayed using colorimetric spectrophotometry. The more hydrogen produced, the more DPIP that is reduced and the more colorless the solution containing DPIP becomes. Therefore, the course of this reaction can be assessed by the bleaching of the artificial hydrogen acceptor. The experimental procedure was selected because it has a high specificity and therefore results will have a low error margin. The chemicals used are readily available were purchased in various forms and reconstituted in the laboratory before the practice according to the manufacture’s guidelines.
- Obtain fresh and boiled chloroplast suspension prepared before the practical time. The boiling of the suspension will render the chloroplasts non-functional and will serve as one of the experimental controls. Allow the solution to return to room temperature before use. The chloroplast is boiled preferably at 100 degrees for 5 to 7 minutes.
- Obtain four clean spectrophotometer cuvettes. Label them 1-4 and prepare them as follows: Cuvette 1: 3.0 ml of phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) and 1.0 ml of boiled chloroplast suspension, Cuvette 2: 3.0 ml of phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) and 1.0 ml of chloroplast suspension, Cuvette 3: 3.0 ml of phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) and 1.0 ml of chloroplast suspension, Cuvette 4: 3.0 ml of phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) and 1.0 ml of chloroplast suspension
- Add 50 μl of the 0.1% DPIP solution to cuvette 4 only. Shake it to mix the solution well. Then add a few (very few) crystals of sodium hydrosulfite (Na2S2O4) to it. Sodium hydrosulfite reduces the DPIP and removes the blue color.
- Be sure that the spectrophotometer is set to 600nm. Use the ‘reduced’ cuvette 4 as a blank to zero the spectrophotometer.
- Add the same amount of DPIP that you added to cuvette 4 to cuvette 1. Mix the solution well and take a reading as quickly as possible using the spectrophotometer, because cuvettes with functional chloroplasts should immediately start producing hydrogen that reduces the DPIP. Record this value as ‘time zero’. Start the digital timer.
- Repeat step 5 for cuvettes 2 and 3. Record the ‘time zero’ values and their starting time points.
- Immediately after taking the first readings, wrap cuvette 3 completely in aluminum foil and place cuvettes 1-3 in a beaker of water at room temperature. Set the light source 10 inches from the cuvettes and turn it on to the highest setting. Note that the water in the beaker serves as a thermal buffer to prevent any experimental artifact due to warming by the source light.
- Every two minutes record the optical density of cuvettes 1 and 2. Leave cuvette 3 in the dark until the end of the procedure.
- Continue taking readings until the optical density reading of cuvette 2 does not change.
- Remove cuvette 3 from its foil wrapping. Quickly read the optical density of this cuvette. Take two-minute readings until the optical density reading does not change for two or three-time points. Make a graphical plot with time as the independent variable and optical density as the dependent variable.
Note: Different colors of light indicate the difference in wavelength thus the use of various colors of cellophane to measure wavelength.
Dependent, independent, and controlled variables
The independent variable is the time of exposure whereby the duration of the reaction is changed to determine the effect of time on the DPIP reduction (visualized as the clearing of the blue color). The dependent variable is the optical density which varies depending on the duration the cuvette was left to react. The controlled variables include the use of the same amount of constituent chemical for each tube, temperature of the reactions where all the tubes are reacted at room temperature.
Threat reduction to internal validity was done by:
Taking measurements immediately after the timed duration had expired; was done to prevent errors in the measurement of the optical density. Providing the same conditions for all measurements taken i.e. the spectrophotometer was blanked by the same solution for all the readings which was done at 600nm. All the necessary conditions for the materials were provided prior to and during the experiment.
Plants form an important part of the food chain. “Green plants manufacture their on food using the photosynthesis process.” (Photosynthesis, 2000, para.1) Sunlight is an important aspect of this process; the practical examines the process of photosynthesis, particularly the role played by light. Therefore:
HA: Light is a fundamental factor for the photosynthetic process where it’s used to reduce carbon dioxide and break the water molecule. In this experiment, the hydrogen from the water molecule reacts with DCIP to reduce its blue color. The spectrophotometer is used to measure the intensity of the reduced color.
Ho: Light is not a fundamental factor in the process of photosynthesis and does not reduce carbon dioxide or break the water molecule to produce hydrogen used in the experiment to reduce DCIP’s blue color that is measured using a spectrophotometer.
Use of appropriate methods, tools, and technologies to collect quantitative data
In this experiment quantitative data was collected as optical density readings. The readings were taken at 600 nm after the spectrophotometer was blanked using cuvette 4 which had 3.0 ml of phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) 1.0 ml of chloroplast suspension and 50 μl of the 0.1% DPIP solution added and the reaction left to complete( color clears). The optical density reading for each cuvette was recorded against the time duration in the lab notebook.

Data Collection
Data collection is an important aspect for the success of any experiment, for this particular experiment, the data was collected by the use of a spectrophotometer. Every reaction was timed according to the manual and on expiry of the time duration, the optical density readings were taken using the spectrophotometer and recorded in the laboratory notebook for use in the tabulation and plotting of graphs for analysis.
Experiment: the hill reaction.
Results of the Experiment
The results for the experimental were plotted as below
This experiment was designed to investigate the photosynthesis process in which light is utilized for energy production. In the hill reaction, the rate of photosynthesis remained the same for cuvettes 1 and 3, there was no evidence of photosynthetic activity in the fourth cuvette. In cuvette 5, the photosynthetic activity decreased with time. From the experiments, it is deduced that photosynthesis occurs in two stages, the light-dependent, and the light-independent stage. Generally, “in the first stage energy is captured and stored in the form of ATP and NADPH.” (Photosynthesis, 2000)
In the second stage light-independent stage the energy stored is used to process sugars using carbon. The results of this experiment agree with the hypothesis that light is a fundamental factor for the photosynthetic process where it’s used to reduce carbon dioxide and break the water molecule. In this experiment, the hydrogen from the water molecule reacts with DCIP to reduce its blue color. The spectrophotometer is used to measure the intensity of the reduced color
The experiment was carried out successfully and the results indicate that indeed plants manufacture their own food using sunlight as a source of energy. Therefore sunlight is an important factor in this process. However, the success of the practical was due to the experimental design which provided all the necessary material and conditions for the laboratory model of photosynthesis. A good experimental design gives results with minimal errors and thus can be used to conclude. “Validity refers how closeness the values are for repeated measures.”(Govindjee, 1997, p. 67) Replication of the above experiment gives results from which comparison can be drawn to give a test of validity for this experimental design.
The experiment can be replicated by another person provided he/she formulates a suitable experimental design that will include the identification, manipulation, and measurement of all the parameters in the investigation. The experimental design must be reliable and carefully selected to reduce the error margin to minimum values as this is an important aspect of this experiment.
Reference list
Govindjee, G. (1997). Experiments in plant biology. Berlin: Springer.
Photosynthesis. (2000). Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, November 30). The Process of Photosynthesis. https://studycorgi.com/the-process-of-photosynthesis/
"The Process of Photosynthesis." StudyCorgi , 30 Nov. 2021, studycorgi.com/the-process-of-photosynthesis/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) 'The Process of Photosynthesis'. 30 November.
1. StudyCorgi . "The Process of Photosynthesis." November 30, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/the-process-of-photosynthesis/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "The Process of Photosynthesis." November 30, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/the-process-of-photosynthesis/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "The Process of Photosynthesis." November 30, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/the-process-of-photosynthesis/.
This paper, “The Process of Photosynthesis”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 30, 2021 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Photosynthesis as a Biological Process Essay
Introduction.
Photosynthesis is a biological process in which plants utilize the available carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to give out oxygen. There is also the presence of a green pigment called chlorophyll is involved in the transfer of unutilized energy to utilizable chemical energy. Mostly the process of photosynthesis involves the utilization of water to release oxygen that we depend on for our lives. Plants which are the only photosynthetic organism to have leaves are viewed as a solar collector packed with photosynthetic cells.
For this process to occur, the following raw material should be available; water and carbon dioxide which after entering the leaf cell it produces oxygen found in the atmosphere. During the process water from the soil is taken up by the roots all the way to the leaves via the xylem. In order for the plants not to dry out they use the stoma so that they can exchange gases. Stomata are the only way in which oxygen can get their way out of the leaf. However during this process a great amount of water is lost. This can be witnessed by the cottonwood trees in dry seasons by loosing a total of 100 gallons daily(Kramer & Kozlowski, 1960).
When you consider this process we can classify plants to be carbon sinks because they play a great role of utilizing the carbon dioxide found in oceans and atmosphere. Plants are also involved in production of carbon dioxide through respiration and used by photosynthesis they too convert energy absorbed from the sunlight into chemical energy with covalent bonds and other carbon dioxide sources including animals. Carbonates in the ocean are formed so that they can balance the presence carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere. (Smith, 1984).
Carbon dioxide plays different roles in the plant’s life cycle. Though in many debates it has never been revealed how higher levels of carbon dioxide will benefit the Earth. This is true because food crops, flowers and trees depend mostly on carbon dioxide. According to the Voluminous scientist, evidence shows that when the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere rises above the current level the rate of plant growth will increase and enlarge due to more efficient photosynthesis and reduced water loss. Extreme temperatures will not harm plants, there will be faster growth rates and pollutants and excessive nutrients will not injure plants. Increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is projected to increase plant productivity, increases the size of a leaf and thickness, the heights of a stem and seed production. This will also lead to an increase in the both numbers and sizes of fruits and flowers (Smith, 1984).
It is also important to note that, though plants through the process of photosynthesis produces oxygen, they will only survive for a few days without oxygen even if everything is provided. If this goes on for sometimes they cannot stay alive. Plants differ from animals due to their abilities to make their own nutrients through the process of photosynthesis. Through this carbohydrates is produced and it’s broken down by plants to get energy. During this process food is created and a reaction is needed so that the created food can be broken down into usable form, and this process requires oxygen, water and nutrients (Wittwer, 1992).
The above discussed can also be applied to people where by they cannot survive without plants. Plants and animals are the two main kingdoms of life. The Earth consists of more than 300,000 species of plant and they can create their own food by means of energy from sunlight. All oxygen is generated by plants. They also make life on the Earth possible by providing humans with food as well as building material. This plant kingdom has different species which can be grouped into; mosses and liverworts, ferns, cone plants and flowering plants (Wittwer, 1992).
According to me life is made possible by plants for example forests and grasslands which supplies oxygen. According to Scientists and conservationists if deforestation goes on without control the survival system on the Earth will be injured. In addition to this plants also act as source of food to the people for example fruits, leaves, roots and tuber, seeds and barks too. Plants can also be seen contributing to the survival of the people whereby they make seeds which are transported to different places of the world spreading it. They are sources of energy, People also depend on plants by exchanging gifts in form of flowers, plants be of assistance when it comes to people surviving the harsh conditions.
Plants reduce the amount of noise in the urban setting and add the aesthetic value to the environment. They also contribute towards the ecology of an area by their roots stabilizing the soils which prevent soil erosion. They also reduce the speed of wind which is mostly used by farmers and provide them with income.
With all this, I would conclude that it will be impossible to say that people can survive without plants. This is so because people need oxygen, food, shelter, building material et cetera which is provided by plants. Therefore I will urge everyone to protect all the trees found on Earth by avoiding degrading activities for example; deforestating and polluting forested areas. By doing so, we will be promoting a healthy life to everyone (Wittwer, 1992).
Kramer, P.J. & Kozlowski, T. (1960). Physiology of trees. New York, NY: McGraw Hill.
Smith, W.H. (1984). Pollutant uptake by plants: In air pollution and plant life. New York, NY: John Wiley.
Wittwer, S.H. (1992). Rising carbon dioxide is great for plants. Journal of Biology, 12(6), 1-9.
- Drosophila Melanogaster: Centriole Reduplication
- Bitter Taste Receptors Critical Review: A Focus on Tas2r38
- Environmental Studies: Photosynthesis Concept
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
- Photosynthesis & Fermentation: Plant Cellular Metabolism
- Rapid Flow Cytometer Test Importance
- Simple Detection of Pseudomonas Cells in Milk
- Anatomy and Physiology of Circulation and Respiration in Worms, Insects, Fish, and Humans
- Biosphere: Sydney in Australia
- Root Modifications in Cyperaceae Species
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, April 1). Photosynthesis as a Biological Process. https://ivypanda.com/essays/photosynthesis-as-a-biological-process/
"Photosynthesis as a Biological Process." IvyPanda , 1 Apr. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/photosynthesis-as-a-biological-process/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Photosynthesis as a Biological Process'. 1 April.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Photosynthesis as a Biological Process." April 1, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/photosynthesis-as-a-biological-process/.
1. IvyPanda . "Photosynthesis as a Biological Process." April 1, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/photosynthesis-as-a-biological-process/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Photosynthesis as a Biological Process." April 1, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/photosynthesis-as-a-biological-process/.
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
- Biology Article
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process by which phototrophs convert light energy into chemical energy, which is later used to fuel cellular activities. The chemical energy is stored in the form of sugars, which are created from water and carbon dioxide.

Table of Contents
- What is Photosynthesis?
- Site of photosynthesis

What Is Photosynthesis in Biology?
The word “ photosynthesis ” is derived from the Greek words phōs (pronounced: “fos”) and σύνθεσις (pronounced: “synthesis “) Phōs means “light” and σύνθεσις means, “combining together.” This means “ combining together with the help of light .”
Photosynthesis also applies to other organisms besides green plants. These include several prokaryotes such as cyanobacteria, purple bacteria and green sulfur bacteria. These organisms exhibit photosynthesis just like green plants.The glucose produced during photosynthesis is then used to fuel various cellular activities. The by-product of this physio-chemical process is oxygen.
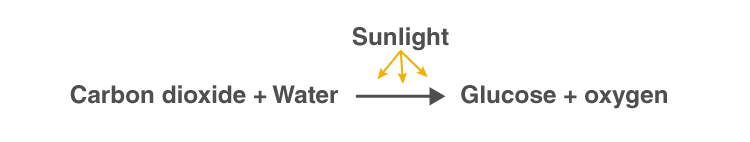
A visual representation of the photosynthesis reaction
- Photosynthesis is also used by algae to convert solar energy into chemical energy. Oxygen is liberated as a by-product and light is considered as a major factor to complete the process of photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis occurs when plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Leaves contain microscopic cellular organelles known as chloroplasts.
- Each chloroplast contains a green-coloured pigment called chlorophyll. Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules whereas carbon dioxide and oxygen enter through the tiny pores of stomata located in the epidermis of leaves.
- Another by-product of photosynthesis is sugars such as glucose and fructose.
- These sugars are then sent to the roots, stems, leaves, fruits, flowers and seeds. In other words, these sugars are used by the plants as an energy source, which helps them to grow. These sugar molecules then combine with each other to form more complex carbohydrates like cellulose and starch. The cellulose is considered as the structural material that is used in plant cell walls.
Where Does This Process Occur?
Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis in plants and blue-green algae. All green parts of a plant, including the green stems, green leaves, and sepals – floral parts comprise of chloroplasts – green colour plastids. These cell organelles are present only in plant cells and are located within the mesophyll cells of leaves.
Also Read: Photosynthesis Early Experiments
Photosynthesis Equation
Photosynthesis reaction involves two reactants, carbon dioxide and water. These two reactants yield two products, namely, oxygen and glucose. Hence, the photosynthesis reaction is considered to be an endothermic reaction. Following is the photosynthesis formula:
Unlike plants, certain bacteria that perform photosynthesis do not produce oxygen as the by-product of photosynthesis. Such bacteria are called anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria. The bacteria that do produce oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis are called oxygenic photosynthetic bacteria.
Structure Of Chlorophyll
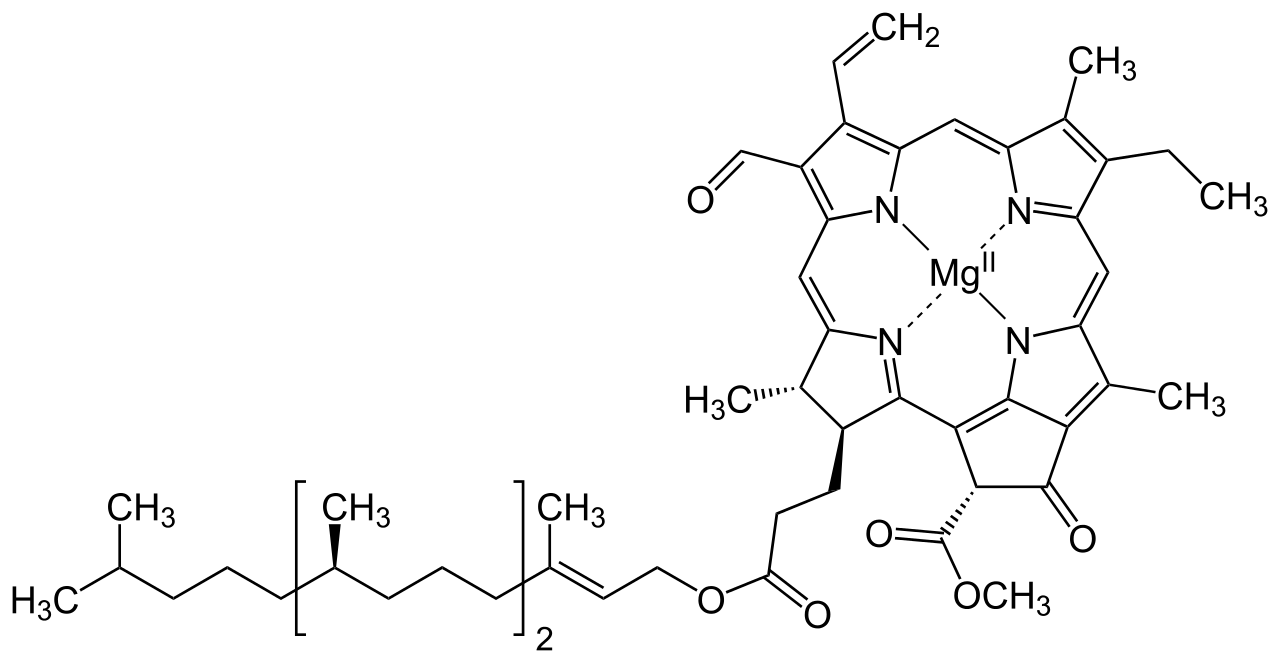
The structure of Chlorophyll consists of 4 nitrogen atoms that surround a magnesium atom. A hydrocarbon tail is also present. Pictured above is chlorophyll- f, which is more effective in near-infrared light than chlorophyll- a
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in the chloroplasts of the plant cell and in the mesosomes of cyanobacteria. This green colour pigment plays a vital role in the process of photosynthesis by permitting plants to absorb energy from sunlight. Chlorophyll is a mixture of chlorophyll- a and chlorophyll- b .Besides green plants, other organisms that perform photosynthesis contain various other forms of chlorophyll such as chlorophyll- c1 , chlorophyll- c2 , chlorophyll- d and chlorophyll- f .
Also Read: Biological Pigments
Process Of Photosynthesis
At the cellular level, the photosynthesis process takes place in cell organelles called chloroplasts. These organelles contain a green-coloured pigment called chlorophyll, which is responsible for the characteristic green colouration of the leaves.
As already stated, photosynthesis occurs in the leaves and the specialized cell organelles responsible for this process is called the chloroplast. Structurally, a leaf comprises a petiole, epidermis and a lamina. The lamina is used for absorption of sunlight and carbon dioxide during photosynthesis.
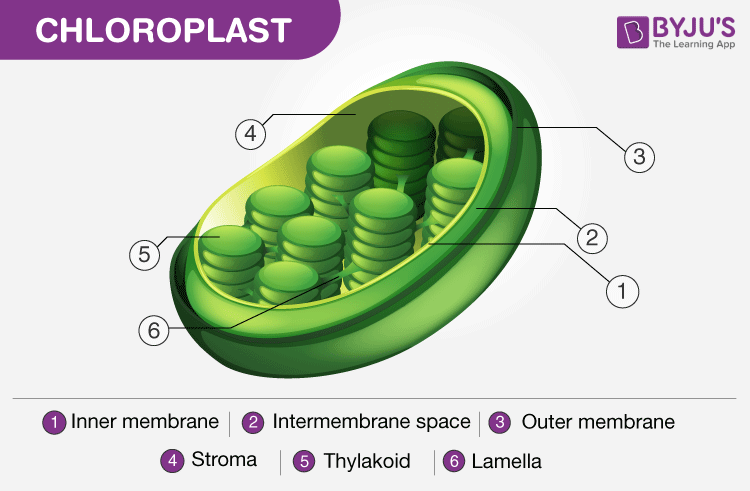
Structure of Chloroplast. Note the presence of the thylakoid
“Photosynthesis Steps:”
- During the process of photosynthesis, carbon dioxide enters through the stomata, water is absorbed by the root hairs from the soil and is carried to the leaves through the xylem vessels. Chlorophyll absorbs the light energy from the sun to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- The hydrogen from water molecules and carbon dioxide absorbed from the air are used in the production of glucose. Furthermore, oxygen is liberated out into the atmosphere through the leaves as a waste product.
- Glucose is a source of food for plants that provide energy for growth and development , while the rest is stored in the roots, leaves and fruits, for their later use.
- Pigments are other fundamental cellular components of photosynthesis. They are the molecules that impart colour and they absorb light at some specific wavelength and reflect back the unabsorbed light. All green plants mainly contain chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids which are present in the thylakoids of chloroplasts. It is primarily used to capture light energy. Chlorophyll-a is the main pigment.
The process of photosynthesis occurs in two stages:
- Light-dependent reaction or light reaction
- Light independent reaction or dark reaction
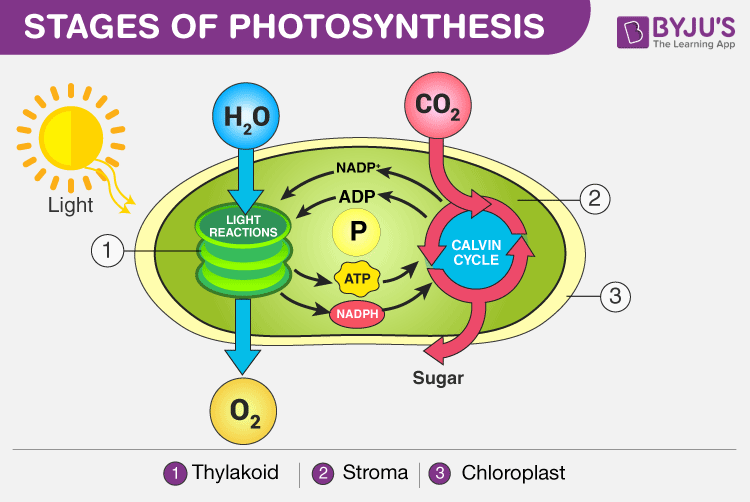
Stages of Photosynthesis in Plants depicting the two phases – Light reaction and Dark reaction
Light Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Light-dependent Reaction
- Photosynthesis begins with the light reaction which is carried out only during the day in the presence of sunlight. In plants, the light-dependent reaction takes place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
- The Grana, membrane-bound sacs like structures present inside the thylakoid functions by gathering light and is called photosystems.
- These photosystems have large complexes of pigment and proteins molecules present within the plant cells, which play the primary role during the process of light reactions of photosynthesis.
- There are two types of photosystems: photosystem I and photosystem II.
- Under the light-dependent reactions, the light energy is converted to ATP and NADPH, which are used in the second phase of photosynthesis.
- During the light reactions, ATP and NADPH are generated by two electron-transport chains, water is used and oxygen is produced.
The chemical equation in the light reaction of photosynthesis can be reduced to:
2H 2 O + 2NADP+ + 3ADP + 3Pi → O 2 + 2NADPH + 3ATP
Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Light-independent Reaction
- Dark reaction is also called carbon-fixing reaction.
- It is a light-independent process in which sugar molecules are formed from the water and carbon dioxide molecules.
- The dark reaction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast where they utilize the NADPH and ATP products of the light reaction.
- Plants capture the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through stomata and proceed to the Calvin photosynthesis cycle.
- In the Calvin cycle , the ATP and NADPH formed during light reaction drive the reaction and convert 6 molecules of carbon dioxide into one sugar molecule or glucose.
The chemical equation for the dark reaction can be reduced to:
3CO 2 + 6 NADPH + 5H 2 O + 9ATP → G3P + 2H+ + 6 NADP+ + 9 ADP + 8 Pi
* G3P – glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
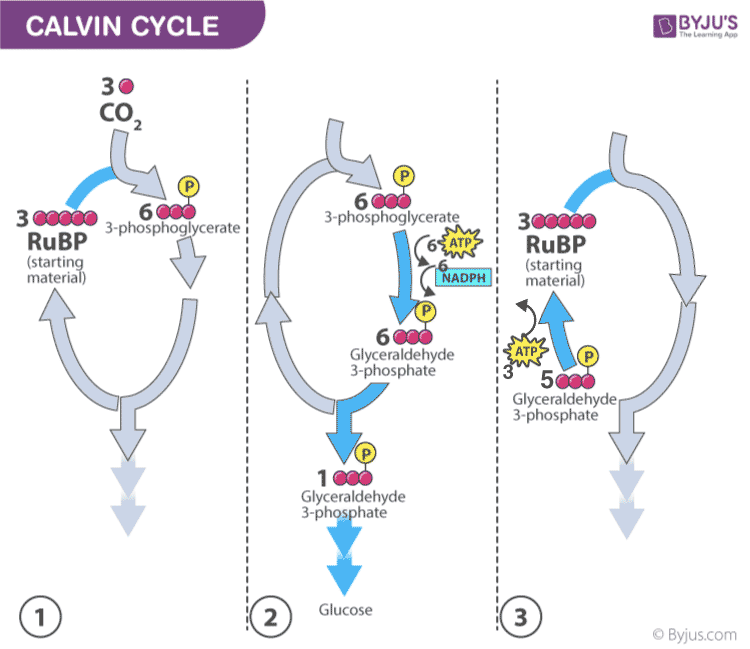
Calvin photosynthesis Cycle (Dark Reaction)
Also Read: Cyclic And Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation
Importance of Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis is essential for the existence of all life on earth. It serves a crucial role in the food chain – the plants create their food using this process, thereby, forming the primary producers.
- Photosynthesis is also responsible for the production of oxygen – which is needed by most organisms for their survival.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what is photosynthesis explain the process of photosynthesis., 2. what is the significance of photosynthesis, 3. list out the factors influencing photosynthesis., 4. what are the different stages of photosynthesis, 5. what is the calvin cycle, 6. write down the photosynthesis equation..

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
very useful
It’s very helpful ☺️
Please What Is Meant By 300-400 PPM
PPM stands for Parts-Per-Million. It corresponds to saying that 300 PPM of carbon dioxide indicates that if one million gas molecules are counted, 300 out of them would be carbon dioxide. The remaining nine hundred ninety-nine thousand seven hundred are other gas molecules.
Thank you very much Byju’s! I couldn’t find the answer anywhere. But luckily I hit upon this website. Awesome explanation and illustration.
byjus = Wow!
It helps me a lot thank you
Thanks in a million I love Byjus!
Super Byjus
Thanks helped a lot
Very interesting and helpful site.
Nice it is very uesful
It’s very useful 👍 Thank you Byju’s
Thank you very much Byju’s! I couldn’t find the answer anywhere. But luckily I hit upon this website. Awesome explanation and illustration.
Thank you BYJU’S for helping me in further clarifying my concepts
Excellent material easy to understand
Indeed, it’s precise and understandable. I like it.
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Home — Essay Samples — Science — Photosynthesis — Study of the Process of the Photosynthesis and Its Features
Study of The Process of The Photosynthesis and Its Features
- Categories: Photosynthesis
About this sample

Words: 1955 |
10 min read
Published: Oct 31, 2018
Words: 1955 | Pages: 4 | 10 min read
Table of contents
Energy for the processes in the organism, light-dependent, production of atp by an electron transport chain, the first step is the carbon fixation, step 2 is the reduction of glycerate phosphate, the third stage is regeneration of rubp, temperature.
- Carboxylation of ribulose bisphosphate
- Reduction of glycerate
- PhosphateRegeneration of ribulose bisphosphate

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Science
+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1563 words
5 pages / 2147 words
1 pages / 330 words
1 pages / 534 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis happens in the light. Cellular respiration happens in the dark. In the process of photosynthesis, the plants need sunlight for energy. Photosynthesis is the process that plants use light energy from the sun to [...]
Humans gain 3 necessities that they depend on from the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a chemical process where plants and that contain chlorophyll get energy from the sun, and use carbon dioxide (CO2) and water [...]
We as heterotrophs rely on photosynthetic organisms for nearly all the organic plant matter that we consume for energy. Photosynthesis is one of the oldest and one of the most fundamental processes of life. ("BIO 1510 Laboratory [...]
Stem cells were discovered around 1981 when the first embryonic cell. These cells were discovered by Dr. James Till and Dr. Ernset McCulloch. There are many experiments that have been conducted such as putting stem cells into [...]
A Computed Tomography (CT) Scanner consists of 3 major elements; a scanning gantry, a data handling unit and a storage. A patient is surrounded by a gantry which consist of several components. The scanning gantry has 4 major [...]
Peroxidases are oxidoreductases created by a number of plants and microorganisms. Lessening of Peroxidases in the nearness of electron giving substrate makes Peroxidases valuable in numerous business applications. Peroxidase [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
COMMENTS
250 Words Essay on Photosynthesis What is Photosynthesis? Photosynthesis is a process used by plants, algae, and some bacteria to turn sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food and oxygen. Think of it like a recipe that plants use to make their own food. This happens in the leaves of plants, which have a green substance called chlorophyll.
Thus, photosynthesis is the main process in which the "radiant light energy is absorbed by the chloroplast's pigment, chlorophyll and converted into chemical energy in the molecular form of ATP and NADH." (Photosynthesis, 2000) The energy is then utilized in driving the Calvin cycle in the production of three-carbon sugars.
In the process of photosynthesis, the plants need sunlight for energy. Photosynthesis is the process that plants use light energy from the sun to make their own food. Cellular respiration is a chemical process plants use to release the stored chemical energy from glucose as usable chemical energy so it can be used by plants.
In this essay we will discuss about Photosynthesis in Plants. After reading this essay you will learn about: 1. Meaning of Photosynthesis 2. ... The process of photosynthesis is a complicated oxidation reduction process resulting ultimately in the oxidation of water and reduction of CO 2. ... Each short flash of light (photon or hv) converts S ...
Prompt Examples for the "Photosynthesis" Essays The Process of Photosynthesis: Breaking It Down Explain the process of photosynthesis in detail, breaking down each step, the key resources involved (light energy, carbon dioxide, water), and the outcomes (glucose and oxygen). How does photosynthesis enable plants to...
Photosynthesis as an oxidation-reduction reaction: In 1931, С. B. Niel suggested that water is the hydrogen donor in the oxidation-reduction that occurs in photosynthesis. The ratio of oxygen evolved to carbon dioxide consumed is one. The over all reaction of photosynthesis is — nН 2 О + nСО 2 → light / chlorophyll nO2+ (CH 2 O) n
Introduction. Photosynthesis is a biological process in which plants utilize the available carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to give out oxygen. There is also the presence of a green pigment called chlorophyll is involved in the transfer of unutilized energy to utilizable chemical energy.
Photosynthesis definition states that the process exclusively takes place in the chloroplasts through photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotene and xanthophyll. All green plants and a few other autotrophic organisms utilize photosynthesis to synthesize nutrients by using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight.
Photosynthesis is a complex and vital process in which plants harness solar energy to produce food. This captivating phenomenon can be divided into two main phases: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle). ... Photosynthesis Essay. (2023, August 16). Edubirdie. Retrieved December 19, 2024, from https ...
Photosynthesis is the process described by this equation This equation shows the complex 2 steps process that takes place in the chloroplast of green... read full [Essay Sample] for free ... Short History of Bionics Essay. Bionics, in the field of medicine, means the replacement or enhancement of organs or other body parts by mechanical ...