How To Write An Essay
Essay Format


Essay Format - An Easy Guide & Examples
11 min read
Published on: Nov 14, 2020
Last updated on: Nov 30, 2024

People also read
How To Write An Essay - "The Secret To Craft an A+ Essay"
Learn How to Title an Essay Like a Professional Writer
How to Write an Essay Outline Like a Pro
What is a Thesis Statement & How to Write a Strong One
Arguable and Strong Thesis Statement Examples for Your Essay
200+ Creative Hook Examples: Ready, Set, Hook
A Guide to Writing a 1000 Word Essay for School or College
All You Need to Know About a 500-word Essay
Different Types of Essay: Definition With Best Examples
Writing An Engaging Essay Introduction | 6 Practical Steps With Examples!
250+ Transition Words for Essays to Improve Your Writing
Jumpstart Your Writing with These Proven Strategies on How to Start an Essay
Learn to Write a Topic Sentence that Stands Out (With Examples & Tips)
How To Write a Conclusion Effectively - Plus Examples!
Amazing Essay Topics & Ideas for Your Next Project (2025)
Explore the Different Types of Sentences with Examples
Share this article
Drafting a perfect college essay is very important for students' academics. And to write a perfect essay, its formatting is important.
An essay is a formal piece of writing. Any formal writing requires proper structure and formatting. You can not just jumble up information and expect your essay to be effective. Its clarity depends on the format you choose.
This blog is written to give a better understanding of an essay format and the general guidelines of each type of format to present the gathered information in a disciplined way.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is an Essay Format?
An essay format is a way in which the information is organized for your essay. The format of an essay has a lot to do with the presentation of the text. If your essay is poorly structured or lacks a format, your readers will have difficulty understanding the main argument and the idea.
Readers will never continue reading something that is confusing or gives the impression that a writer is sloppy.
A standard format to write your essay or paper is the linear approach. In this, each idea is presented to make it easier for the readers to understand. If you know how to structure an essay, you are halfway through.

Need help organizing your essay? Let us format it!
Types of Essay Formats
There are 3 basic formatting styles or types in which all essays and papers are formatted. They are:
Whether you are writing a research paper or a general essay , you have to choose a format to draft it. Students are often assigned a format by their instructors, so they should read the guidelines carefully.
How to Write an Essay in MLA Format?
MLA format style is quite common in the humanities world. Papers and essays that are to be written in this format should fulfill the following requirements.
- The font you are using should be Times New Roman in 12pt.
- Double spacing.
- No extra space between the new paragraphs
- One inch margin on both sides of the paper
- Page number in the header.
- Essay title in the center of the page.
- Sources mentioned in “work cited”
MLA vs. APA
Before we move to another common essay format APA, you should know that MLA and APA are different from each other.
Look at the table below and know their differences and similarities.
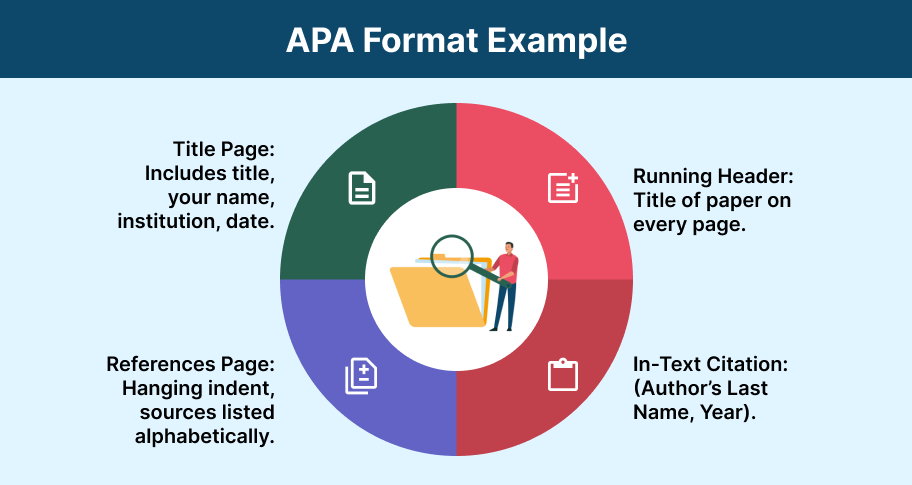
How to Write an Essay in APA Format?
Unlike MLA format, the APA format is used for scientific papers and essays. Essays are written for behavioral or social sciences follow this format. Following are the guidelines for the American Psychological Association format:
- Font or Text in Times New Roman 12pt
- One inch margin (both sides)
- Double spacing in the text
- A short title on the upper left-hand corner in the header
- The page number on the right in the header
- A title page with the information, including the writer’s name, institution, instructor, and date.
- Reference page (for the citation)
APA Format Essay Example
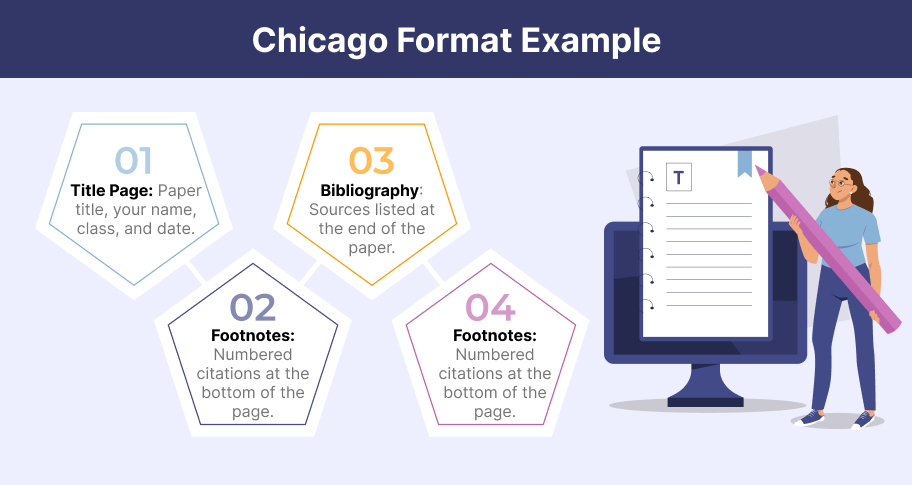
Chicago Essay Format
Chicago style essay format is a bit similar to the other format style guides. This format includes;
- Double spacing
- Margins (one inch both left margin and right margin)
- Times New Roman 12pt font size
- Page number in the header
- Footnotes on quoted and paraphrased passages
- An alphabetical arrangement of citations on the bibliography page.
Chicago Format Essay Example
Basic Parts of an Essay Format
A typical and general format that an essay uses is simple. Every type of essay can be written in that format. Following are the parts that an essay format is based on:
In order to make sure that your academic essay is effective, each of the parts should be drafted professionally.
Here is an essay structure!
Continue reading to understand each part in detail.
1. Cover Or Title Page
The cover or title page is the first page on which the topic or title of the essay is presented. Along with this, the title page includes other information such as the name of the writer, instructor, institution, course, and the submission date. 2. An Abstract
An abstract is a brief summary of your essay or research paper. It is usually a 300-word long paragraph and precisely presents the purpose of the essay, the main thesis statement, and the study’s design.
3. Table Of Contents
When you are drafting a long essay or paper, a table of content is developed. In this table, headings and subheadings are presented along with their page numbers. The reader navigates your work using this table of content.
4. Introduction
An introduction is the first section of your essay. When writing a short essay of about 300 - 1000 words, a writer directly starts with an introduction after stating the essay topic.
An introduction of an essay is as important as the body of it. The essay introduction discloses the main idea of the essay and attempts to motivate readers to read the essay. Apart from the presentation of the main idea, it also contains background information about the topic.
A writer then forms a thesis statement which is the main argument of an essay. A thesis statement is the essence of the essay, and all other information provided in the body of an essay justifies it and proves it.
5. Main Body
The main body is the soul of an essay. Without it, the thesis statement will just be meaningless. The information you gather on the topic is presented in the body, which acts as evidence to prove the argument right or wrong depending on the writer.
An essay format helps the body give a logical flow that walks the reader towards the end. The point to prove your argument is to persuade the reader that your thesis statement is right. Make sure you give a topic sentence to all your body paragraphs.
6. Conclusion
Then comes the conclusion part of the essay. This is the final verdict of an essay writer. In this, a writer avoids giving new ideas to the readers and tries to sum up the whole conversation. This is done by restating the thesis statement in different words and summarizing the key ideas.
7. Appendix
An appendix is formulated when a writer uses unusual terms, phrases, and words in the document. This is a list prepared to describe those unordinary words for the readers.
8. Bibliography
When gathering information for your essay or paper, a writer has to consult different sources. Therefore, when using such sources and information in your content, a bibliography is created to provide their references.
A bibliography is a reference list presented at the end of the essay where all the cited sources are given along with the details.

Struggling with essay organization? Let us fix it!
Formatting an Essay
Formatting an essay means working on the essay structure. When writing an academic essay, make sure that every part is drafted according to format. Your title page, in-text citation, essay outline, and reference list should be following the chosen format.
To understand the formatting of the different parts better, continue reading.
- Title Page Format
According to the MLA style, the title page of an essay should be written in the following way:
- Writing the name of the writer, course, instructor, and date.
- Double spacing between paragraphs
- Institute’s name in the top center of a page
- Title of your essay or paper
- Font Times New Roman (12pt)
If you are using an APA style formatting for your essay, make sure to format your title page in the following way:
- Title written in all caps
- The margin on both sides (1 inch)
- 12pt font Times New Roman
- Name of writer and institute
A title page is the first thing that an instructor sees in your assignment. Therefore, it is very important to form it in a neat format.
- First Page of an Essay
Before you start writing your essay, format your first page. To do this, add a header in which you give your last name and the page number. Place the header on the right-hand corner of your page.
Follow this for every page of your essay except the last page; the “work cited” page.
On the left upper corner, write your name, instructor’s, course’s, and the date. Put the title in the center and use double-spacing throughout the essay.
- Cite According to Essay Format
When you are conducting research for your essay, you will come across a lot of text which will complement your essay topic. Without knowing the consequences, people take the text from the internet and add it to the essay.
Citing the source properly is essential. If you do not cite the sources properly, you will be accused of plagiarism, a crime in the writing world. Therefore, even if you are using other’s words in the form of quotation marks or rephrasing it, it needs to be cited to avoid plagiarism.
Get to know which style of the in-text citations is recommended by your instructor and follow that. In APA format, the citation is done in the following way:
- Give the author’s name (last name), followed by the publication date and the paragraph number of the original work.
The other way is to cite in MLA style:
- Give the author’s last name and the page number of the publication you are taking words from.
Therefore, cite your sources according to the essay format and make your essay writing phase easy.
- Format The Bibliography
The last page of your essay is the “works cited” page. This page is written in the way presented below:
- Sources are alphabetically arranged
- Double spacing is used on the entire page
- Hanging indention is also used.
Essay Format Examples
There are several types of academic essays that students get assigned. No matter which type of essay you're writing, it must be properly formatted. Carefully examine the formats provided below for the different essay types:
Argumentative Essay Format
College Essay Format
Narrative Essay Format
Descriptive Essay Format
Scholarship Essay Format
Persuasive Essay Format
Essay Format for University
Expository Essay Format
Essay Format Template
Essay Format Outline
Writing a good essay includes the proper representation of the text. For this purpose, formatting is done. Unfortunately, when students rush to finish their assignments, they often end up with poorly formatted content.
Looking for an exceptional essay writing service for students ? You've found it!
We specialize in essay writing for students, providing top-notch assistance tailored to your academic needs.
You can also supercharge your writing with our AI essay writing tool !
Barbara P (Literature, Marketing)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Need Help With Your Essay?
Also get FREE title page, Turnitin report, unlimited revisions, and more!
Keep reading

OFF ON CUSTOM ESSAYS
Essay Services
- Argumentative Essay Service
- Descriptive Essay Service
- Persuasive Essay Service
- Narrative Essay Service
- Analytical Essay Service
- Expository Essay Service
- Comparison Essay Service
Writing Help
- Term Paper Writing Help
- Research Writing Help
- Thesis Help
- Dissertation Help
- Report Writing Help
- Speech Writing Help
- Assignment Help
Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
The 3 Popular Essay Formats: Which Should You Use?
General Education

Not sure which path your essay should follow? Formatting an essay may not be as interesting as choosing a topic to write about or carefully crafting elegant sentences, but it’s an extremely important part of creating a high-quality paper. In this article, we’ll explain essay formatting rules for three of the most popular essay styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago.
For each, we’ll do a high-level overview of what your essay’s structure and references should look like, then we include a comparison chart with nitty-gritty details for each style, such as which font you should use for each and whether they’re a proponent of the Oxford comma. We also include information on why essay formatting is important and what you should do if you’re not sure which style to use.
Why Is Your Essay Format Important?
Does it really matter which font size you use or exactly how you cite a source in your paper? It can! Style formats were developed as a way to standardize how pieces of writing and their works cited lists should look.
Why is this necessary? Imagine you’re a teacher, researcher, or publisher who reviews dozens of papers a week. If the papers didn’t follow the same formatting rules, you could waste a lot of time trying to figure out which sources were used, if certain information is a direct quote or paraphrased, even who the paper’s author is. Having essay formatting rules to follow makes things easier for everyone involved. Writers can follow a set of guidelines without trying to decide for themselves which formatting choices are best, and readers don’t need to go hunting for the information they’re trying to find.
Next, we’ll discuss the three most common style formats for essays.
MLA Essay Format
MLA style was designed by the Modern Language Association, and it has become the most popular college essay format for students writing papers for class. It was originally developed for students and researchers in the literature and language fields to have a standardized way of formatting their papers, but it is now used by people in all disciplines, particularly humanities. MLA is often the style teachers prefer their students to use because it has simple, clear rules to follow without extraneous inclusions often not needed for school papers. For example, unlike APA or Chicago styles, MLA doesn’t require a title page for a paper, only a header in the upper left-hand corner of the page.
MLA style doesn’t have any specific requirements for how to write your essay, but an MLA format essay will typically follow the standard essay format of an introduction (ending with a thesis statement), several body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
One of the nice things about creating your works cited for MLA is that all references are structured the same way, regardless of whether they’re a book, newspaper, etc. It’s the only essay format style that makes citing references this easy! Here is a guide on how to cite any source in MLA format. When typing up your works cited, here are a few MLA format essay rules to keep in mind:
- The works cited page should be the last paper of your paper.
- This page should still be double-spaced and include the running header of your last name and page number.
- It should begin with “Works Cited” at the top of the page, centered.
- Your works cited should be organized in alphabetical order, based on the first word of the citation.
APA Essay Format
APA stands for the American Psychological Association. This format type is most often used for research papers, specifically those in behavioral sciences (such as psychology and neuroscience) and social sciences (ranging from archeology to economics). Because APA is often used for more research-focused papers, they have a more specific format to follow compared to, say, MLA style.
All APA style papers begin with a title page, which contains the title of the paper (in capital letters), your name, and your institutional affiliation (if you’re a student, then this is simply the name of the school you attend). The APA recommends the title of your paper not be longer than 12 words.
After your title page, your paper begins with an abstract. The abstract is a single paragraph, typically between 150 to 250 words, that sums up your research. It should include the topic you’re researching, research questions, methods, results, analysis, and a conclusion that touches on the significance of the research. Many people find it easier to write the abstract last, after completing the paper.
After the abstract comes the paper itself. APA essay format recommends papers be short, direct, and make their point clearly and concisely. This isn’t the time to use flowery language or extraneous descriptions. Your paper should include all the sections mentioned in the abstract, each expanded upon.
Following the paper is the list of references used. Unlike MLA style, in APA essay format, every source type is referenced differently. So the rules for referencing a book are different from those for referencing a journal article are different from those referencing an interview. Here’s a guide for how to reference different source types in APA format . Your references should begin on a new page that says “REFERENCES” at the top, centered. The references should be listed in alphabetical order.

Chicago Essay Format
Chicago style (sometimes referred to as “Turabian style”) was developed by the University of Chicago Press and is typically the least-used by students of the three major essay style formats. The Chicago Manual of Style (currently on its 17th edition) contains within its 1000+ pages every rule you need to know for this style. This is a very comprehensive style, with a rule for everything. It’s most often used in history-related fields, although many people refer to The Chicago Manual of Style for help with a tricky citation or essay format question. Many book authors use this style as well.
Like APA, Chicago style begins with a title page, and it has very specific format rules for doing this which are laid out in the chart below. After the title page may come an abstract, depending on whether you’re writing a research paper or not. Then comes the essay itself. The essay can either follow the introduction → body → conclusion format of MLA or the different sections included in the APA section. Again, this depends on whether you’re writing a paper on research you conducted or not.
Unlike MLA or APA, Chicago style typically uses footnotes or endnotes instead of in-text or parenthetical citations. You’ll place the superscript number at the end of the sentence (for a footnote) or end of the page (for an endnote), then have an abbreviated source reference at the bottom of the page. The sources will then be fully referenced at the end of the paper, in the order of their footnote/endnote numbers. The reference page should be titled “Bibliography” if you used footnotes/endnotes or “References” if you used parenthetical author/date in-text citations.
Comparison Chart
Below is a chart comparing different formatting rules for APA, Chicago, and MLA styles.
How Should You Format Your Essay If Your Teacher Hasn’t Specified a Format?
What if your teacher hasn’t specified which essay format they want you to use? The easiest way to solve this problem is simply to ask your teacher which essay format they prefer. However, if you can’t get ahold of them or they don’t have a preference, we recommend following MLA format. It’s the most commonly-used essay style for students writing papers that aren’t based on their own research, and its formatting rules are general enough that a teacher of any subject shouldn’t have a problem with an MLA format essay. The fact that this style has one of the simplest sets of rules for citing sources is an added bonus!

What's Next?
Thinking about taking an AP English class? Read our guide on AP English classes to learn whether you should take AP English Language or AP English Literature (or both!)
Compound sentences are an importance sentence type to know. Read our guide on compound sentences for everything you need to know about compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences.
Need ideas for a research paper topic? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
- Study Documents
- Learning Tools
Writing Guides
- Citation Generator
- Flash Card Generator
- Homework Help
- Essay Examples
- Essay Title Generator
- Essay Topic Generator
- Essay Outline Generator
- Flashcard Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Introduction Generator
- Literature Review Generator
- Hypothesis Generator
- Human Editing Service
- Essay Hook Generator
- Essay Paragraph Generator
- Lesson Plan Generator
Writing Guides / Complete Guide to Essay Format: MLA, APA, and Chicago Explained
Complete Guide to Essay Format: MLA, APA, and Chicago Explained

Introduction
Content is king, but mastering the mechanics of academic writing is equally important. That’s why formatting your essay matters. Proper formatting allows you to present your essays and term papers clearly, logically, and academically so that it is easy for readers to follow your argument and for instructors to assess your work. Poor formatting, on the other hand, can lead to point deductions, even if the content of your essay is strong.
What is Proper Essay Format?
The format of an essay refers to its basic structure, layout, and appearance on the page. It includes elements such as margins, font size, line spacing, and citation style, among others. Although it may seem daunting at first, mastering the different essay formats is not as difficult as it might appear. The more essays you write, the more familiar you will become with these formats. (Check out this article for more info on how to write an essay ).
Importance of Following Proper Format
Understanding and applying the correct essay format is essential for several reasons. First, it demonstrates your attention to detail and your ability to follow academic conventions. Proper formatting also improves the readability of your essay, allowing your ideas to be presented in a clear and organized manner. Proper formatting is what lets you meet the academic standards expected in your field of study.
Overview of Main Formats
There are several widely recognized essay formats, each commonly used in different academic disciplines. The Modern Language Association ( MLA ) format is often used in the humanities, particularly in literature and language studies. The American Psychological Association ( APA ) format is typically used in the social sciences, such as psychology and education. The Chicago Manual of Style, or Chicago format , is frequently used in history and some social science fields. Each format has its own set of rules for citations, references, and overall layout.
View 120,000+ High Quality Essay Examples
Learn-by-example to improve your academic writing
Standard College Essay Format
There is no universally “right” college essay format, be we do have some commonly accepted guidelines. Professors may have specific preferences, so understanding the standard structure and formatting rules will help you adapt to any requirements.
Basic Components of Any Essay
- Title Page : This usually includes the title of your essay, your name, the course name, the instructor’s name, and the date of submission. The title should be centered and written in a standard font, without italics or underlining.
- Introduction : The introduction is the opening paragraph of your essay, where you present the topic and your thesis statement . It should contain a hook, a brief overview of the main points that will be discussed in the body of the essay, and your main point.
- Body : The body of the essay is where you develop your arguments or analysis in detail. Each paragraph of the body should focus on a specific point or piece of evidence that supports your thesis.
- Conclusion : The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay, where you summarize the main points and restate your thesis in light of the evidence presented. It should contain no new info, but should leave lasting impression on the reader so as to reinforce the significance of your essay.
- Bibliography : Also known as the Works Cited or References page, the bibliography lists all the sources you cited in your essay. The format of the bibliography varies depending on the citation style (MLA, APA, Chicago, etc.), but it typically includes the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and date.
General Formatting Rules
- Fonts : Standard college essays typically use a uniform font for consistency and readability. Times New Roman is the most widely accepted font, though Arial is sometimes permitted. The font size is usually set to 12 points. Font should be consistent across the entire document.
- Line Spacing : Most college essays require double spacing. Occasionally, you may be asked to use single spacing or 1.5 spacing, depending on the instructor’s preference or the specific assignment guidelines.
- Margins : The standard margin size for college essays is one inch on all sides (top, bottom, left, and right). This margin size is typically the default setting in Word.
- Page Numbers : Including page numbers in your essay is generally expected, especially for longer assignments. Page numbers are usually placed in the upper right corner of each page, sometimes accompanied by your last name or the title of the essay.
- Title Page : Short essays often do not require a title page, but for longer essays or research papers, a title page will probably be mandatory. If required, the title page should follow the specific format outlined by your instructor (APA, MLA, etc.), typically including the title of the essay, your name, course details, and submission date.
MLA Essay Format
Mla structure and layout.
MLA format is known for its simplicity. The following are the basic components of an essay written in MLA format:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman) : Times New Roman in 12-point font is the standard typeface used in MLA format.
- First Line Indent : Each paragraph in an MLA-formatted essay begins with an indentation of the first line, typically set at half an inch from the left margin. This indentation visually separates paragraphs, which makes the essay easy to read.
- Double-Spacing : The entire essay should be double-spaced, including the text, block quotes, and the Works Cited page. Double spacing should be consistent throughout. It is especially helpful as it allows space for instructors to make annotations.
- 1-Inch Margins : MLA format requires uniform 1-inch margins on all sides of the page (top, bottom, left, and right), which keeps the page balanced in appearance.
- Header : Unlike APA format, MLA does not usually require a title page. Instead, your name, your professor’s name, the course name, and the date should be listed in the upper left-hand corner of the first page. Below this information, the title of the essay should be centered and written in standard title case (capitalizing the first and main words of the title). A header with your last name and page number should appear in the upper right corner of each page, beginning with the first page.
MLA In-Text Citations and Works Cited
MLA format has specific guidelines for citing sources both within the text and in the Works Cited page. These citations are crucial for giving credit to the original authors and for allowing readers to trace the sources of your information.
- In-Text Citations : In MLA format, in-text citations are brief and are usually placed at the end of the sentence before the period. They include the author’s last name and the page number where the information was found, all within parentheses. For example: (Smith 123). If the author’s name is mentioned in the sentence, only the page number is required in the citation: (123). Even when paraphrasing or summarizing, the page number must be included, which can be a challenge but is essential to meet MLA standards.
- Works Cited Page : The Works Cited page appears at the end of the essay and lists all the sources referenced in your paper. Each entry should be formatted with a hanging indent, where the first line of the citation is flush with the left margin, and subsequent lines are indented. Entries are listed alphabetically by the author’s last name or by the title if no author is provided. The general format for a book citation in MLA is: Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . Publisher, Year of Publication.

MLA Common Mistakes to Avoid
While MLA format is straightforward, there are common mistakes that students often make:
- Incorrect In-Text Citations : Failing to include the page number, using the wrong format for the author’s name, or placing the period outside the parentheses are frequent errors. Always double-check your in-text citations for accuracy.
- Improper Works Cited Formatting : Not following the correct order, incorrect use of italics or quotation marks, and missing publication details are common pitfalls. Ensure each entry adheres to MLA guidelines.
- Missing or Incorrect Header : Forgetting to include the header with your last name and page number on each page can lead to a lower grade. Also, ensure that the header is properly aligned with the right margin.
Example of MLA Format
Here’s a simplified example of how the first page of an MLA-formatted essay might look:
First Page of an MLA Paper :

APA Essay Format
Apa structure and layout.
APA format follows a set structure that includes a title page, abstract, body, and references.
- Title Page : The title page in APA format is crucial as it sets the tone for your paper. It includes the title of your essay, your name, and your institutional affiliation, all centered on the page. The title should be concise and informative, reflecting the content of your paper. Below the title, your name appears, followed by your institution (e.g., university name). Some instructors may ask for additional information like the course title, instructor’s name, and the date.
- Abstract : The abstract is a brief summary of your paper, usually between 150-250 words. It gives a summary of your research, including the research question, methods, results, and conclusions. The abstract appears on its own page, right after the title page, and is typically a single paragraph without indentation. Abstracts are used in longer research papers and dissertations to give readers a quick snapshot of the study’s content and findings.
- Body : The body of an APA paper is where you present your argument or findings. It starts on a new page after the abstract and is divided into sections such as the introduction, method, results, discussion, and conclusion, depending on the type of paper you are writing. Each section may include subheadings to improve organization and readability.
- References : The reference page, which comes at the end of your paper, lists all the sources cited in the text. This page follows specific APA formatting rules, including the use of a hanging indent and alphabetical order by the authors’ last names. The reference entries must include detailed information about each source, such as the author’s name, publication year, title of the work, and source.
APA In-Text Citations and References
APA style uses the author-date citation method, which includes the author’s last name and the publication year in the text. This method allows readers to locate the full citation in the reference list easily.
- In-Text Citations : In-text citations in APA format are concise. For example, if you’re citing a book by John Doe published in 2020, the citation would appear as (Marve, 2024). If you directly quote a source, you must also include the page number: (Smith & Wesson, 2023, p. 15). These citations are usually placed at the end of a sentence before the period.
- References : Every in-text citation must correspond to an entry in the reference list. The reference list provides full details about the source, formatted in a specific way. For a book, the format is: Author’s Last Name, First Initial(s). (Year). Title of the book . Publisher.

APA Headings and Subheadings
Headings and subheadings are essential in APA format as they help organize the content and guide readers through the paper. APA uses a specific hierarchy of headings:
- Level 1 Heading : Centered, Bold, Title Case (e.g., Introduction)
- Level 2 Heading : Flush Left, Bold, Title Case (e.g., Review of Literature)
- Level 3 Heading : Indented, Bold, Sentence case, ending with a period. (e.g., Methods)
Subheadings break down sections into more detailed parts, making your essay easier to follow.
Example of APA Format

Chicago Essay Format
Overview of chicago style.
Chicago style follows a standard set of formatting guidelines, which include:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman) : Chicago style typically uses Times New Roman in 12-point font, which is considered a classic and highly readable typeface.
- First Line Indent : Each paragraph should begin with a half-inch indent, creating a clear separation between sections of text.
- Double-Spacing : The entire document, including block quotes, notes, and bibliography, should be double-spaced, providing ample room for comments or corrections.
- 1-Inch Margins : Chicago style requires 1-inch margins on all sides of the page, which is standard for most academic papers.
Chicago style is known for its flexibility, especially in the way it handles citations. Unlike MLA or APA formats, which rely on in-text parenthetical citations, Chicago style allows for the use of either footnotes or endnotes, which are a less obtrusive way to cite sources.
Chicago Footnotes vs. Endnotes
- Footnotes : Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page on which the reference is made. They are numbered consecutively throughout the essay. Footnotes are preferred when you want the reader to have immediate access to the source or explanation while reading the text. For example, after quoting a source, a small superscript number is placed at the end of the sentence, corresponding to a footnote at the bottom of the page, where full citation details are provided.
- Endnotes : Endnotes, like footnotes, are numbered consecutively but are placed at the end of the essay, just before the bibliography. Endnotes are often used in longer works where multiple citations might overwhelm the page layout. While they serve the same purpose as footnotes, they require the reader to flip to the end of the document to see the citation, which some writers prefer to keep the main text uncluttered.
Both footnotes and endnotes in Chicago style include detailed citation information, such as the author’s name, title of the work, publication details, and page numbers. The choice between footnotes and endnotes often depends on the nature of the paper and the instructor’s preference.
Chicago Bibliography Format
The bibliography in Chicago style lists all sources referenced in the paper. The bibliography page appears at the end of the essay and should follow these guidelines:
- Alphabetical Order : Entries in the bibliography are listed alphabetically by the author’s last name. If no author is provided, the title of the work is used.
- Hanging Indent : Each entry begins flush with the left margin, and subsequent lines are indented by half an inch. This format is known as a hanging indent.
- Detailed Citations : Each entry should include the author’s name, the title of the work (italicized), the place of publication, the publisher, and the year of publication. For example: Smith, John. The History of Modern Europe . New York: Random House, 2020.
Example of Chicago Format
Here’s an example of how a Chicago-style essay might look:
Title Page Example :

Key Differences Between MLA, APA, and Chicago
Citation styles.
- MLA (Modern Language Association) : MLA style is typically used in the humanities, particularly in literature, philosophy, and the arts. Citations are made using brief parenthetical references within the text, including the author’s last name and page number (e.g., Mason 413). The full citation details are provided in a Works Cited page at the end of the document.
- APA (American Psychological Association) : APA format is prevalent in the social sciences, including psychology, sociology, and education. It uses the author-date method for in-text citations, where the author’s last name and the year of publication are included (e.g., Como, 2020). A References page at the end lists all sources in full detail.
- Chicago Style : Chicago style, often used in history, political science, and the arts, offers two citation methods: the Notes and Bibliography system, which uses footnotes or endnotes along with a bibliography, and the Author-Date system, similar to APA but less commonly used. Footnotes or endnotes provide detailed source information at the bottom of the page or at the end of the paper, making this style flexible for detailed commentary.
Paper Structure
The structure of a paper also varies among these formats:
- MLA : MLA format is straightforward, typically consisting of a title page (optional), an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. It does not require a separate title page; instead, the student’s name, instructor’s name, course, and date are placed at the top of the first page.
- APA : APA format is more structured and includes a title page, abstract, main body, and references. The title page presents the title, author’s name, and institutional affiliation, while the abstract provides a brief summary of the paper. APA also often uses headings and subheadings to organize content clearly.
- Chicago : Chicago format is flexible and can vary based on the type of paper. A typical Chicago-style paper includes a title page, the main body of text, and a bibliography. When using the Notes and Bibliography system, Chicago style also incorporates footnotes or endnotes, which can make the structure appear more complex.
Where and When to Use Each Format
Each format is suited to specific academic disciplines:
- MLA : Best used in humanities subjects, especially in writing-intensive courses where the focus is on literary analysis, criticism, or cultural studies.
- APA : Ideal for the social sciences, where research often involves data analysis, experiments, and empirical studies. APA’s structured format helps present research findings clearly.
- Chicago : Often required in history, art history, and some social sciences. It is particularly useful when extensive citation or commentary is needed, thanks to its footnote and endnote options.
Special Essay Formats
When you’re applying for a scholarship, submitting a college application, or crafting a research or persuasive essay, know that each format has unique elements that guide how you should present your work.
Scholarship Essay Format
Scholarship essays are critical for students aiming to secure financial aid for their education. Unlike standard academic essays, a scholarship essay is deeply personal and written in the first person. It focuses on your achievements, goals, and reasons for deserving the scholarship. Here are some key aspects of the scholarship essay format:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman or Arial) : This is the standard for readability.
- First Line Indent : Each paragraph should begin with an indentation, creating a clear structure.
- Double-Spacing : Double-spacing improves readability and allows room for comments.
- 1-Inch Margins : Standard margins provide a clean, professional look.
Unlike academic essays that are typically written in the third person, scholarship essays are personal narratives. The essay should show your determination, goals, and the unique qualities that make you a worthy candidate. Discuss your academic achievements, community involvement, and future aspirations, while avoiding generic statements. Tailor each essay to the specific scholarship, addressing the organization’s values and how they align with your goals.
College Application Essay Format
College application essays are crucial in the admissions process. They offer a glimpse into your personality, values, and potential contributions to the college community. These essays are also written in the first person and vary in length, from short responses to longer personal statements. Key formatting elements include:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman or Arial) : Consistency in font choice helps maintain a formal tone.
- First Line Indent : Indenting paragraphs helps organize your thoughts.
- Double-Spacing : This spacing standard enhances readability and presentation.
- 1-Inch Margins : Uniform margins contribute to a polished appearance.
A strong college application essay often begins with a thoughtful introduction, perhaps a personal anecdote or a significant experience that shaped your character. The body of the essay should go into your interests, goals, and why you are drawn to the specific college or program. Be authentic and reflective. This essay is your chance to stand out among many applicants, so it’s important to convey your own unique story.
Research Essays (Extended Essays, IB Essays)
Research essays, such as those required for International Baccalaureate (IB) programs or extended essays, are more formal and structured than personal essays. These essays require rigorous research and a thorough analysis of the topic. The format for research essays generally includes:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman or Arial) : A professional and readable font choice.
- First Line Indent : Each paragraph should be clearly indented.
- Double-Spacing : Allows for clear presentation and space for feedback.
- 1-Inch Margins : Standard for most academic papers.
- Title Page and Abstract : Depending on the requirements, these elements may be necessary, particularly in extended essays or formal research papers.
Research essays are structured around a thesis statement, with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. The body should be divided into sections, each addressing different aspects of the research question, supported by evidence from credible sources. Use proper citation to avoid plagiarism charges and to give credit to original ideas.
Reflective and Persuasive Essays
Reflective and persuasive essays require different approaches but share some formatting similarities with standard essays.
Reflective Essay : Reflective essays explore personal experiences and the insights gained from them. The format may include:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman or Arial) .
- First Line Indent .
- Double-Spacing .
- 1-Inch Margins .
In a reflective essay, you may be asked to consider a personal experience or react to a text, event, or artwork. The essay should include a description of the experience or object of reflection, followed by an analysis of its impact on you. The tone can be informal, but the structure should remain coherent and well-organized.
Persuasive Essay : Persuasive essays aim to convince the reader of a particular point of view. They follow a more traditional academic structure:
Persuasive essays require a strong thesis statement, clear arguments supported by evidence, and a conclusion that reinforces your position. Use rhetorical strategies like ethos, pathos, and logos to strengthen your argument and persuade the reader effectively. Acknowledge opposing views and refute them to build a more compelling case.
Additional Formatting Tips
Creating an outline.
An outline helps you organize your thoughts and structure your essay logically. It serves as a roadmap, guiding you through each section of your paper and ensuring that your arguments flow coherently. An effective outline typically includes:
- Introduction : Start with your thesis statement, followed by a brief overview of the main points you will discuss.
- Body Paragraphs : List the key points or arguments you plan to make, organized into sections. For each section, include supporting evidence or examples.
- Conclusion : Summarize your main points and restate your thesis in a new light, reflecting the arguments made in the body.
Using bullet points or numbering in your outline can help you maintain a clear hierarchy of ideas. While the outline itself is not part of the final essay, creating one can save time during the writing process and improve the overall structure of your paper.
Formatting Headings and Subheadings
Headings and subheadings are essential for breaking up the text and guiding readers through your essay. They provide a clear structure, making it easier for readers to follow your argument. Different formatting styles have specific rules for headings and subheadings:
- MLA : Generally does not require headings, but when used, they should be formatted consistently without a boldface or italics.
- APA : APA uses a five-level heading system. Level 1 is centered and bold, Level 2 is flush left and bold, and so on, down to Level 5, which is indented, bold, and italicized.
- Chicago : Offers flexibility, but generally, headings are bolded or italicized, and subheadings are formatted similarly but in a smaller font size or with less emphasis.
Using clear and consistent formatting for your headings and subheadings helps organize the content and makes your essay more reader-friendly.
Formatting Tables, Charts, and Appendices
Including tables, charts, and appendices in your essay can be an effective way to present data, summarize information, or provide additional context without overcrowding the main text. Proper formatting of these elements is crucial to maintain the professionalism of your document.
- Labeling : Each table and chart should be labeled with a number (e.g., Table 1, Figure 2) and a descriptive title.
- Placement : Tables and charts can be placed within the text close to where they are referenced or included at the end of the document in an appendix.
- Formatting : Ensure that tables are clear, with consistent font and spacing, and that charts are accurately labeled with legends if needed.
- Purpose : Appendices are used to include supplementary material that is relevant but not essential to the main text, such as raw data, questionnaires, or detailed explanations.
- Labeling : Appendices should be labeled (e.g., Appendix A, Appendix B) and referenced in the main text.
- Content : Each appendix should start on a new page, with the title clearly labeled at the top.
Formatting is a big aspect of academic writing that goes beyond mere aesthetics. Proper formatting gives clarity, readability, and professionalism. Whether you’re using MLA, APA, Chicago, or another style, adhering to the specific guidelines of each format will show your attention to detail and your commitment to academic standards.
A well-formatted essay not only makes your work more accessible to readers but it also improves the credibility of your arguments. Be careful about organizing your content with appropriate headings, citations, and supplementary materials like tables or appendices, so that you can turn in a well-structured and persuasive piece of writing.
Final tips: always double-check the specific requirements of your assignment and seek clarification from your instructor if needed. Utilize tools like outlines to plan your essay structure, and pay attention to the nuances of each style, such as citation formats and the use of footnotes or endnotes. Master these elements, and you’ll be able to effectively communicate your ideas and enjoy academic success.
Take the first step to becoming a better academic writer.
Writing tools.
- How to write a research proposal 2021 guide
- Guide to citing in MLA
- Guide to citing in APA format
- Chicago style citation guide
- Harvard referencing and citing guide
- How to complete an informative essay outline

How to Choose the Best Essay Topics

AI Text Detection Services

Unlock Your Writing Potential with Our AI Essay Writing Assistant

The Negative Impacts of Artificial Intelligence on Tactile Learning
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Forums Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Format an Essay
Last Updated: July 29, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Carrie Adkins, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Aly Rusciano . Carrie Adkins is the cofounder of NursingClio, an open access, peer-reviewed, collaborative blog that connects historical scholarship to current issues in gender and medicine. She completed her PhD in American History at the University of Oregon in 2013. While completing her PhD, she earned numerous competitive research grants, teaching fellowships, and writing awards. There are 15 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 98,238 times.
You’re opening your laptop to write an essay, knowing exactly what you want to write, but then it hits you: you don’t know how to format it! Using the correct format when writing an essay can help your paper look polished and professional while earning you full credit. In this article, we'll teach you the basics of formatting an essay according to three common styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago Style.
Setting Up Your Document

- If you can’t find information on the style guide you should be following, talk to your instructor after class to discuss the assignment or send them a quick email with your questions.
- If your instructor lets you pick the format of your essay, opt for the style that matches your course or degree best: MLA is best for English and humanities; APA is typically for education, psychology, and sciences; Chicago Style is common for business, history, and fine arts.

- Most word processors default to 1 inch (2.5 cm) margins.

- Do not change the font size, style, or color throughout your essay.

- Change the spacing on Google Docs by clicking on Format , and then selecting “Line spacing.”
- Click on Layout in Microsoft Word, and then click the arrow at the bottom left of the “paragraph” section.

- Using the page number function will create consecutive numbering.
- When using Chicago Style, don’t include a page number on your title page. The first page after the title page should be numbered starting at 2. [5] X Research source
- In APA format, a running heading may be required in the left-hand header. This is a maximum of 50 characters that’s the full or abbreviated version of your essay’s title. [6] X Research source

- For APA formatting, place the title in bold at the center of the page 3 to 4 lines down from the top. Insert one double-spaced line under the title and type your name. Under your name, in separate centered lines, type out the name of your school, course, instructor, and assignment due date. [8] X Research source
- For Chicago Style, set your cursor ⅓ of the way down the page, then type your title. In the very center of your page, put your name. Move your cursor ⅔ down the page, then write your course number, followed by your instructor’s name and paper due date on separate, double-spaced lines. [9] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- Double-space the heading like the rest of your paper.
Writing the Essay Body

- Use standard capitalization rules for your title.
- Do not underline, italicize, or put quotation marks around your title, unless you include other titles of referred texts.

- A good hook might include a quote, statistic, or rhetorical question.
- For example, you might write, “Every day in the United States, accidents caused by distracted drivers kill 9 people and injure more than 1,000 others.”

- "Action must be taken to reduce accidents caused by distracted driving, including enacting laws against texting while driving, educating the public about the risks, and giving strong punishments to offenders."
- "Although passing and enforcing new laws can be challenging, the best way to reduce accidents caused by distracted driving is to enact a law against texting, educate the public about the new law, and levy strong penalties."

- Use transitions between paragraphs so your paper flows well. For example, say, “In addition to,” “Similarly,” or “On the other hand.” [16] X Research source

- A statement of impact might be, "Every day that distracted driving goes unaddressed, another 9 families must plan a funeral."
- A call to action might read, “Fewer distracted driving accidents are possible, but only if every driver keeps their focus on the road.”
Using References

- In MLA format, citations should include the author’s last name and the page number where you found the information. If the author's name appears in the sentence, use just the page number. [18] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- For APA format, include the author’s last name and the publication year. If the author’s name appears in the sentence, use just the year. [19] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- If you don’t use parenthetical or internal citations, your instructor may accuse you of plagiarizing.

- At the bottom of the page, include the source’s information from your bibliography page next to the footnote number. [20] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Each footnote should be numbered consecutively.

- If you’re using MLA format, this page will be titled “Works Cited.”
- In APA and Chicago Style, title the page “References.”

- If you have more than one work from the same author, list alphabetically following the title name for MLA and by earliest to latest publication year for APA and Chicago Style.
- Double-space the references page like the rest of your paper.
- Use a hanging indent of 0.5 inches (1.3 cm) if your citations are longer than one line. Press Tab to indent any lines after the first. [23] X Research source
- Citations should include (when applicable) the author(s)’s name(s), title of the work, publication date and/or year, and page numbers.
- Sites like Grammarly , EasyBib , and MyBib can help generate citations if you get stuck.
Formatting Resources

Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- ↑ https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-englishcomposition1/chapter/text-mla-document-formatting/
- ↑ https://www.une.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/392149/WE_Formatting-your-essay.pdf
- ↑ https://content.nroc.org/DevelopmentalEnglish/unit10/Foundations/formatting-a-college-essay-mla-style.html
- ↑ https://camosun.libguides.com/Chicago-17thEd/titlePage
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/page-header
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/title-page
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/chicago_manual_17th_edition/cmos_formatting_and_style_guide/general_format.html
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/writing-speaking-resources/mla-8-style-format
- ↑ https://cflibguides.lonestar.edu/chicago/paperformat
- ↑ https://www.uvu.edu/writingcenter/docs/basicessayformat.pdf
- ↑ https://www.deanza.edu/faculty/cruzmayra/basicessayformat.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://monroecollege.libguides.com/c.php?g=589208&p=4073046
- ↑ https://library.menloschool.org/chicago
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Maansi Richard
May 8, 2019
Did this article help you?

Jan 7, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Make Your Essay Structure Rock-Solid with These Tips

So you’ve been assigned an essay. Or, probably more realistically, two, three, or four essays . . . and they’re all due the same week.
We’ve all been there: overwhelmed, staring down that blank screen, and not sure which essay to start with or how to get it started.
In high school and college, it’s not enough to just write strong essays. One of the most important skills to develop is writing strong essays efficiently . And the foundation of that skill is knowing how to structure an essay. With a template for the basic essay structure in hand, you can focus on what really matters when you’re writing essays: your arguments and the evidence you’re using to support them. Take a look at the basic essay structure below and see how the parts of an essay work together to present a coherent, well-reasoned position, no matter what topic you’re writing about.
Make your essays shine. Polish your writing with Grammarly Write with Grammarly
Basic essay structure: the 3 main parts of an essay
Almost every single essay that’s ever been written follows the same basic structure:
Introduction
Body paragraphs.
This structure has stood the test of time for one simple reason: It works. It clearly presents the writer’s position, supports that position with relevant examples, and neatly ties their supporting arguments together in a way that makes their position evident.
It all starts here. This is where you introduce the topic you’re discussing in your essay and briefly summarize the points you’ll make in the paragraphs that follow.
This is also where you state your thesis. Your thesis is the most important part of your essay because it’s the point you’re making . It needs to take a clear stance and shouldn’t include hedging language that undermines that stance like “seems to” or “possibly could.”
Here are a few examples of thesis statements:
- In the final scene of The Awakening , Edna Pontellier’s decision demonstrates that it was impossible for her to have the lifestyle she truly wanted in the society in which she lived.
- Due to its volatility and lack of government regulation, Bitcoin cannot become a viable currency for everyday purchases.
- While the habitability of Mars has not yet been proven, evidence suggests that it was once possible due to bacteria samples found on the Red Planet.
An easy way to write your thesis statement is to think of it as a summary of your essay. Your thesis makes and supports your essay’s point in one concise sentence.
When you proofread your finished essay, make sure your thesis is clearly stated in your introduction paragraph. If it’s not clear, go back and write a definitive thesis statement.
>>Read More: How to Write a Persuasive Essay
Your essay’s body paragraphs are where you support your thesis statement with facts and evidence. Each body paragraph should focus on one supporting argument for your thesis by discussing related data, content, or events.
If you’re not sure whether you should include a specific point or detail in your body paragraphs, refer back to your thesis statement. If the detail supports your thesis, it should be in your essay. If it doesn’t, leave it out. Your thesis statement is the core of your basic essay structure, so everything else in the essay needs to relate to it in some way.
In your essay’s conclusion paragraph , you summarize the points you made and bring your argument to its logical conclusion. Because your reader is now familiar with your thesis, the summary in your conclusion paragraph can be more direct and conclusive than the one in your intro paragraph.
>>Read More: 7 Writing Tips from Professors to Help you Crush your First Essays
How many paragraphs are in an essay?
There’s no hard-and-fast requirement for college essays. In high school, you were probably taught to write five-paragraph essays. This is a solid essay structure to work with, but in college, you generally have more flexibility with assignment lengths and formats.
Now, consider five the minimum—not the standard—number of paragraphs you should include in your essays.
Essay structure examples
There are a few different ways to present information in an essay. Often, your assignment will tell you what kind of essay to write, such as a chronological, compare and contrast, or problems-methods-solution essay. If you’re not sure which is best for your assignment, ask your instructor.
Chronological
A chronological essay guides the reader through a series of events. This essay structure is ideal if you’re writing about:
- A current or historical event
- A book or article you read for class
- A process or procedure
With this kind of essay, you first introduce your topic and summarize the series of events in your introduction paragraph. Then, each body paragraph takes the reader through a key stage in that series, which might be a decisive battle in history, a pivotal scene in a novel, or a critical stage in a judicial process. In your conclusion, you present the end result of the series you discussed, underscoring your thesis with this result.
Compare and contrast
A compare-and-contrast essay has a structure that discusses multiple subjects, like several novels, concepts, or essays you’ve been assigned to read.
There are a few different ways to structure a compare-and-contrast essay. The most obvious is to spend one paragraph discussing the similarities between the topics you’re covering (comparing), then one paragraph detailing their differences (contrasting), followed by a paragraph that explores whether they’re more alike or more different from each other.
Another method is to only compare, where each of your body paragraphs discusses a similarity between the topics at hand. Or you can go the only-contrast route, where your body paragraphs explore the differences. Whichever you decide on, make sure each paragraph is focused on one topic sentence . Every new comparison or contrast should occupy its own paragraph.
Problems-methods-solution
As its name implies, this kind of essay structure presents the writer’s position in three segments:
- Ways to resolve the problem
- The solution achieved by using these strategies to resolve the problem
This kind of essay works great if you’re discussing methods for resolving a problem, like knowing how to distinguish between credible and non-credible sources when you’re doing research for assignments. It can also work when you’re tasked with explaining why certain solutions haven’t worked to fix the problems they were created for.
With this kind of essay, begin by introducing the problem at hand. In the subsequent body paragraphs, cover possible methods for resolving the problem, discussing how each is suited to fixing the problem, and potential challenges that can arise with each. You can certainly state which you think is the best choice—that could even be your thesis statement. In your conclusion paragraph, summarize the problem again and the desired resolution, endorsing your method of choice (if you have one).
In this kind of essay, you can also include a call to action in your final paragraph. A call to action is a direct order for the reader to take a specific action, like “call your congressperson today and tell them to vote no” or “visit grammarly.com today to add Grammarly browser extension for free.”
>>Read More: How to Write Better Essays: 5 Concepts you Must Master
With the basic essay structure down, you can get to writing
For a lot of students, getting started is the hardest part of writing an essay. Knowing how to structure an essay can get you past this seemingly insurmountable first step because it gives you a clear skeleton upon which to flesh out your thoughts. With that step conquered, you’re on your way to crushing your assignment.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples. Published on September 4, 2020 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on July 23, 2023. An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays.
Unlike a narrative essay, which tells a story, a descriptive essay has a narrower scope and focuses on one particular aspect of a story. 3. Argumentative essays. An argumentative essay is a type of essay that aims to persuade the reader to adopt a particular stance based on factual evidence and is one of the most common forms of college essays. 4.
Once you have your thesis, you may want to start with an essay map. The essay map breaks the thesis down into parts to be discussed in the body of the paper. The essay map is generally one or two sentences that precede the thesis statement. The essay must be grammatically parallel, which will help keep your meaning very clear to your reader.
Types of Essay Formats . There are 3 basic formatting styles or types in which all essays and papers are formatted. They are: MLA; APA; Chicago; Whether you are writing a research paper or a general essay, you have to choose a format to draft it.Students are often assigned a format by their instructors, so they should read the guidelines carefully.
In this article, we'll explain essay formatting rules for three of the most popular essay styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago. For each, we'll do a high-level overview of what your essay's structure and references should look like, then we include a comparison chart with nitty-gritty details for each style, such as which font you should use for ...
An essay is a piece of short-form, nonfiction writing that focuses on a specific topic. Writers typically use the essay format to argue a thesis or to provide their viewpoint on a subject. Essays come in many different forms—from persuasive essays, which make an argument, to narrative essays, which tell a story. Essays can be any length ...
Title Page: Short essays often do not require a title page, but for longer essays or research papers, a title page will probably be mandatory. If required, the title page should follow the specific format outlined by your instructor (APA, MLA, etc.), typically including the title of the essay, your name, course details, and submission date.
The essay overview. In longer essays whose body is split into multiple named sections, the introduction often ends with an overview of the rest of the essay. This gives a brief description of the main idea or argument of each section. The overview allows the reader to immediately understand what will be covered in the essay and in what order.
Open your essay with an introduction. Write your introduction with a "hook" that grabs your reader's attention. Keep the information in your introduction general. Provide enough details to summarize what you'll be talking about in your essay, but don't give too much away—all those details will be provided in the body of your paper.
A chronological essay guides the reader through a series of events. This essay structure is ideal if you're writing about: A current or historical event; A book or article you read for class; A process or procedure; With this kind of essay, you first introduce your topic and summarize the series of events in your introduction paragraph.